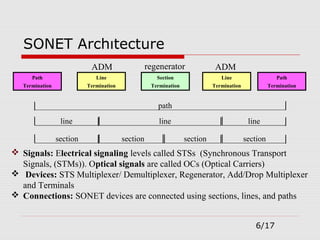
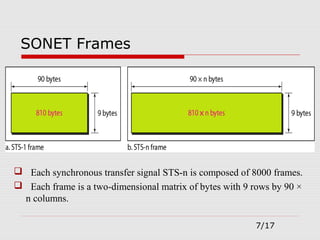
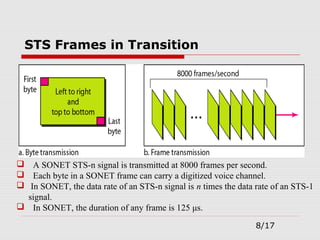
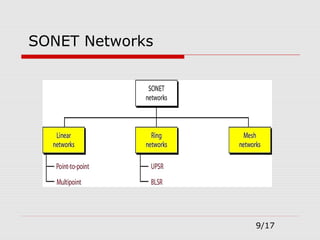
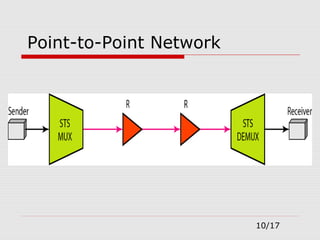
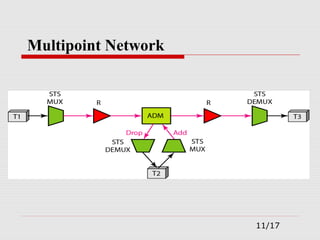
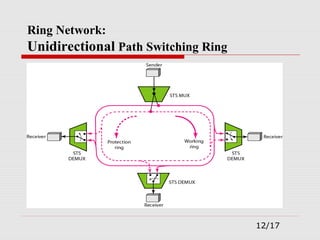
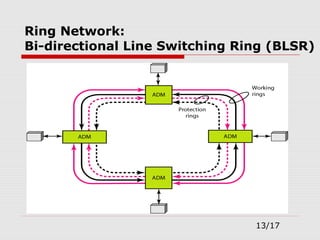
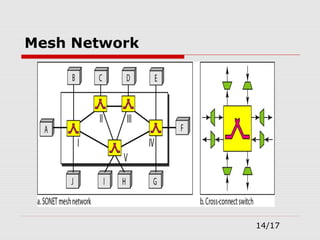
The document provides an overview of Synchronous Optical Network (SONET), including its standards for optical telecommunications transport, architecture, and types of networks. It details SONET layers, rates, and advantages such as high data rates and flexible topologies, alongside disadvantages like high costs and complexity compared to Ethernet. Key components discussed include synchronous transport signals (STS), optical carriers (OC), and various network configurations.