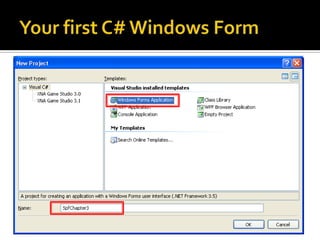
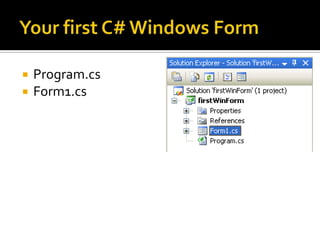
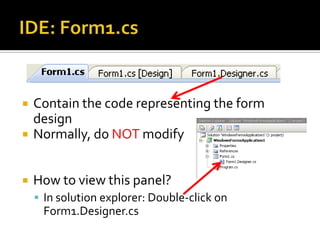
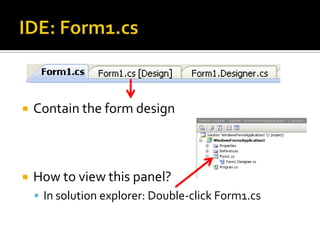
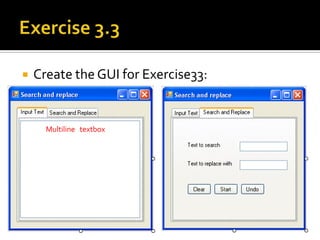
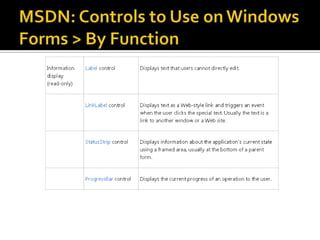
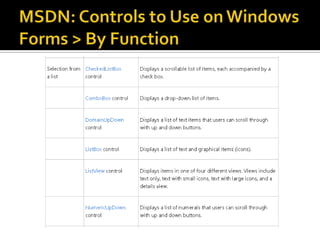
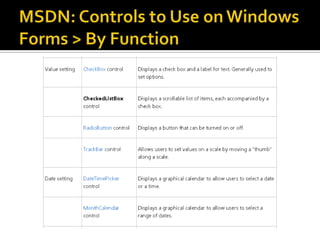
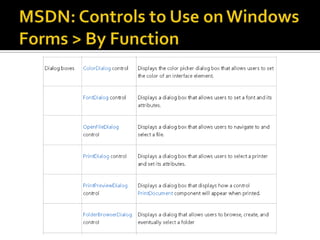
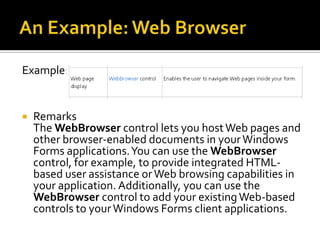
This document provides an overview of creating a C# Windows Forms application in Visual Studio. It discusses the two main files - Program.cs and Form1.cs - used to create the application and form. It describes using the toolbar and properties window to design the GUI. Various controls like buttons, textboxes and labels are demonstrated. Handling events like button clicks to add interactivity is covered. Finally, it provides examples of solving common programming problems using the Windows Forms environment.


![Program.csWindow Applications allow multi-threadingSingle Threaded Apartment [STAThread]Multi Thread Apartment [MTAThread][STAThread] // Attribute for Main() method static void Main()Application.Run(new Form1());// Begins running a standard // application on the current // thread](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter03updated2-100420164700-phpapp02/85/Spf-chapter-03-WinForm-5-320.jpg)
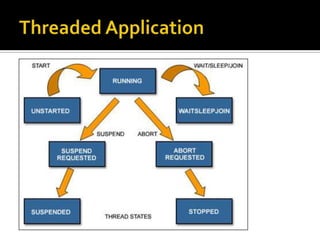
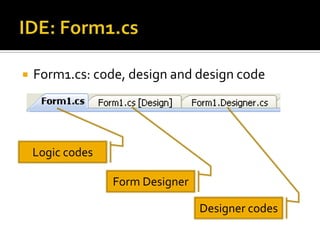
![IDE: Form1.csContain the logic you put inHow to view this panel?In solution explorer: Double-click Form1.csMenu: View > code OR click on [view code icon]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter03updated2-100420164700-phpapp02/85/Spf-chapter-03-WinForm-8-320.jpg)
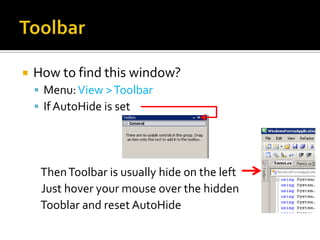
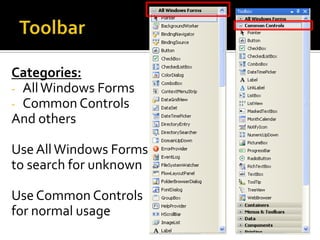
![ToolbarToolbar window is Context sensitiveIt will show the controls ONLY in the Design View: Eg Form1.cs [Design]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter03updated2-100420164700-phpapp02/85/Spf-chapter-03-WinForm-12-320.jpg)

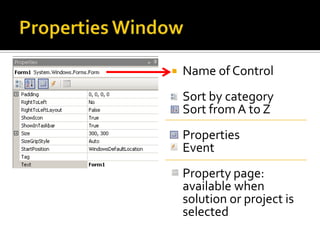
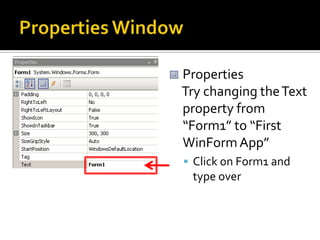
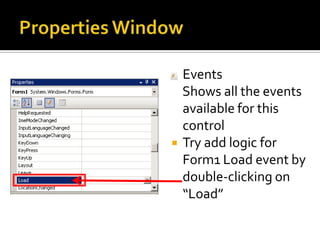



![Button with its Click EventIn Form1.cs [Design] viewFrom the Toolbar, drag a button onto the form OR double-click on buttonDrag the button to the centre of the form](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter03updated2-100420164700-phpapp02/85/Spf-chapter-03-WinForm-21-320.jpg)




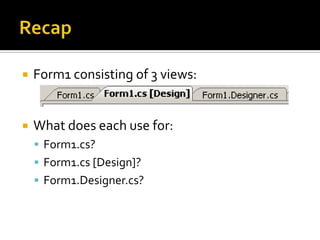
![RecapForm1 consisting of 3 views:What does each use for:Form1.cs?Form1.cs [Design]?Form1.Designer.cs?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter03updated2-100420164700-phpapp02/85/Spf-chapter-03-WinForm-28-320.jpg)

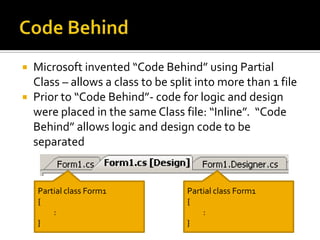





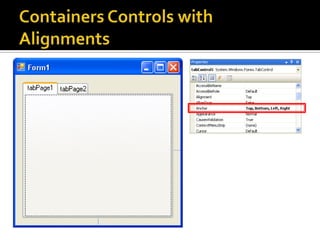
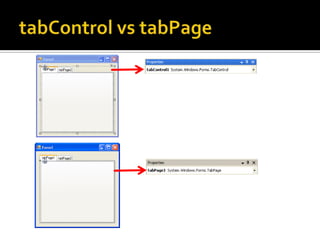










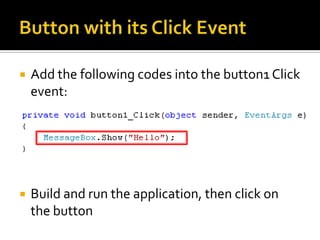
![Guided Handson: Exercise 3.5Double click on [Process] button and add code to buttonProcess_Click event: string input; // Declare 2 string var string output; input = textBoxInput.Text; // Get input string // Set output string output = input + “ “ + input + “ “ + input + “ “ + input + “ “ + input ;textBoxOutput.Text = output; // Set onto screen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spfchapter03updated2-100420164700-phpapp02/85/Spf-chapter-03-WinForm-54-320.jpg)