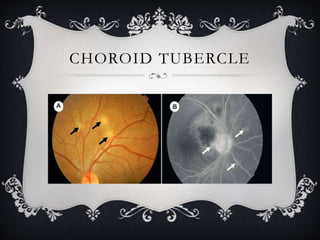
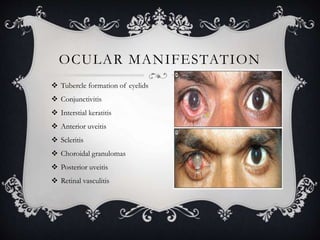
This document discusses tubercular uveitis, which occurs in 1-2% of patients with tuberculosis. Tubercular uveitis can involve both the anterior and posterior segments of the eye. Common manifestations include granulomatous iritis, interstitial keratitis, phlyctenular keratoconjunctivitis, choroidal granulomas, posterior uveitis, and retinal vasculitis. Diagnosis is difficult as obtaining ocular tissue samples is hard to justify, but a positive PPD test, interferon-γ release assay, or Quantiferon-TB Gold test provides supporting evidence. Treatment involves a combination of antibiotics like isoniazid and rifampin over several months along