Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




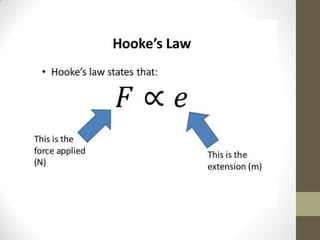




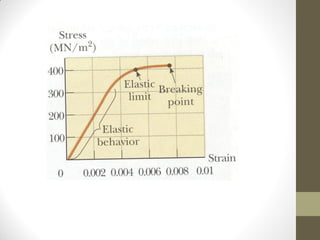




This document defines and explains key concepts related to elasticity, including Hooke's law, stress, strain, and the Young modulus. Hooke's law states that the extension of an elastic object is proportional to the applied force up to the limit of proportionality. Stress is defined as the external force acting on an object per unit of cross-sectional area. Strain is the ratio of extension to original length. The Young modulus is the ratio of stress to strain and provides a measure of an object's elasticity.













