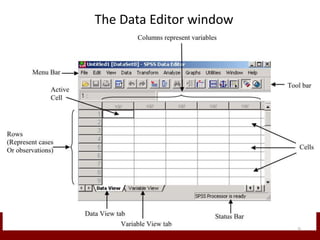
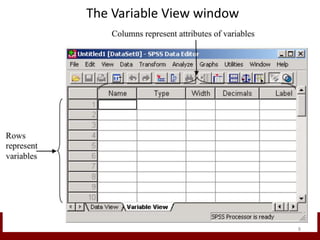
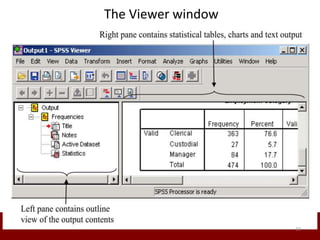
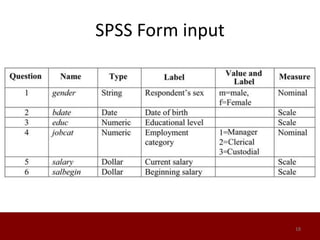
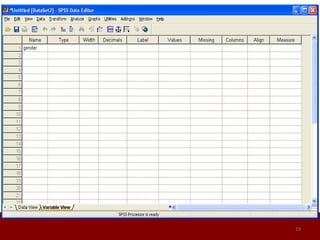
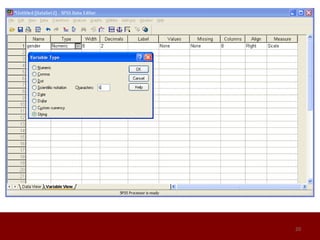
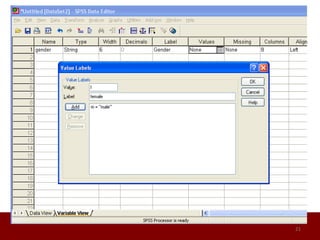
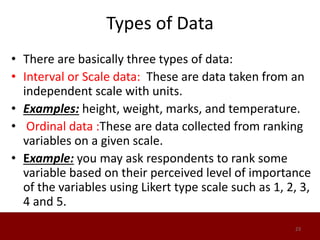
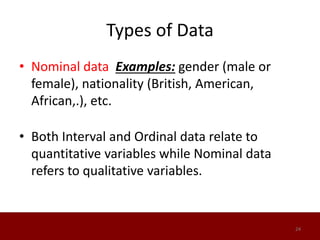
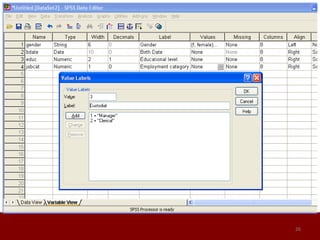
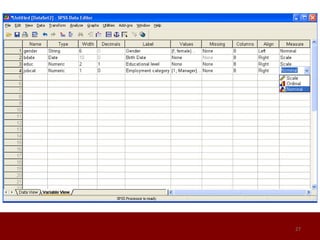
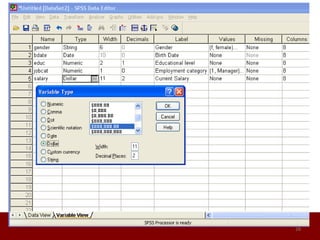
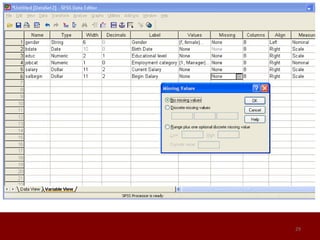
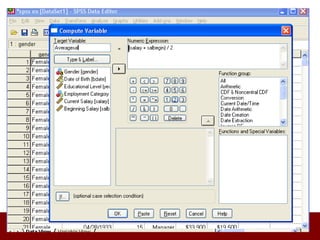
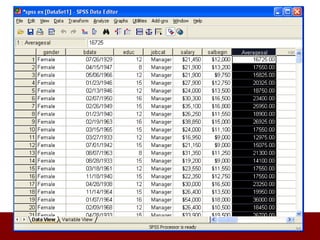
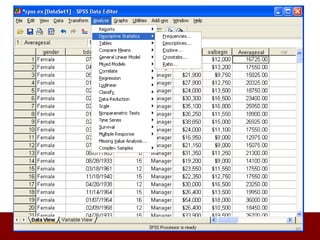
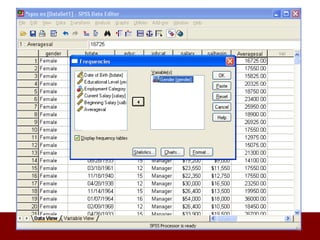
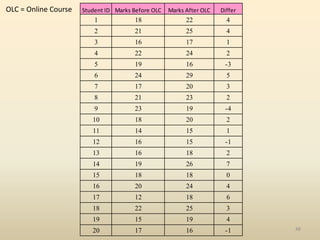
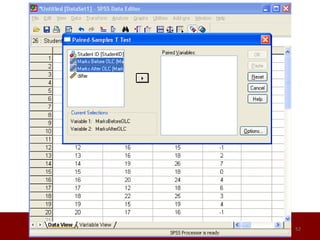
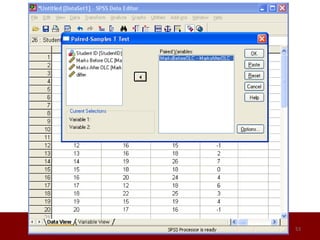
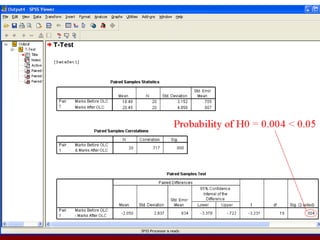
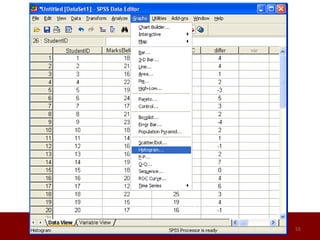
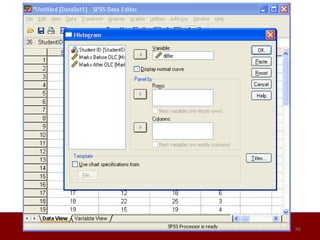
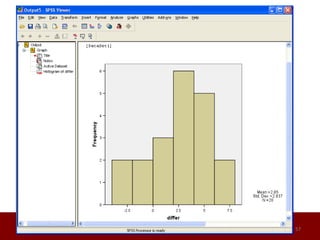
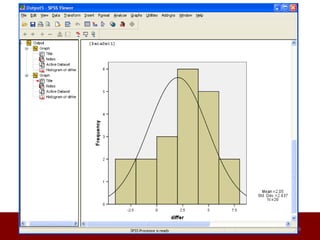
SPSS is a statistical software package used for data management and analysis. It allows users to enter and manage large amounts of data, perform a wide range of statistical analyses, and output results in tables and graphs. The main SPSS windows are the Data Editor, used to enter and view data, and the Viewer, which displays output of statistical analyses. Common analysis techniques demonstrated in the document include independent and paired t-tests to compare group means. The document provides guidance on using SPSS for questionnaire design and statistical analysis to efficiently analyze social science and business data.