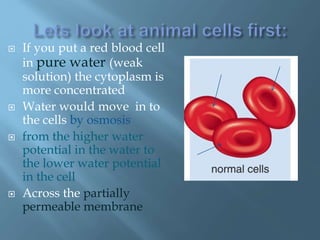
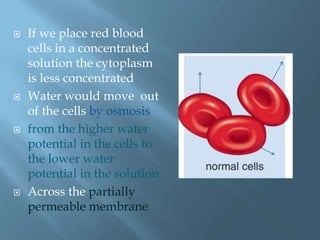
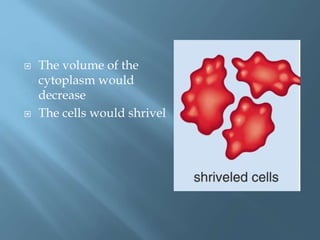
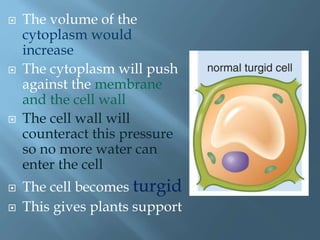
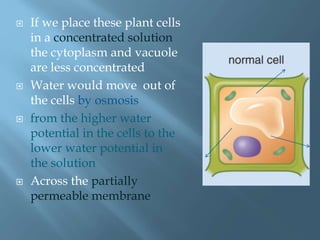
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water potential to lower water potential. The cell surface membrane and vacuole membrane in plant cells are partially permeable, allowing water but not solutes like sugar to pass through. If a cell is placed in a solution with higher or lower solute concentration than the cell cytoplasm, water will move in or out of the cell by osmosis to equalize the water potential across the membrane. This can cause the cell to burst, shrivel, become turgid and rigid, or become flaccid and plasmolyzed depending on the direction of water flow.