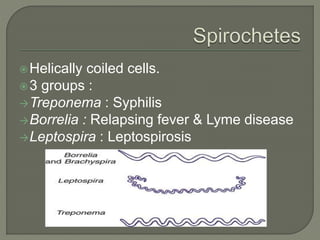
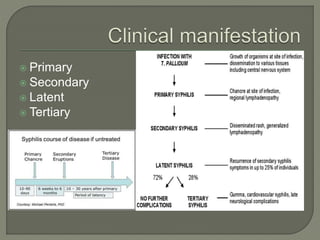
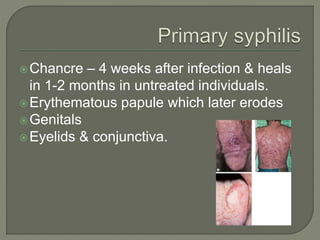
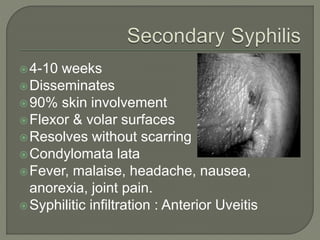
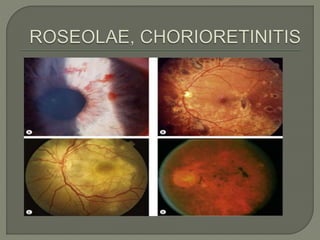
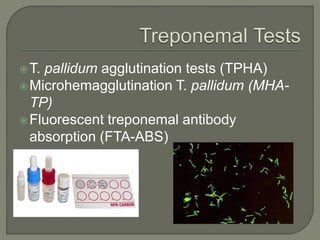
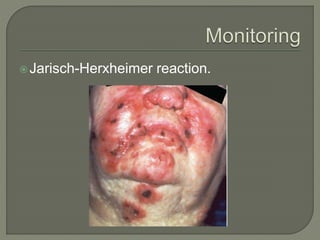
This document discusses syphilis, a sexually transmitted disease caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. It provides details on the classification, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of syphilis. Key points include that syphilis presents in primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary stages, and can cause ocular manifestations such as uveitis. Diagnosis involves serological tests like VDRL and FTA-ABS. Treatment depends on the stage of syphilis and may include penicillin or doxycycline. Congenital syphilis is also discussed.