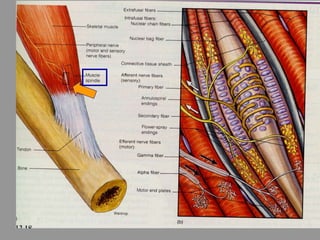
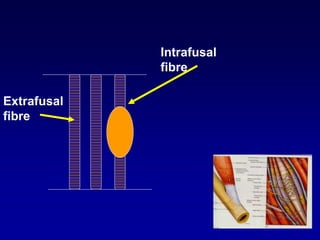
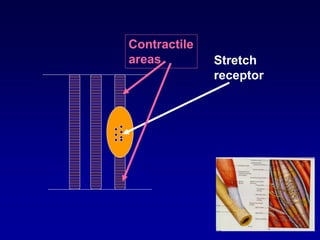
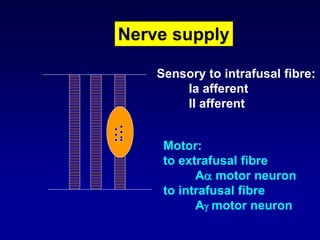
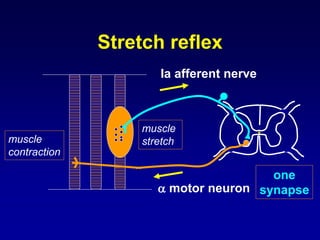
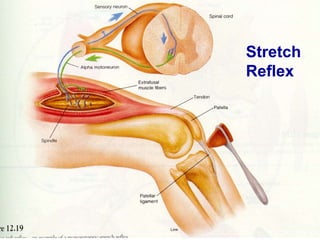
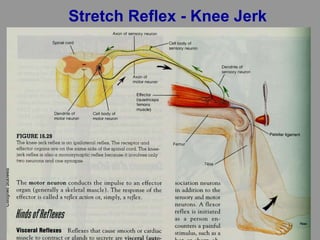
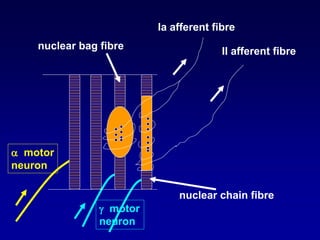
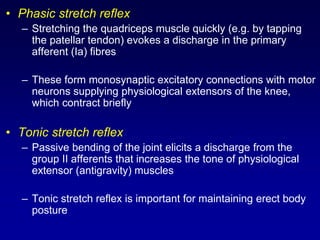
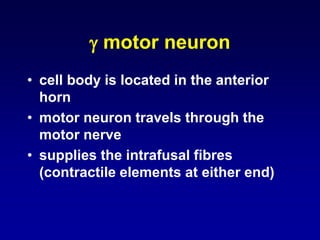
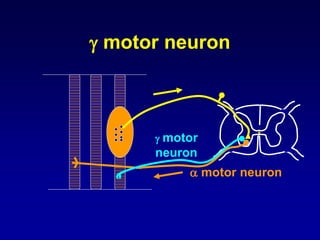
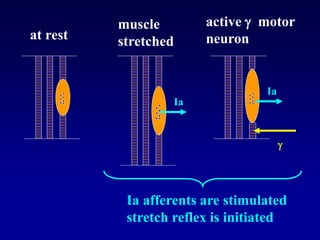
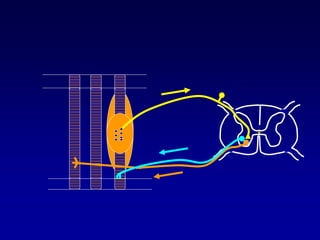
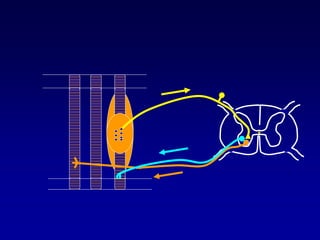
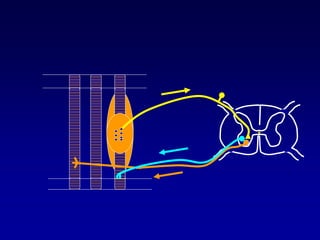
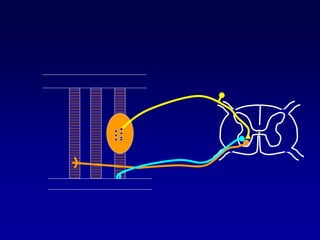
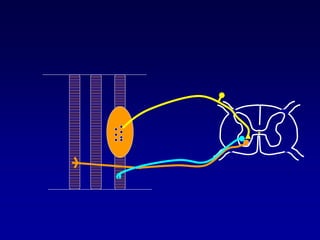
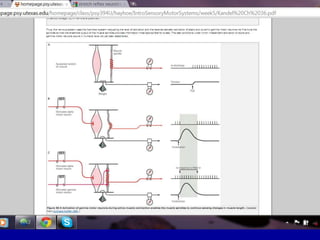
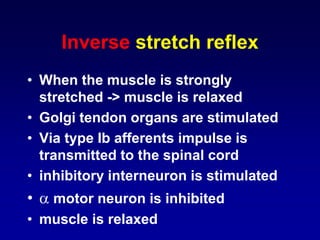
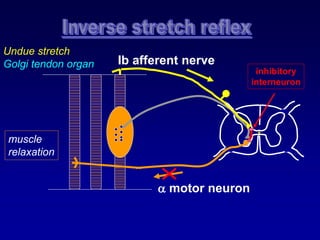
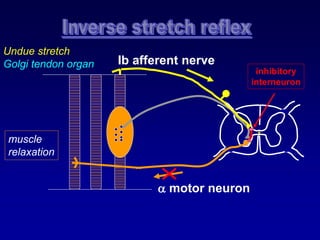
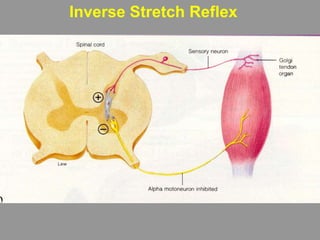
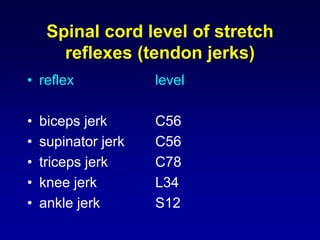
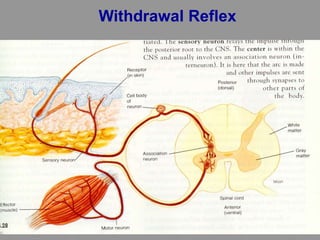
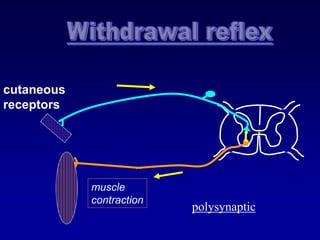
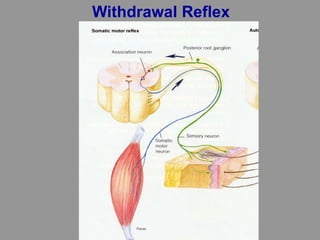
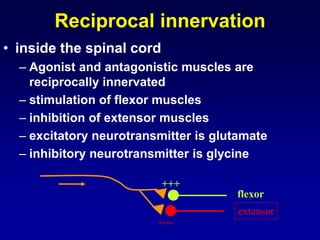
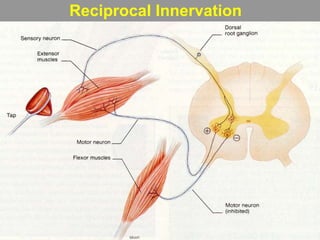
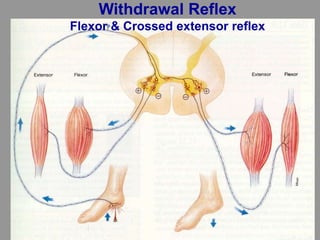
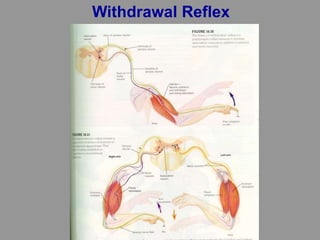
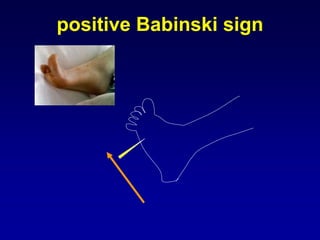
This document discusses motor reflexes and their components. It begins by defining reflexes as involuntary responses to stimuli that do not involve significant brain involvement. It then discusses the stretch reflex in detail, including the roles of muscle spindles, Ia afferent fibers, and alpha and gamma motor neurons. Additional reflexes discussed include withdrawal reflexes, reciprocal innervation, and primitive reflexes seen in infants. The clinical importance of assessing reflexes to localize lesions in the motor system is also mentioned.