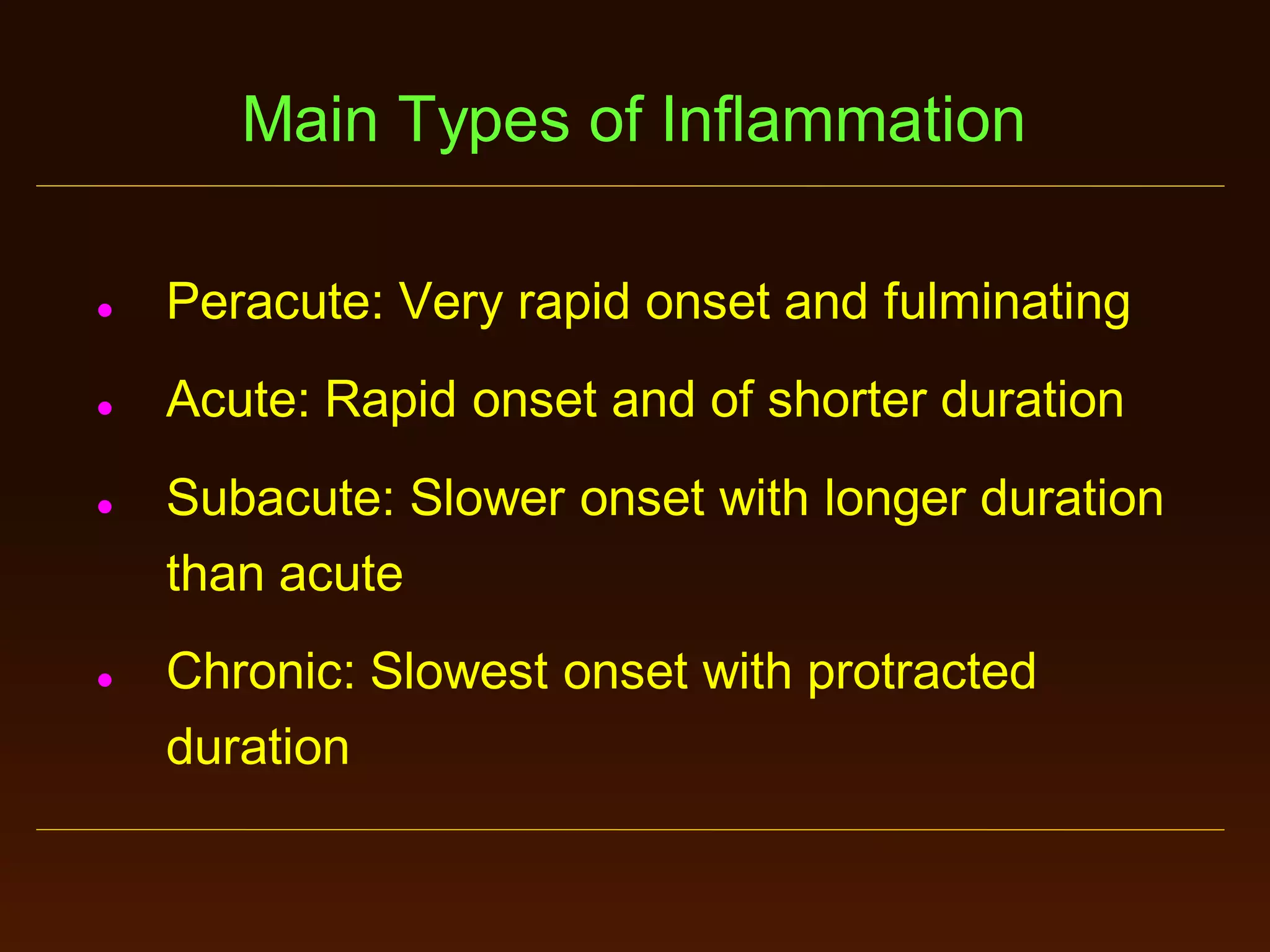
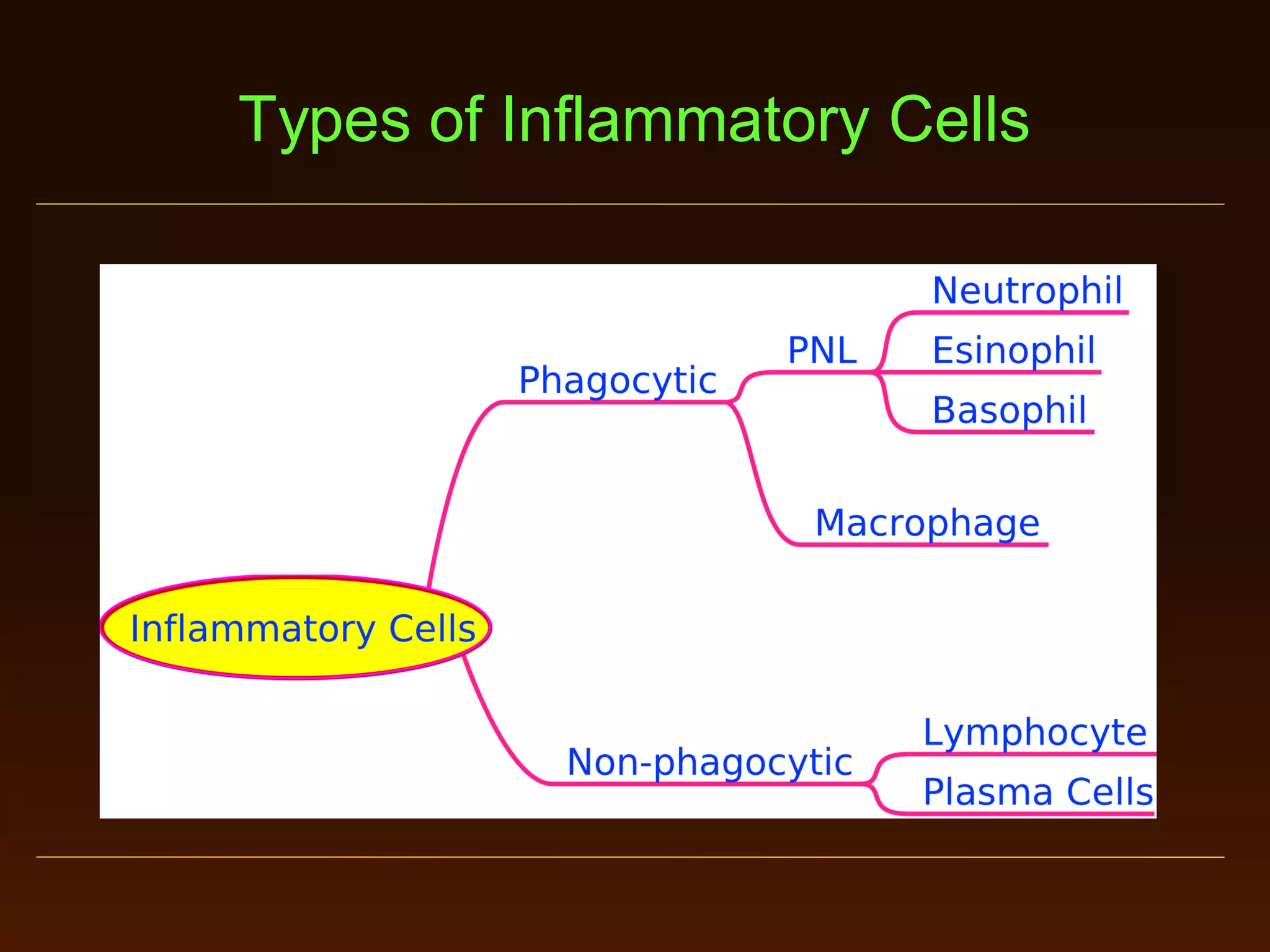
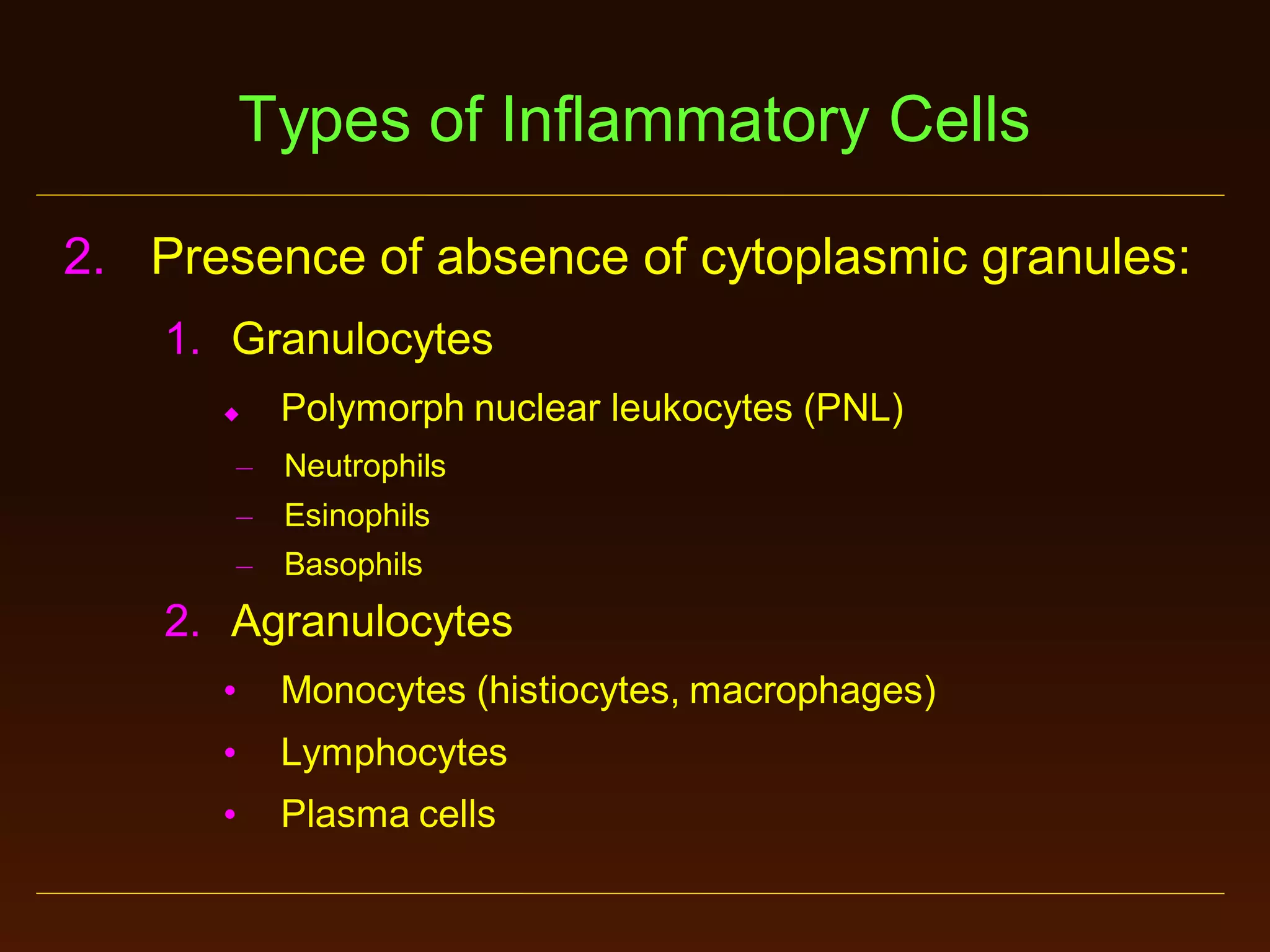
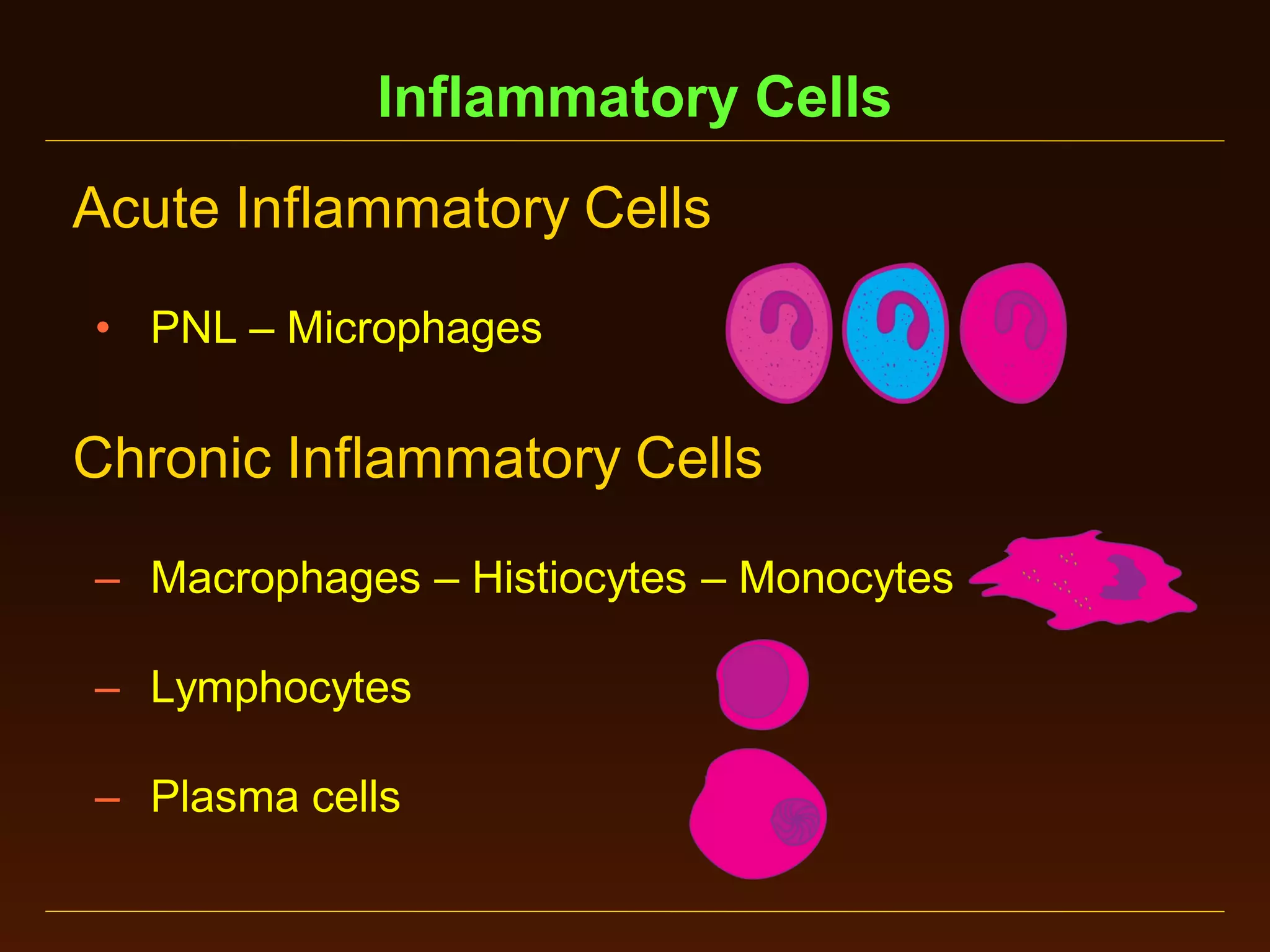
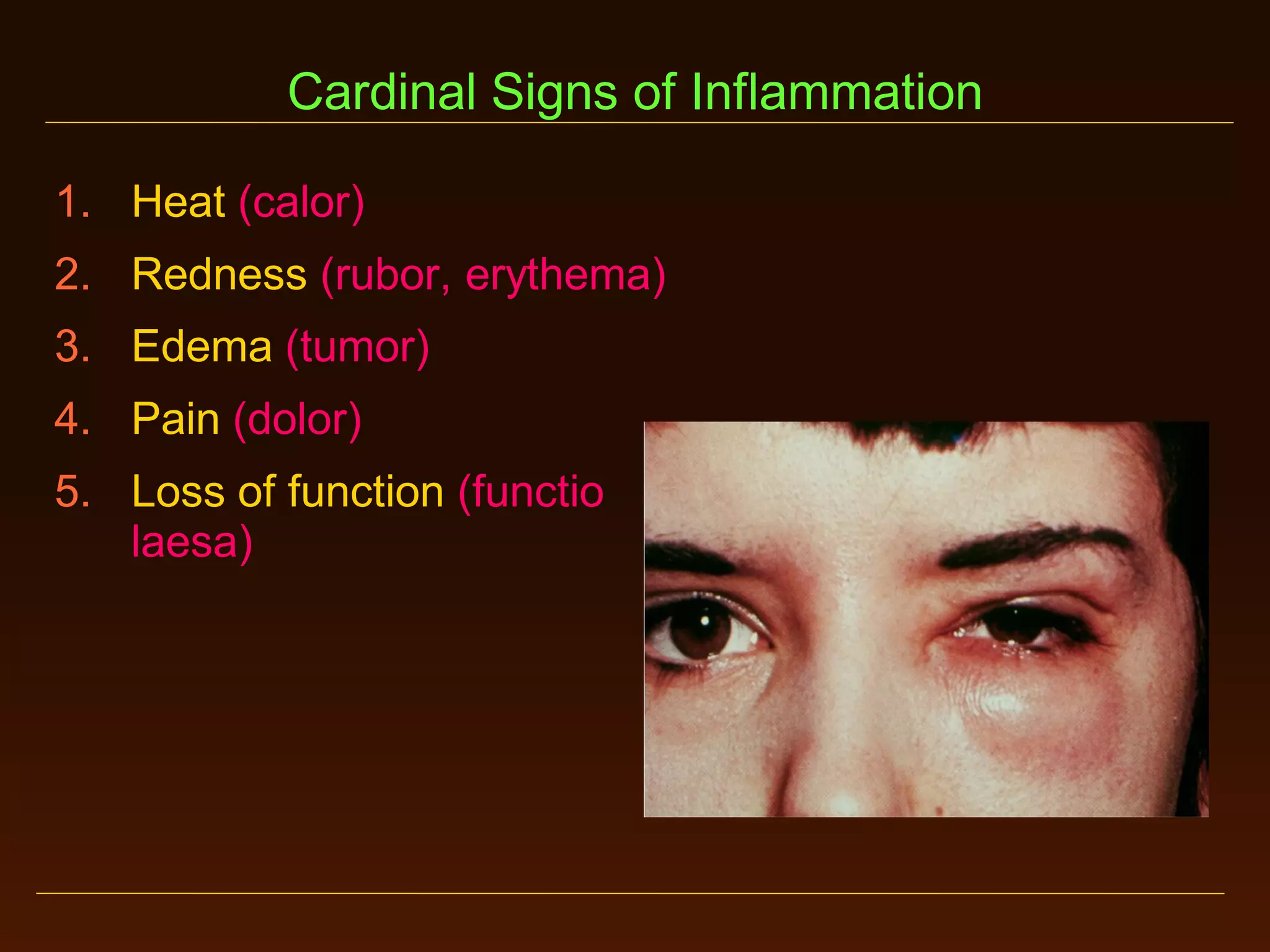
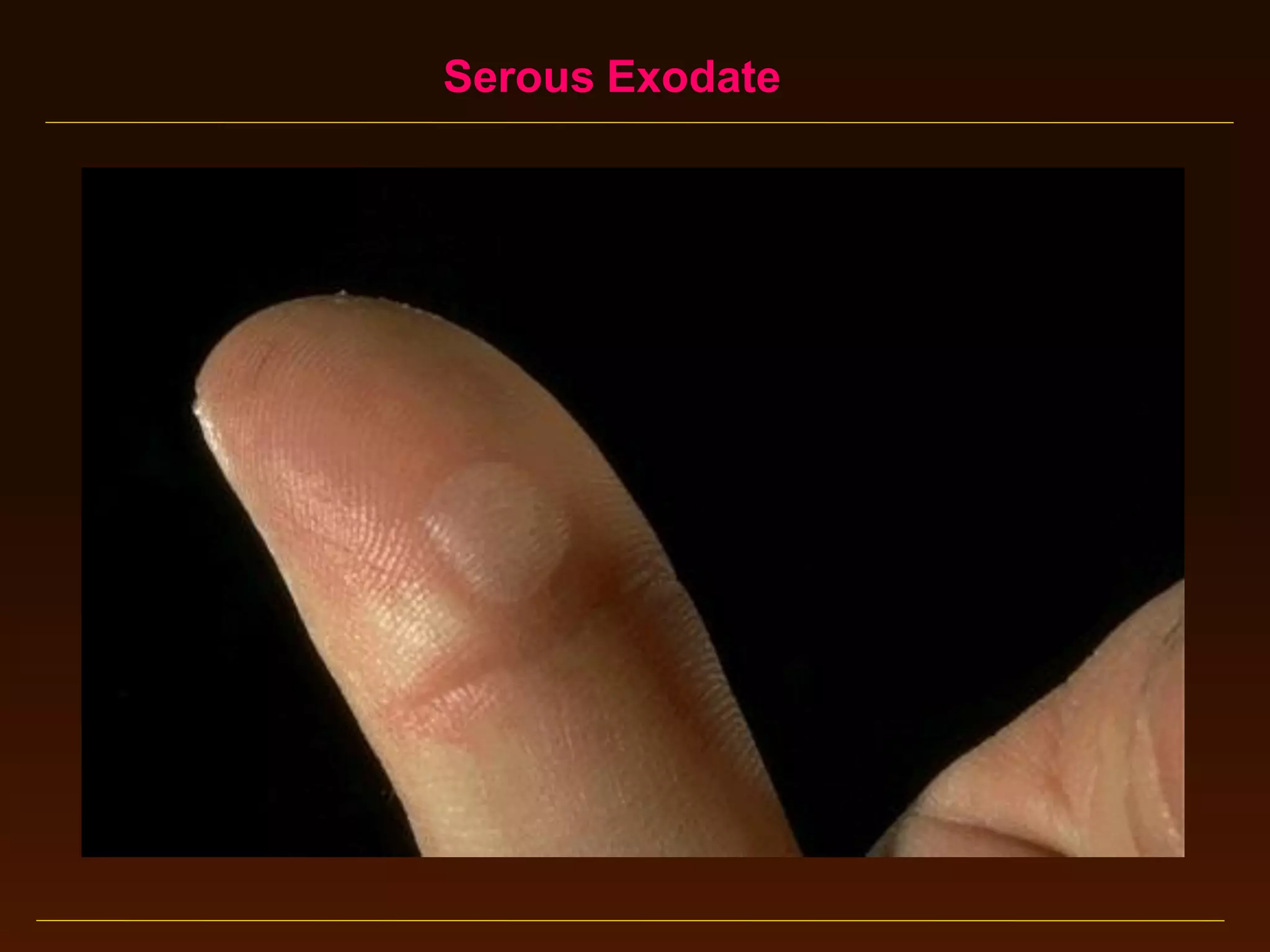
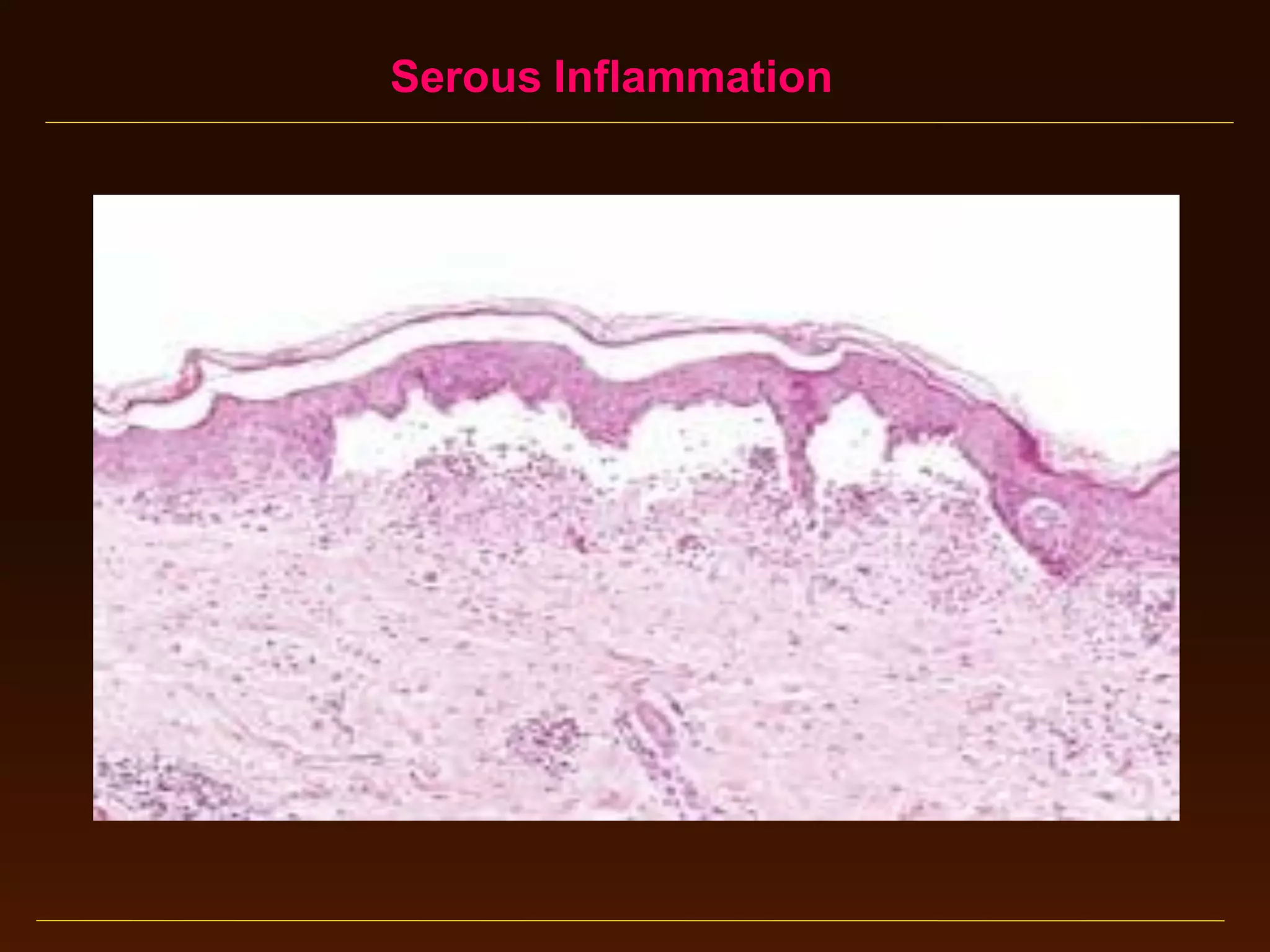
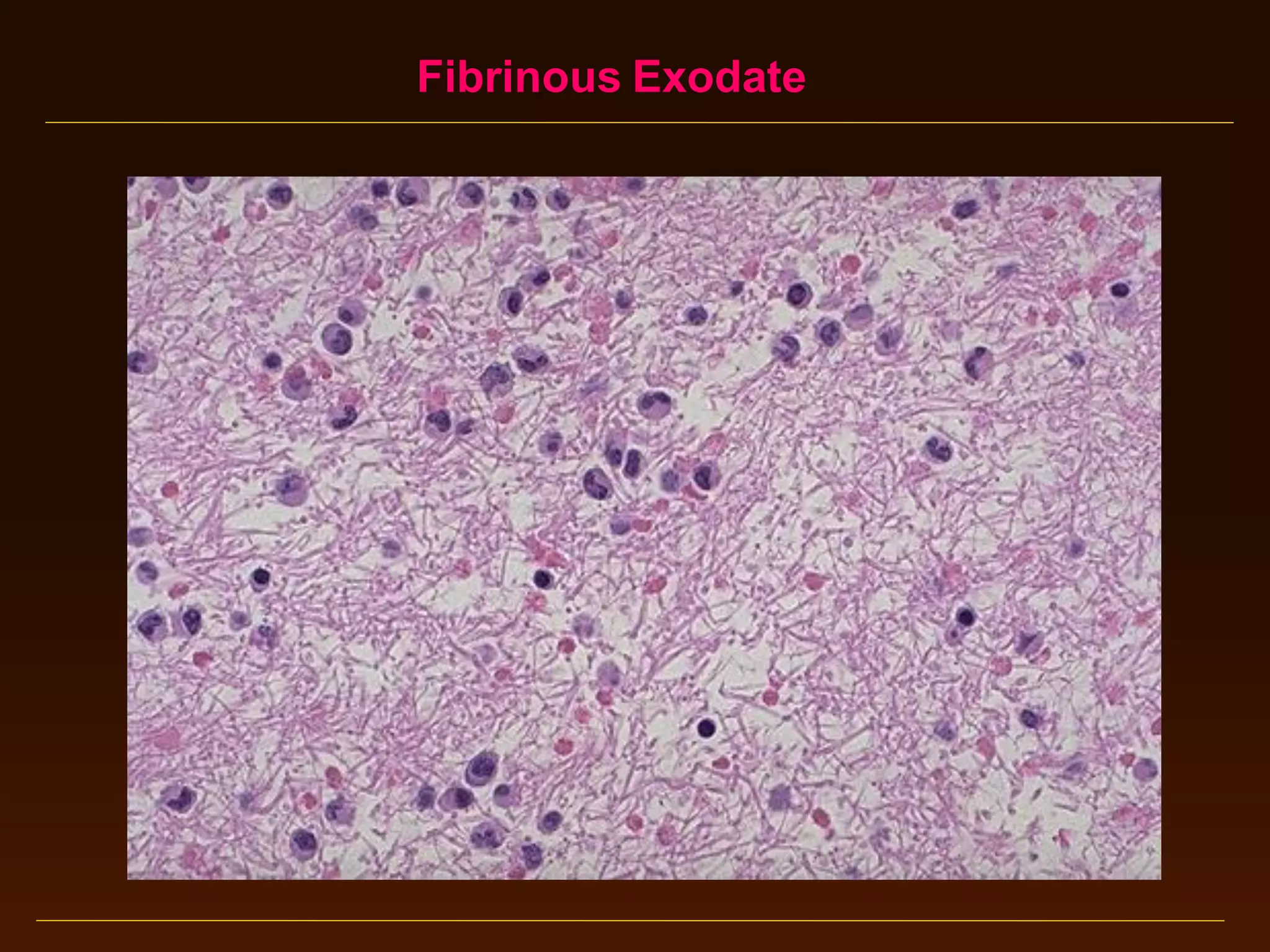
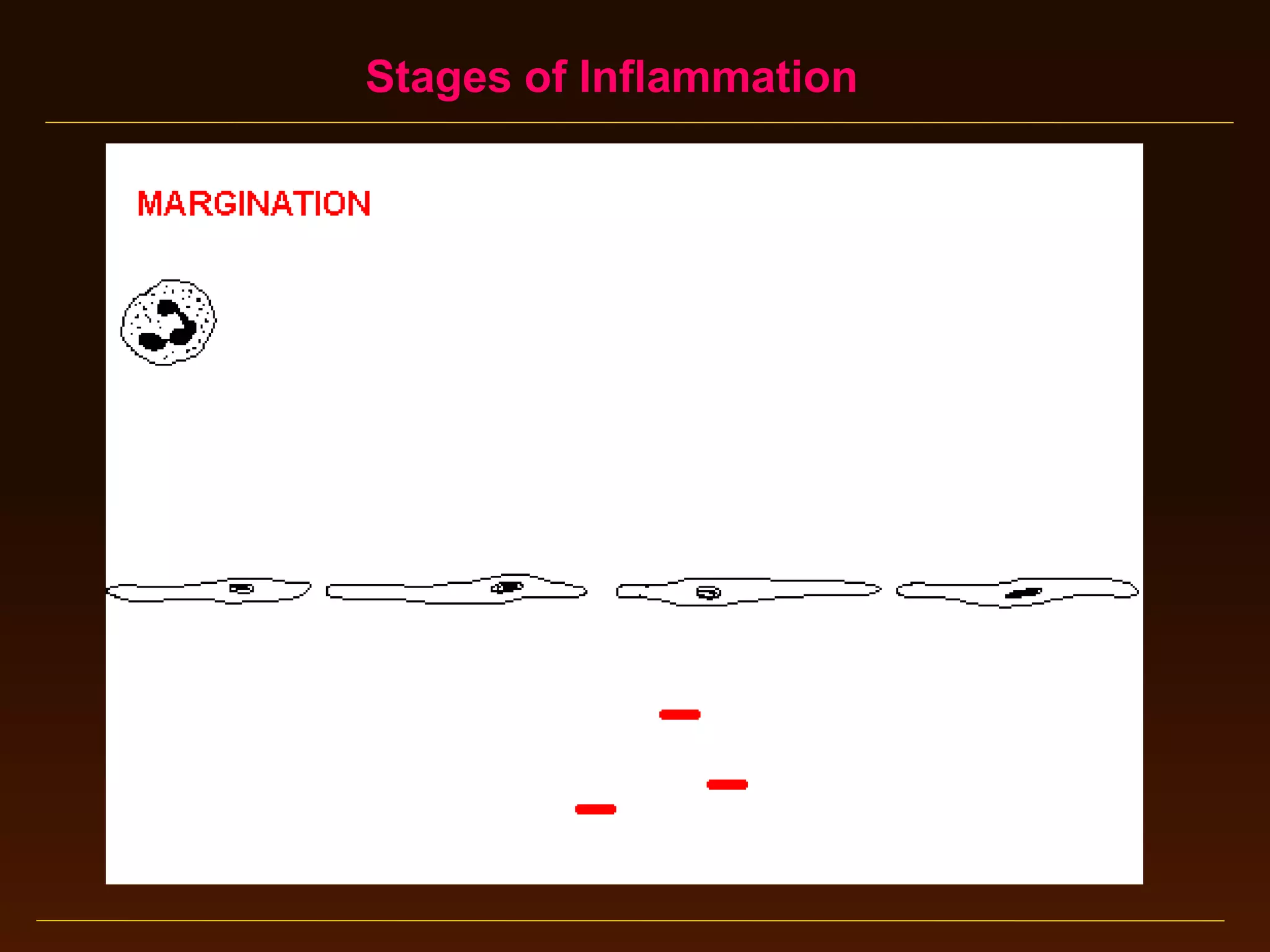
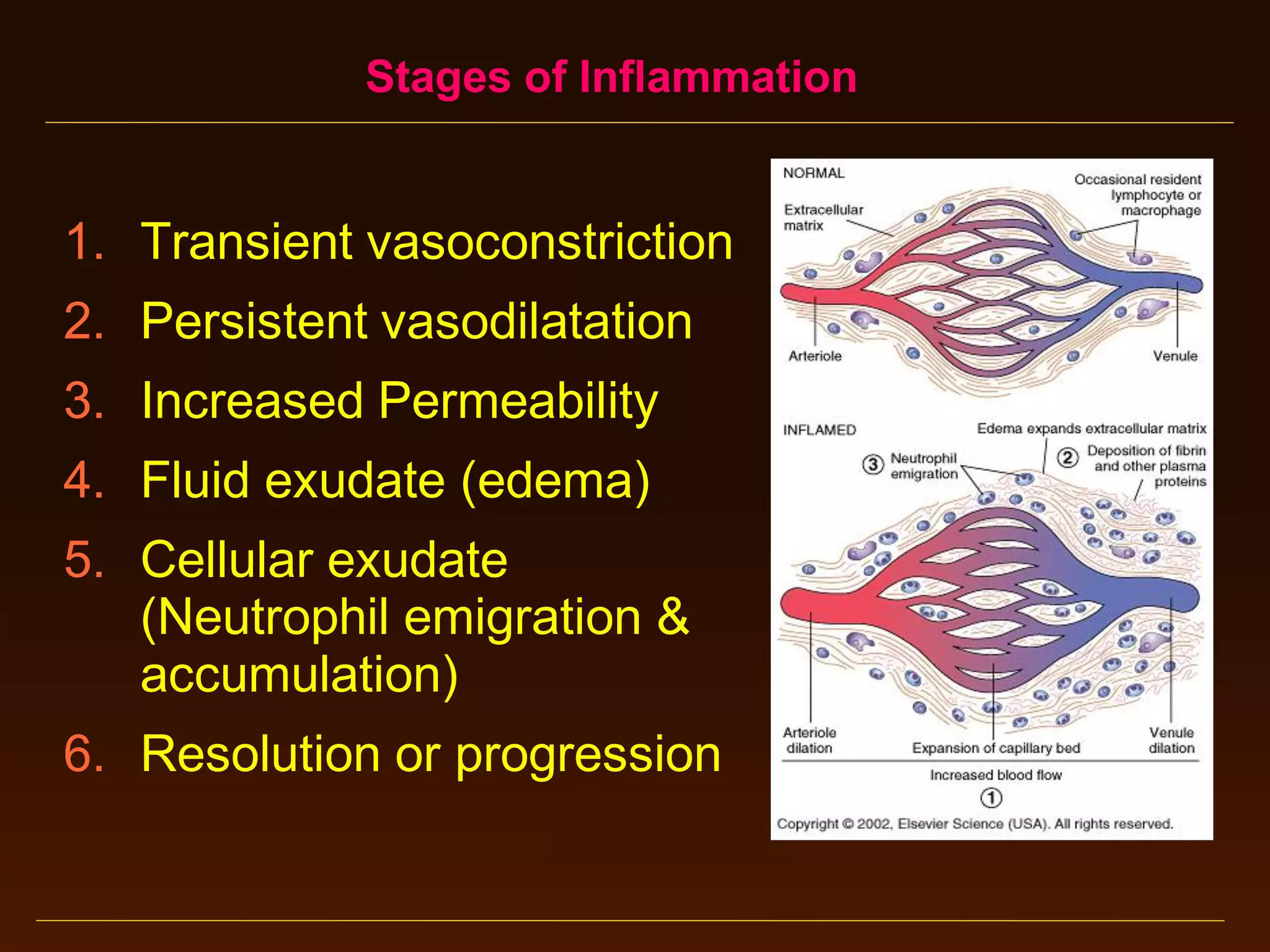
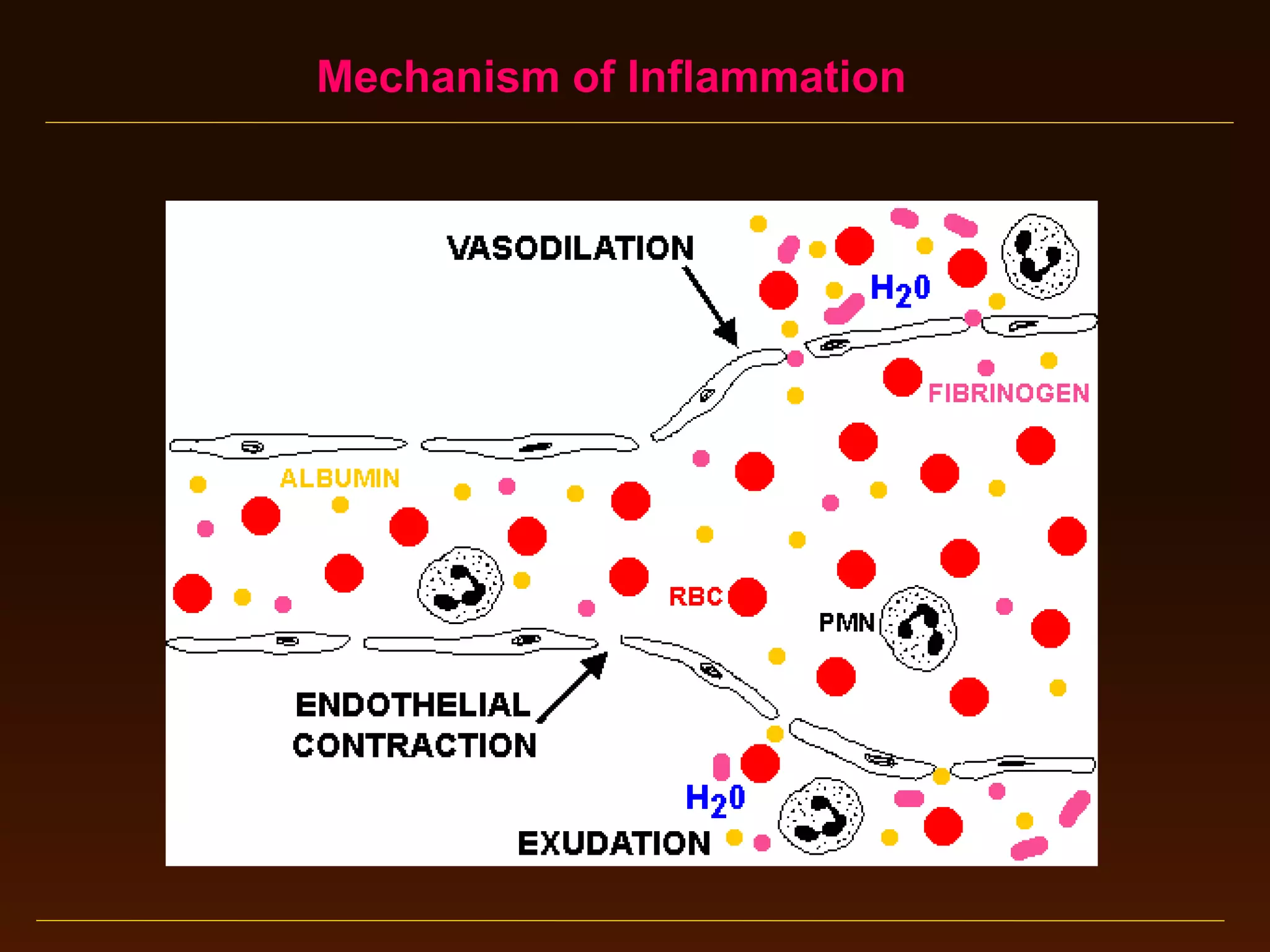
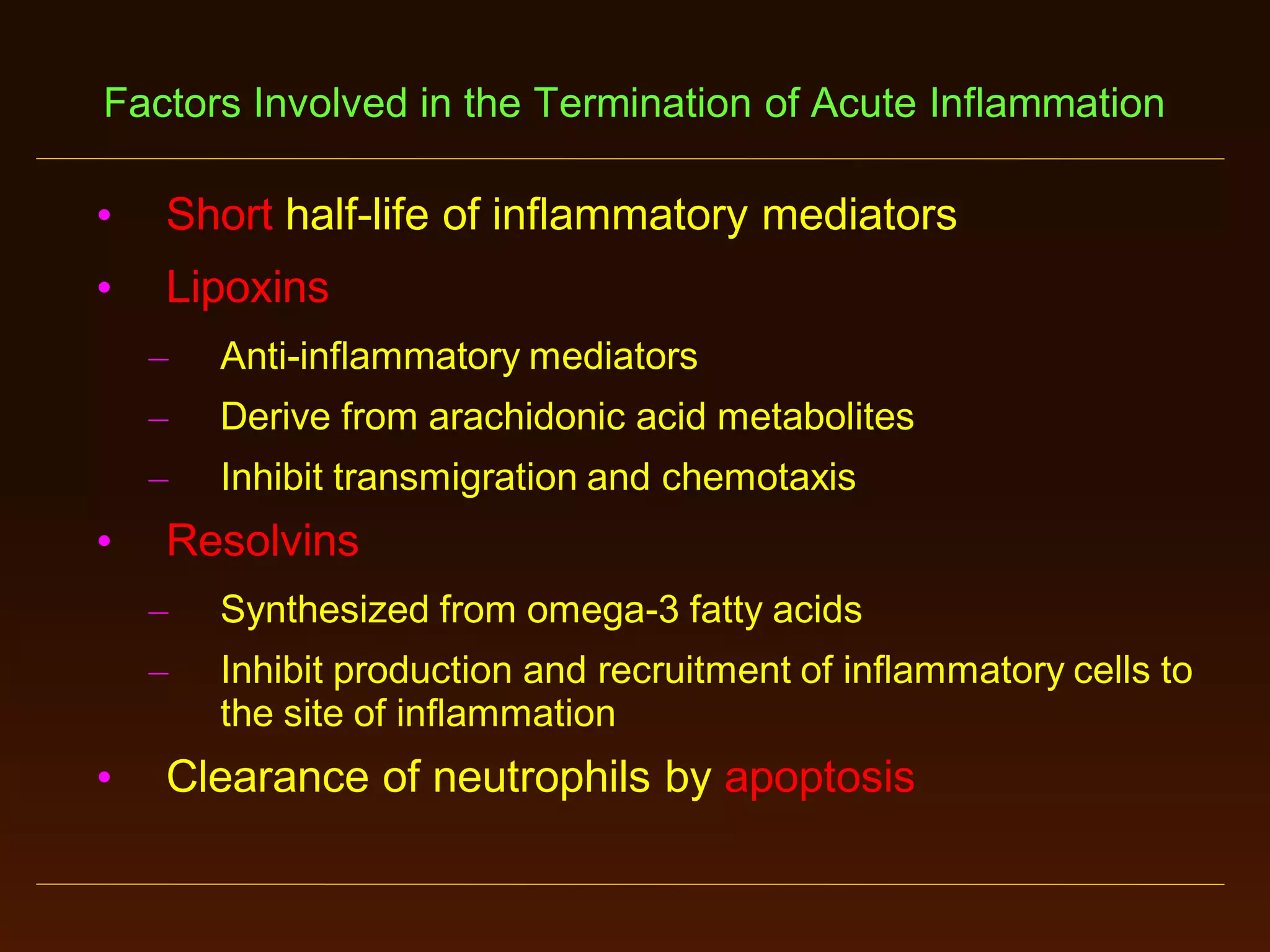
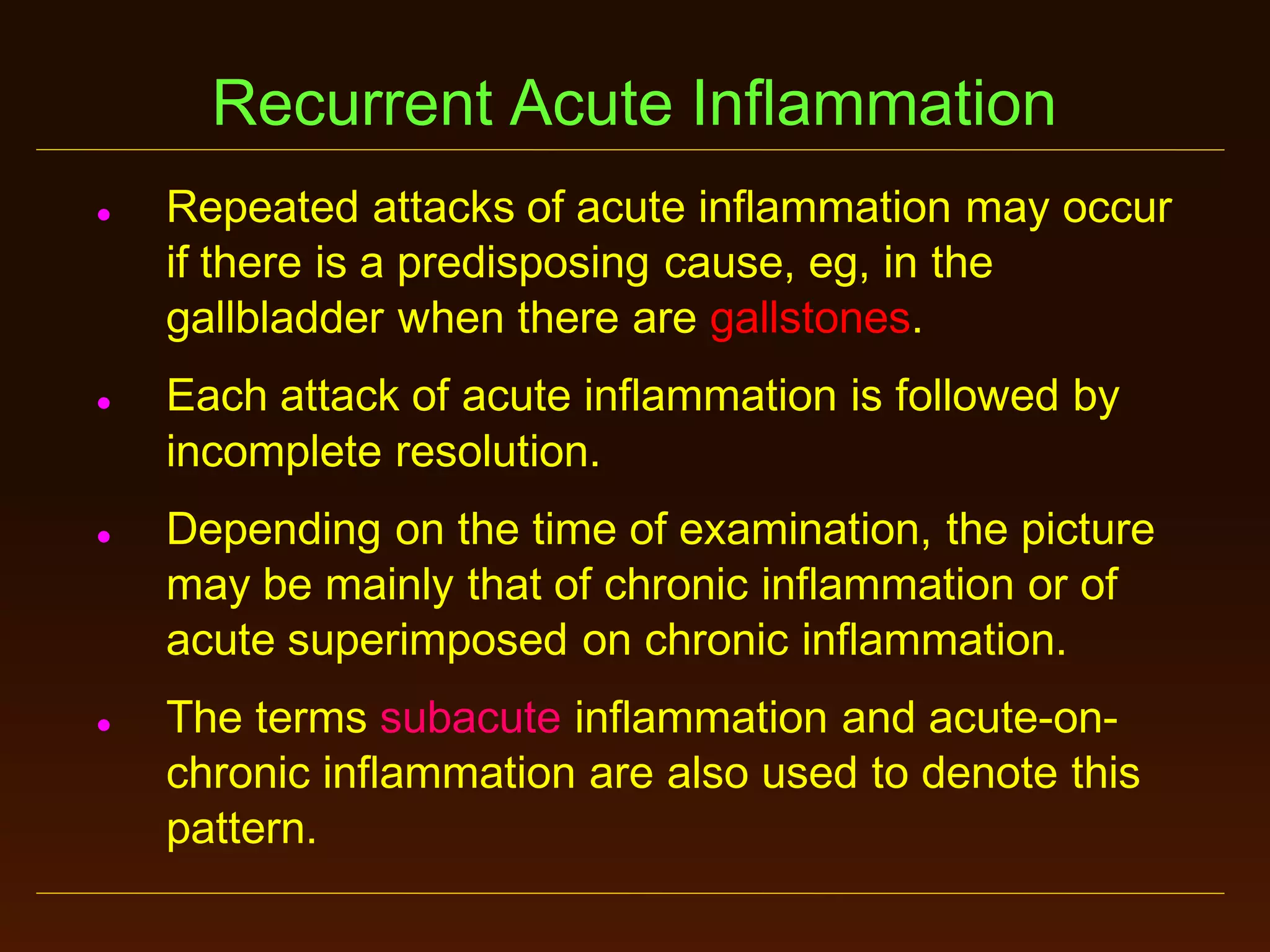
This document provides an overview of acute and chronic inflammation. It defines inflammation and outlines the main types, including acute and chronic inflammation. Acute inflammation is defined as a rapid, transient response and its stages are described as transient vasoconstriction, persistent vasodilation, increased permeability, fluid exudate formation, cellular exudate accumulation, and resolution or progression. Chronic inflammation is defined as prolonged inflammation that involves attempts at repair. Its causes include persisting infections or irritants and autoimmune reactions. The document outlines the cells involved in chronic inflammation and types of mixed acute and chronic inflammation.