Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times
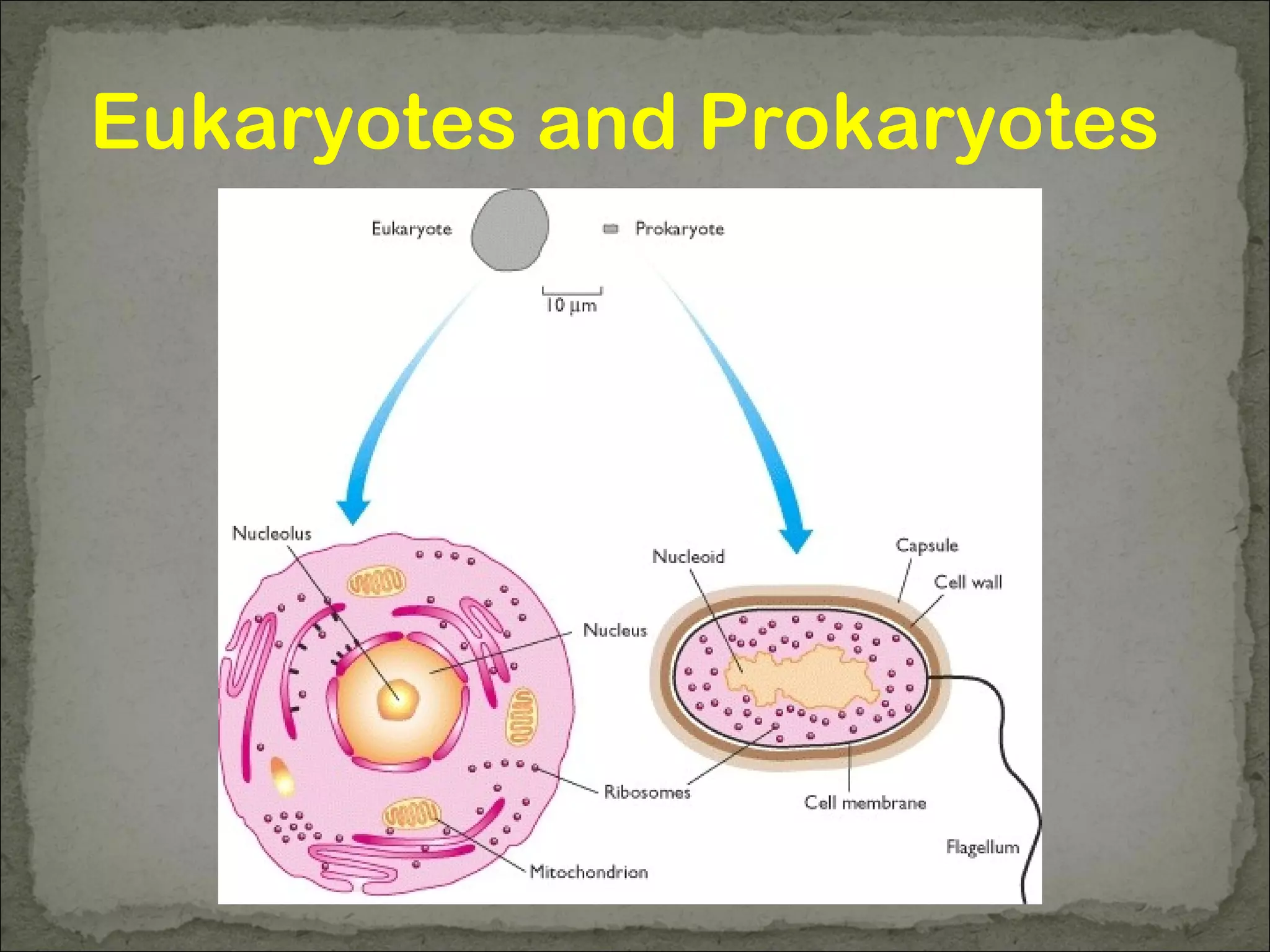
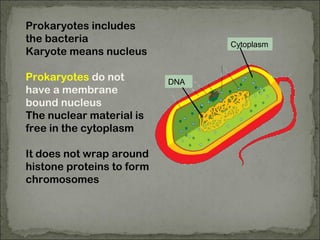
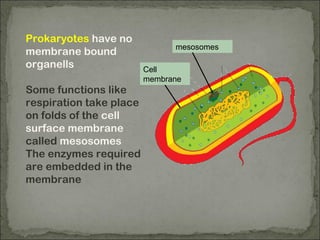
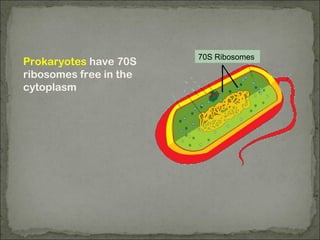
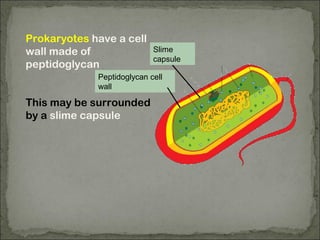
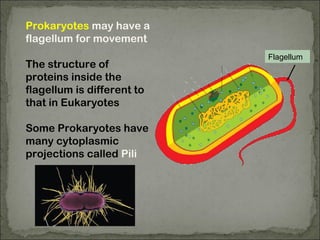
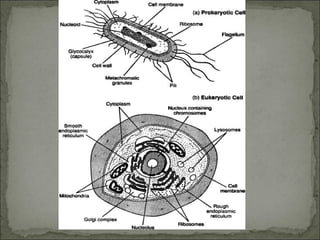
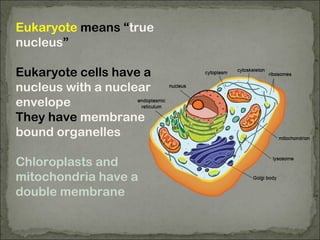

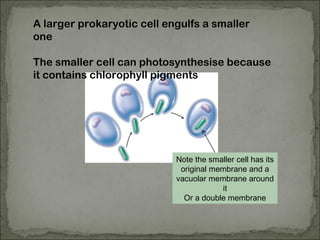

Eukaryotes have a membrane-bound nucleus that contains DNA wrapped around histone proteins to form chromosomes, while prokaryotes do not have a membrane-bound nucleus and their DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm. Prokaryotes also lack membrane-bound organelles and instead have structures like mesosomes embedded in the cell membrane to carry out functions like respiration. They have 70S ribosomes free in the cytoplasm, a cell wall made of peptidoglycan that may be surrounded by a slime capsule, and may possess flagella or pili for movement. The endosymbiont theory suggests that organelles like chloroplasts and mitochondria were once free-living prokaryotic cells that became










