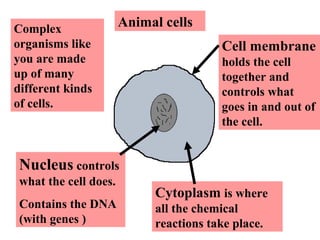
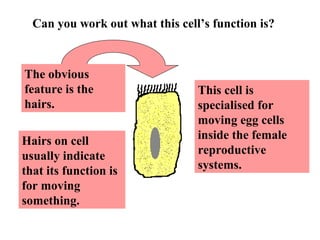
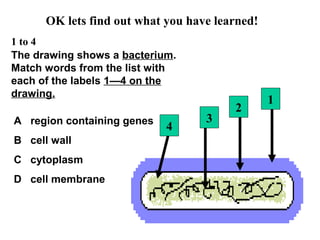
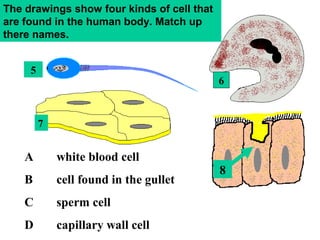
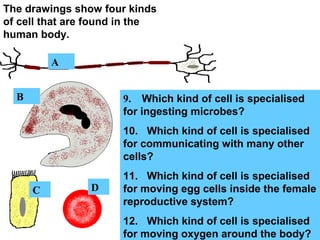
Plant and animal cells have several key similarities and differences. Both contain a nucleus that controls the cell's functions, cytoplasm where chemical reactions occur, and a cell membrane that holds the cell together and regulates what enters and exits. However, plant cells also have a cell wall, vacuoles, and chloroplasts for photosynthesis. Animal cells come in many specialized types, while plant cell specializations allow them to trap sunlight and store energy as food. The structure and features of a cell provide clues to its specific functions in the body or organism.