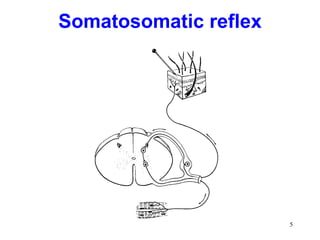
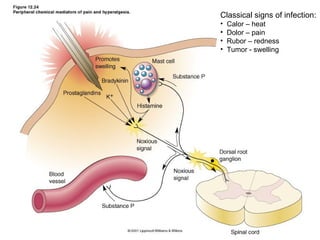
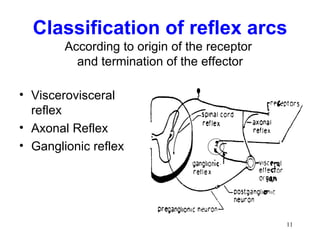
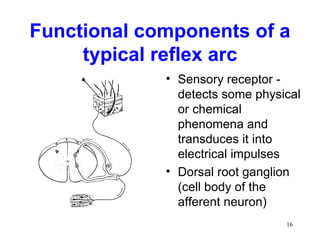
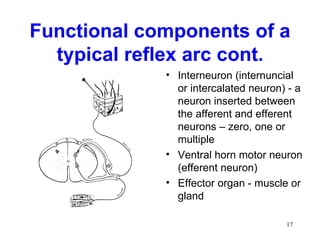
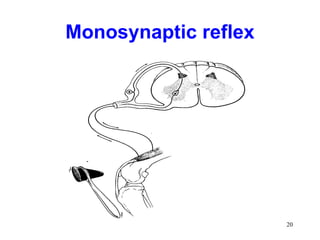
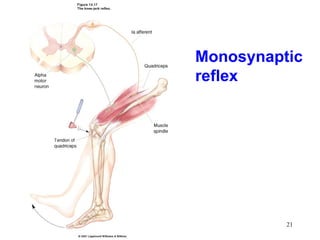
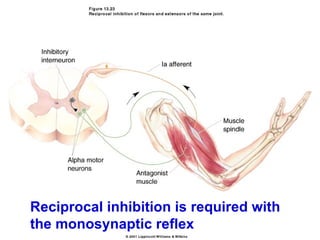
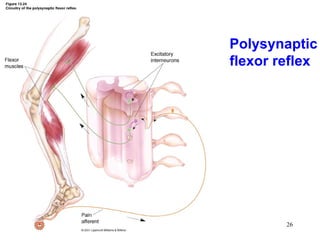
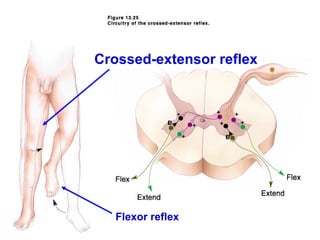
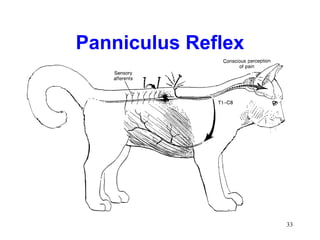
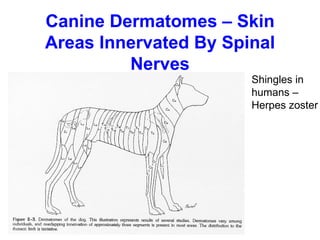
Spinal cord reflexes are neuronal circuits extending from peripheral receptors through the spinal cord to effectors. Reflexes are classified by the origin and termination of the receptor and effector. Major reflexes include the monosynaptic stretch reflex, flexor withdrawal reflex, reciprocal innervation, crossed extensor reflex, extensor thrust reflex, scratch reflex, and panniculus reflex. These reflexes maintain posture, remove the body from harm, and protect skin from irritants.