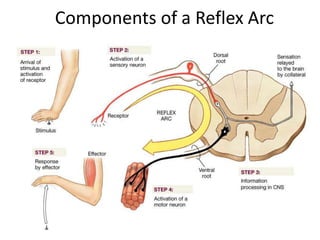
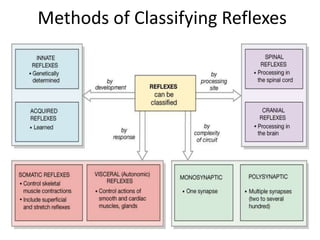
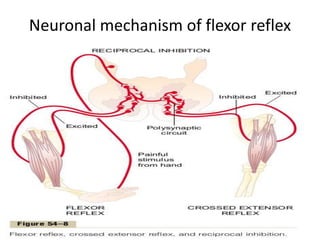
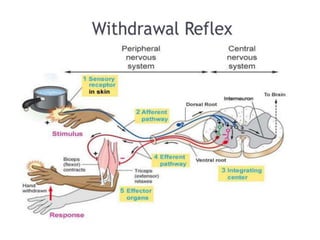
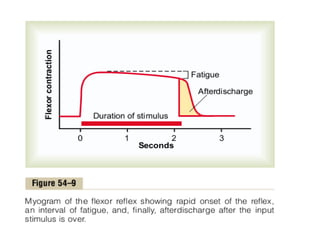
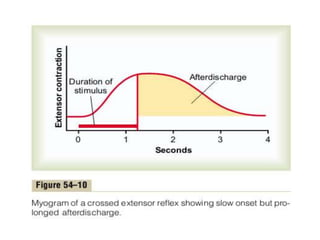
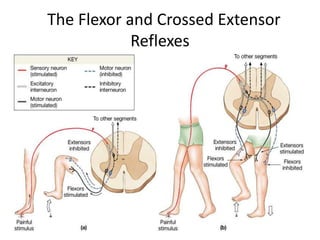
Reflexes are automatic responses to stimuli that involve a reflex arc consisting of sensory receptors, sensory neurons, processing in the central nervous system, motor neurons, and effectors. Reflexes maintain homeostasis, carry out automatic actions like swallowing and sneezing, and maintain balance and posture through spinal reflexes controlling trunk and limb muscles. There are different types of reflexes including flexor reflexes which cause limb flexion in response to stimuli, and crossed extensor reflexes which cause the opposite limb to extend about 0.2 to 0.5 seconds after a flexor reflex is elicited in one limb. Reciprocal inhibition occurs when a stretch reflex excites one muscle while simultaneously inhibiting the antagonist muscle through reciprocal innervation.