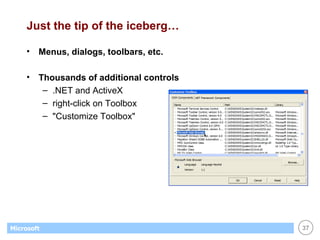
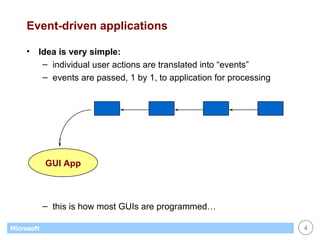
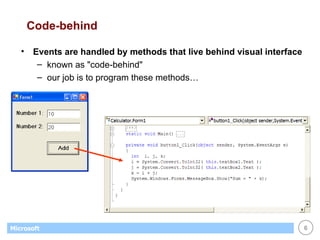
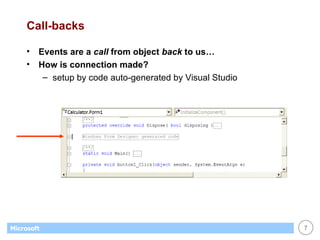
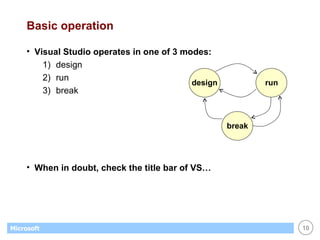
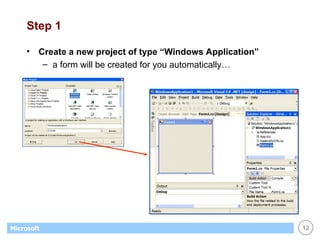
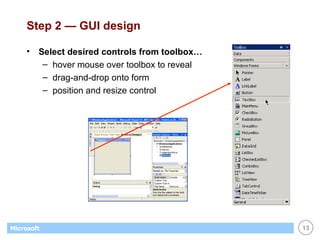
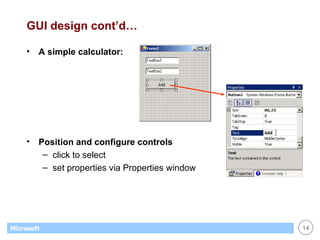
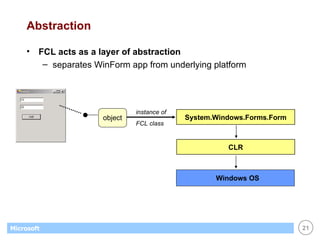
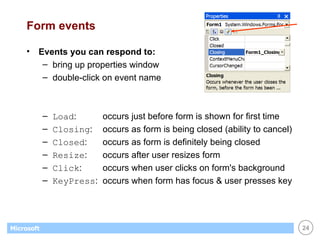
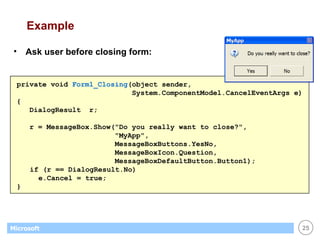
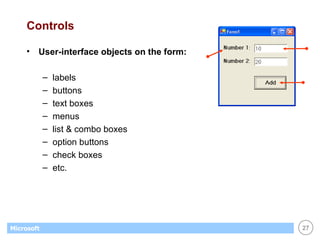
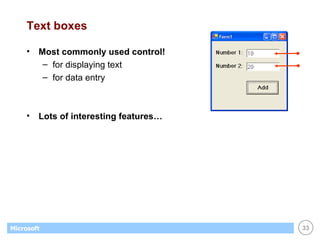
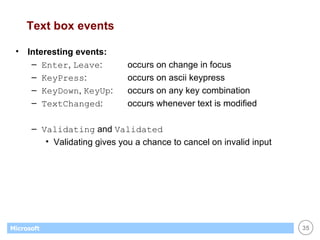
This document provides an overview of WinForms GUI programming in .NET. It discusses how event-driven programming works in WinForms applications and how Visual Studio supports drag-and-drop design of WinForms. It also describes some key concepts like forms, controls, properties and events. The document explains how to set up a basic WinForms application and interact with common controls like labels, text boxes and buttons.







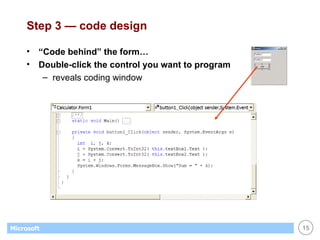
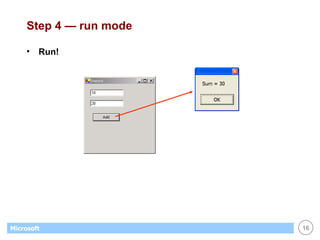
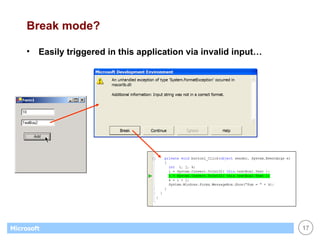
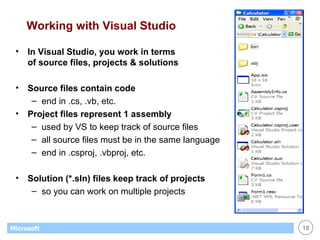





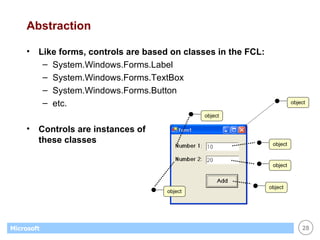
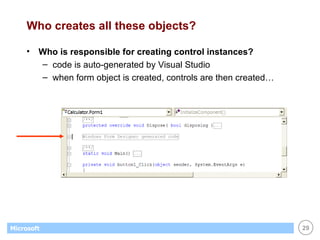

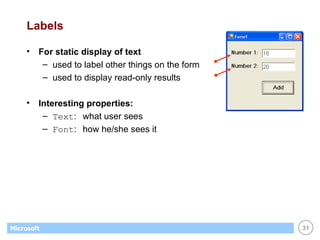
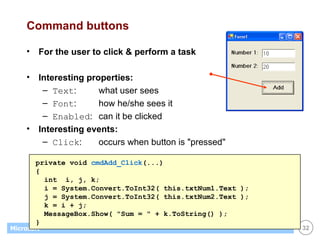

![List Boxes Great for displaying / maintaining list of data list of strings list of objects (list box calls ToString() to display) Customer[] customers; . . // create & fill array with objects... . // display customers in list box foreach (Customer c in customers) this.listBox1.Items.Add(c); // display name of selected customer (if any) Customer c; c = (Customer) this.listBox1.SelectedItem; if (c == null) return; else MessageBox.Show(c.Name);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06winforms-110307020055-phpapp02/85/06-win-forms-36-320.jpg)