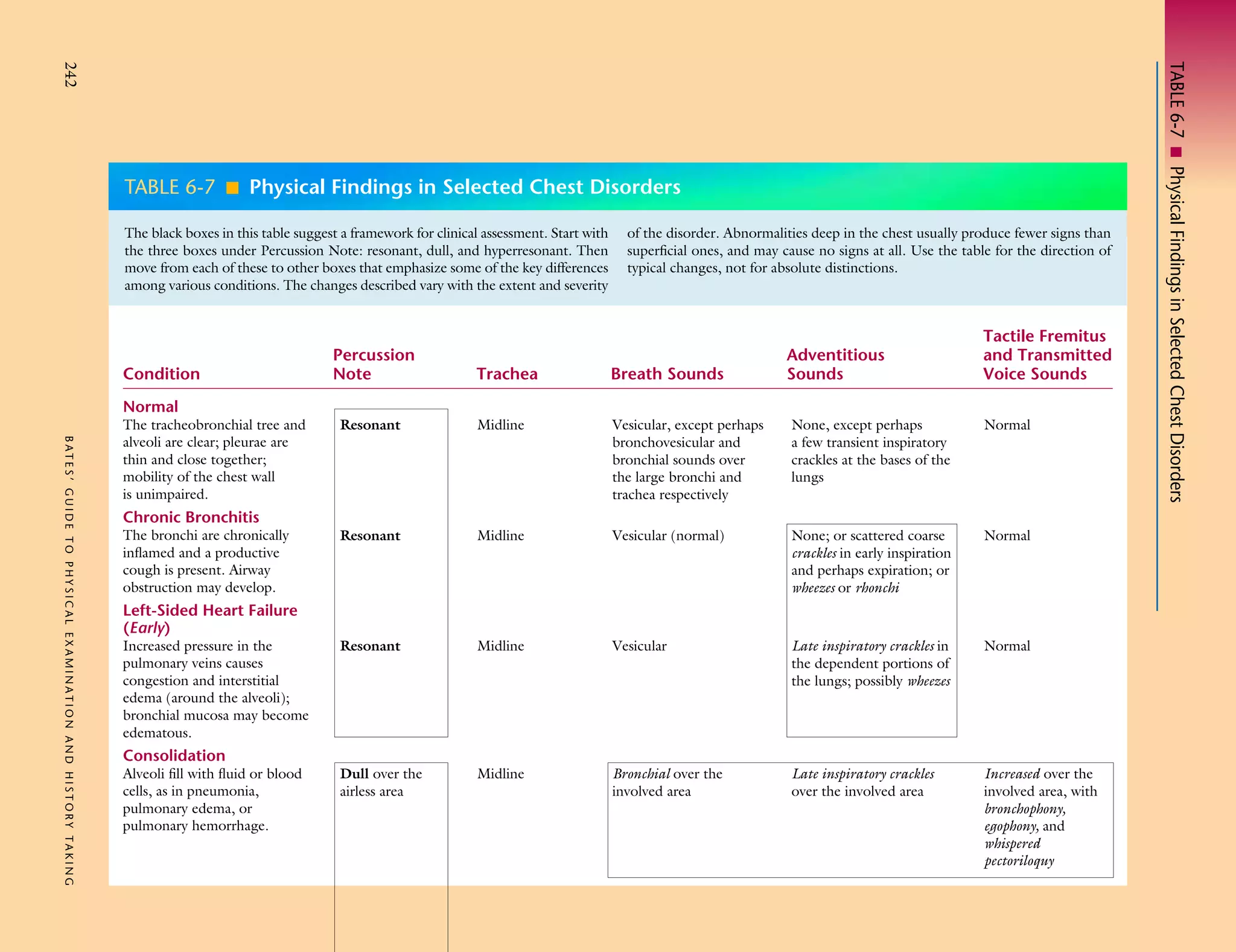
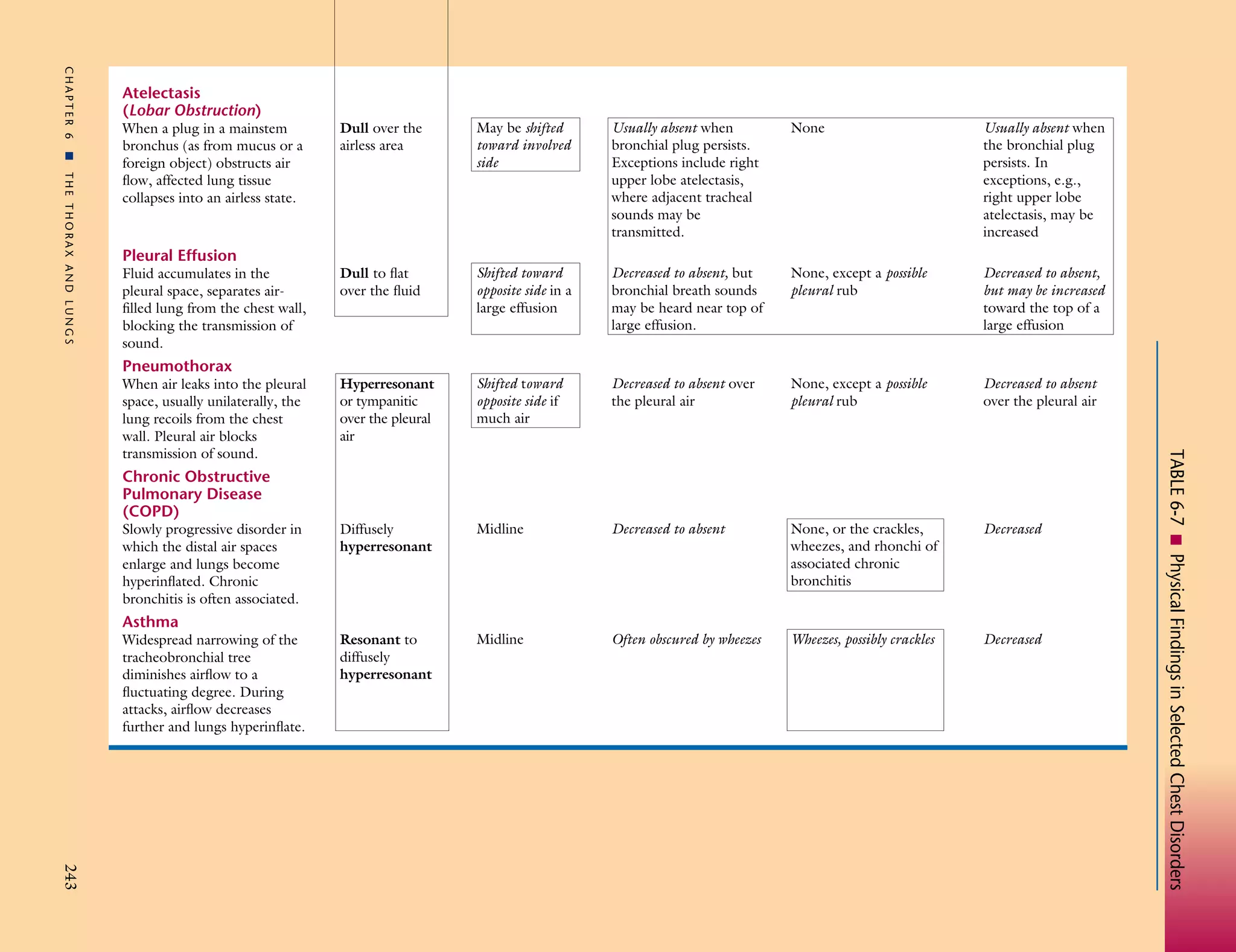
The document provides a framework for assessing clinical conditions of the chest through percussion notes, adventitious sounds, tactile fremitus and transmitted voice sounds, and breath sounds. It compares these findings for normal lungs versus conditions such as chronic bronchitis, left-sided heart failure, consolidation, atelectasis, pleural effusion, pneumothorax, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and asthma. The table acts as a guide for how physical exam findings may change with different chest disorders and their locations and severity.