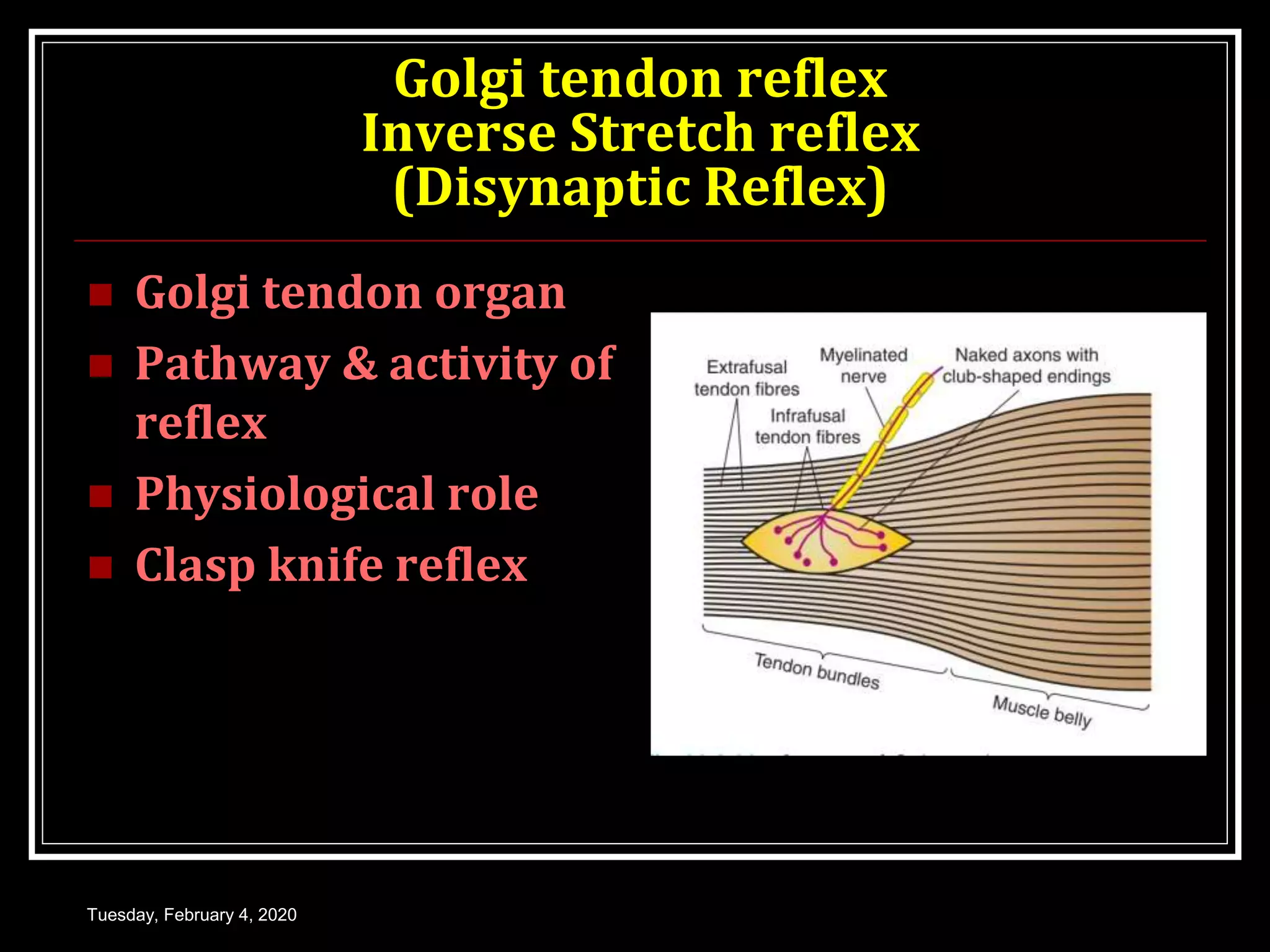
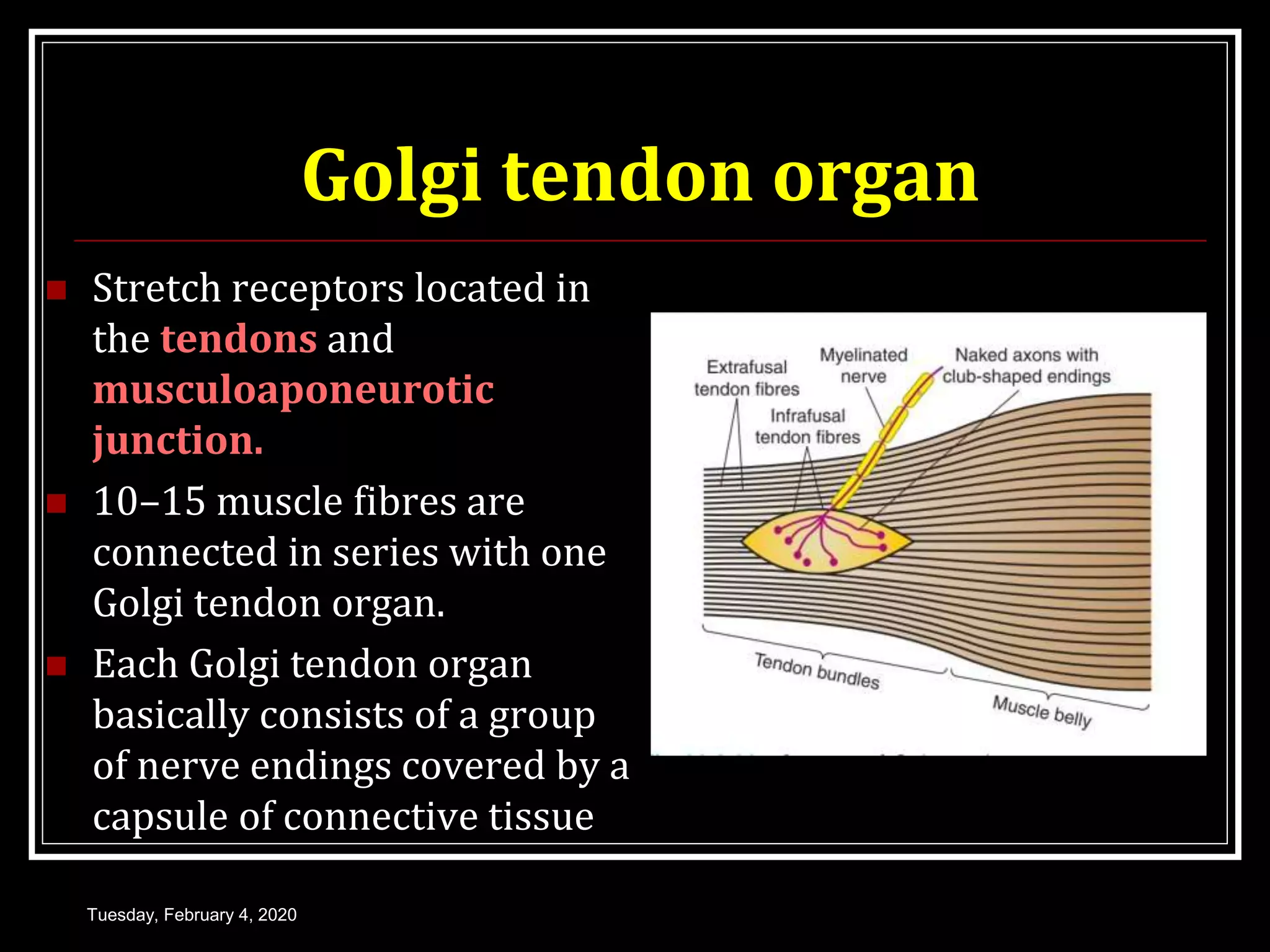
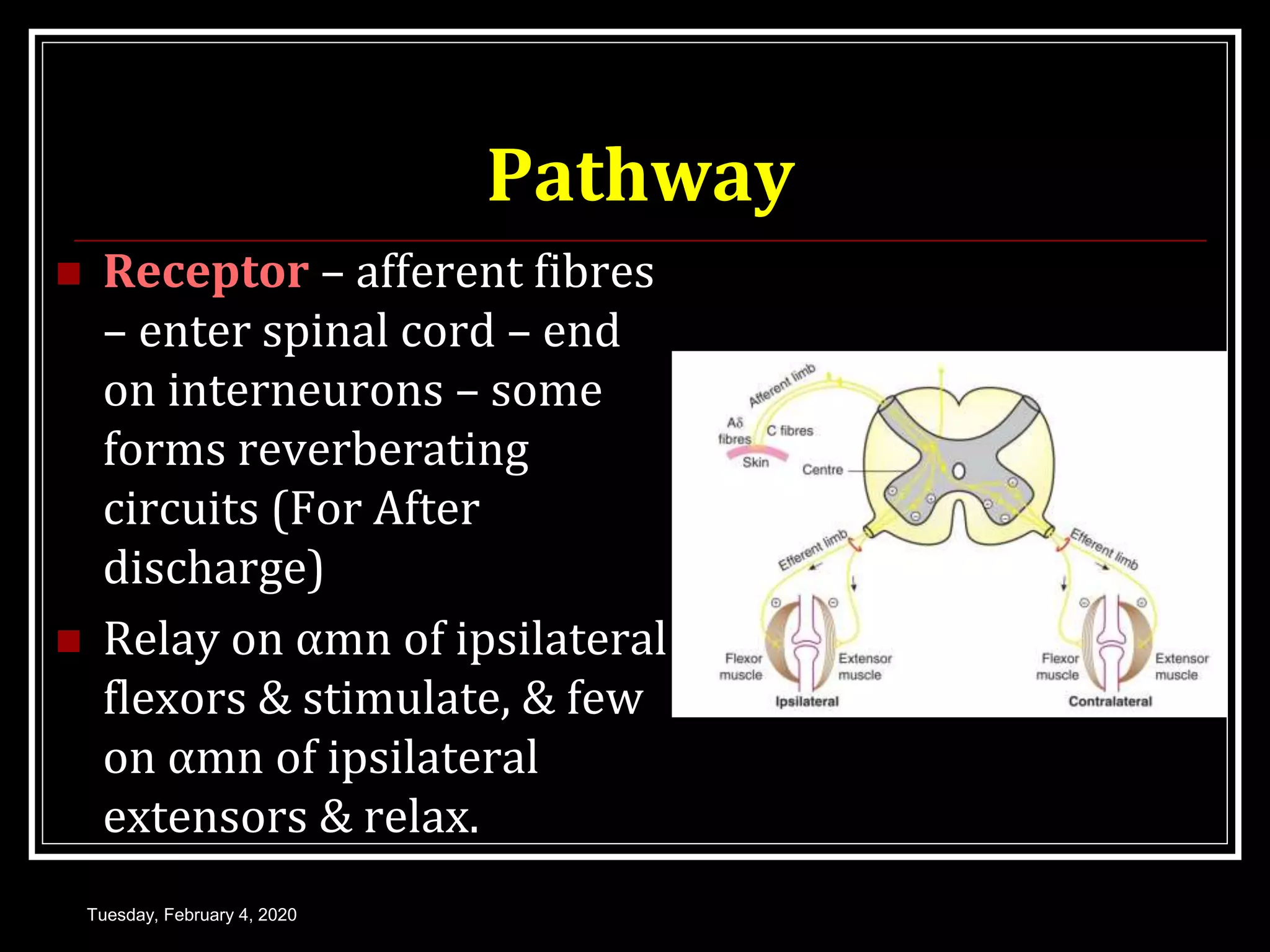
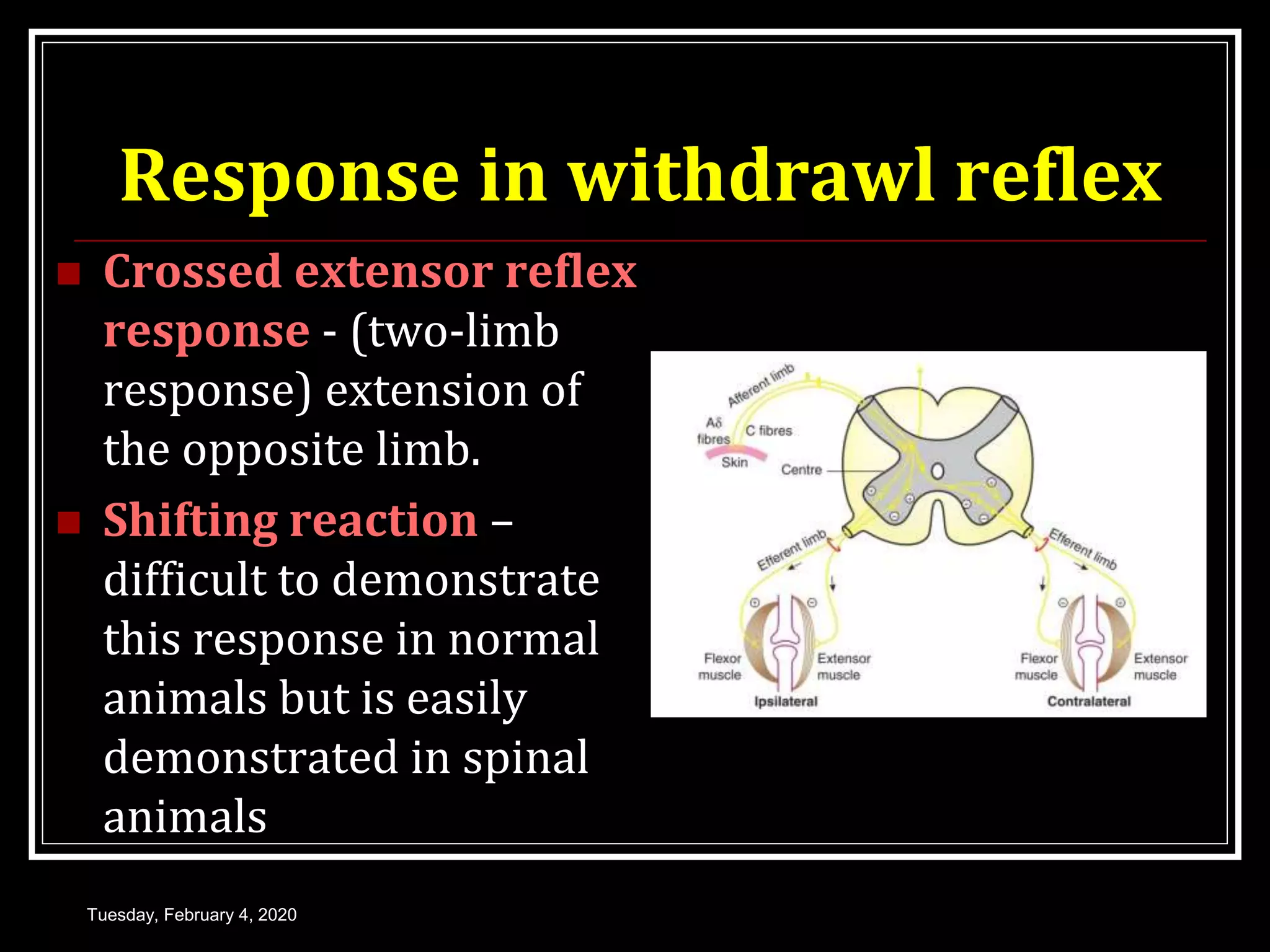
This document discusses the Golgi tendon organ and reflex, as well as the withdrawal reflex. It begins by describing the Golgi tendon organ as stretch receptors located in tendons and musculoaponeurotic junctions. It then explains the pathway and function of the Golgi tendon reflex, which protects muscles from overcontraction via autogenic inhibition. Next, it defines the withdrawal reflex as a polysynaptic reflex that causes limb removal in response to painful stimuli, and describes the neural pathway and variations in withdrawal response, including crossed extensor response and widespread withdrawal. It concludes by discussing the protective function of withdrawal reflexes and comparing physiological and pathological clinical reflexes.