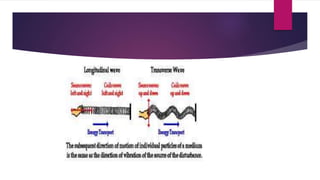
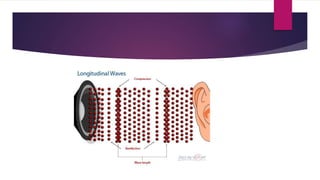
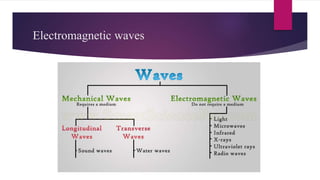
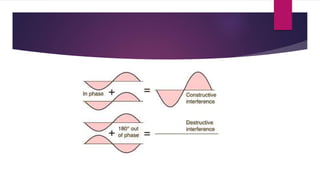
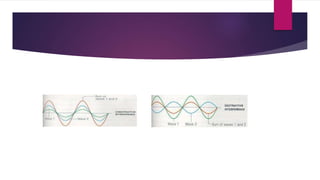
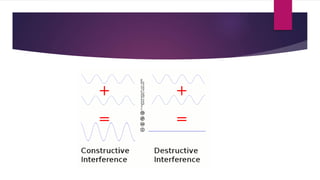
Sound waves are longitudinal mechanical waves that require a medium such as air or water to propagate. There are two types of mechanical waves: longitudinal waves where particles of the medium move parallel to the wave direction, and transverse waves where particles move perpendicular. Interference occurs when sound waves from different sources meet and combine to produce a new wave. Constructive interference amplifies the waves while destructive interference cancels them out. Infrasonic waves have frequencies below 20 Hz and ultrasonic waves are above 20,000 Hz, the normal human hearing range. Both have applications like monitoring earthquakes and welding.