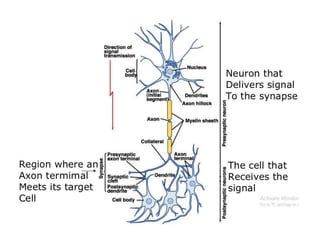
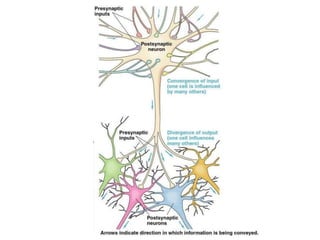
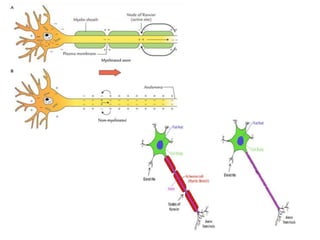
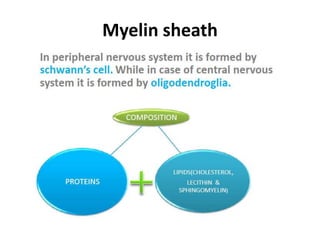
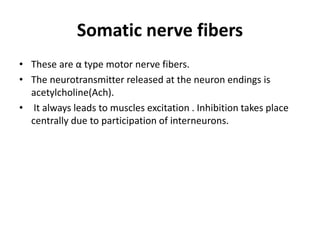
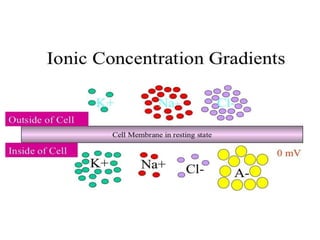
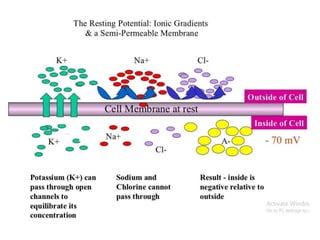
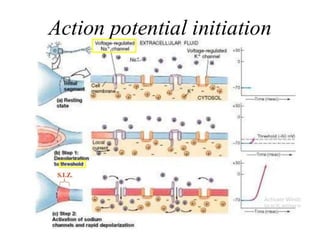
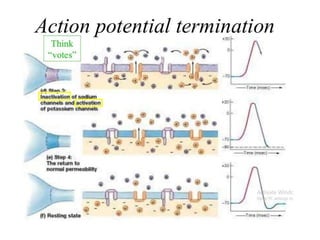
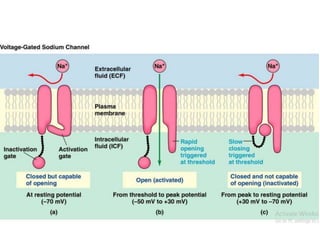
Nerve fibers can be classified based on their structure and distribution. There are two main types - myelinated and unmyelinated fibers. Nerve fibers also include somatic and autonomic fibers. Somatic fibers innervate skeletal muscles and the neurotransmitter is acetylcholine, leading to muscle excitation or central inhibition. Autonomic fibers innervate smooth, cardiac muscles and glands to maintain homeostasis, causing excitation or inhibition. Important properties of nerve fibers include excitability, conductivity, unfatigability, refractory periods, all-or-none response, summation, and accommodation.