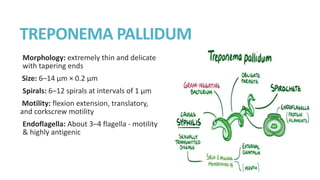
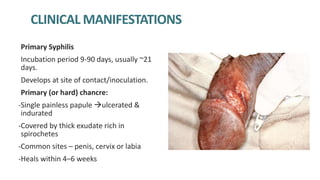
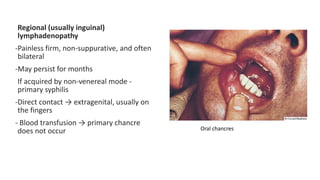
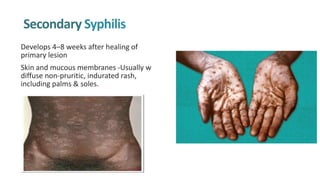
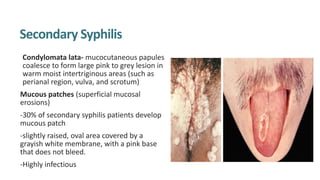
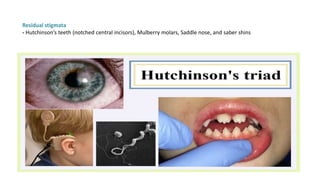
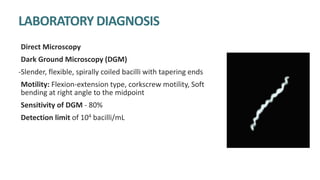
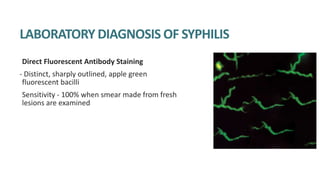
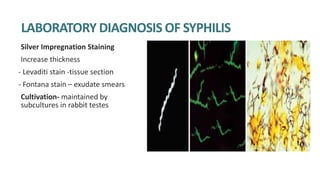
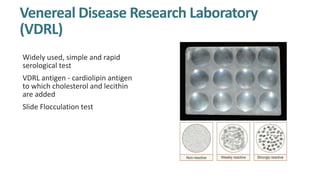
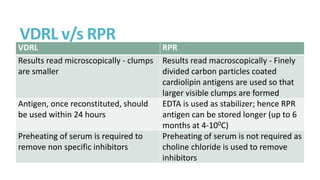
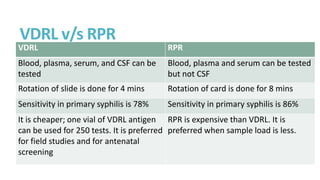
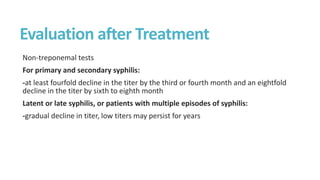
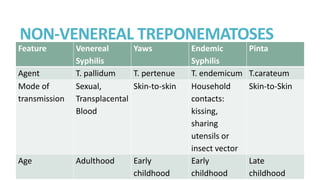
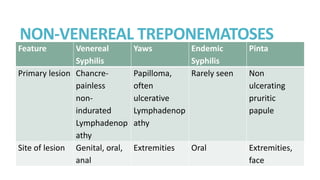
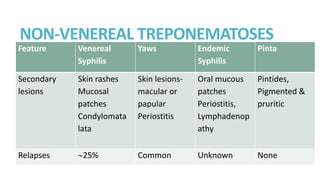
Syphilis is caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. It is transmitted sexually or congenitally from mother to fetus. Syphilis increases the risk of HIV transmission. It has various stages including primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary syphilis. Laboratory diagnosis involves direct visualization of T. pallidum via darkfield microscopy or detection of antibodies to T. pallidum via non-treponemal and treponemal tests. Penicillin is the treatment of choice for all stages of syphilis.