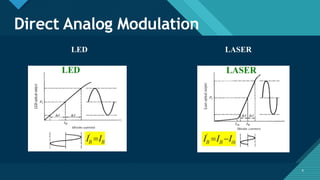
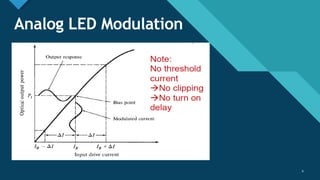
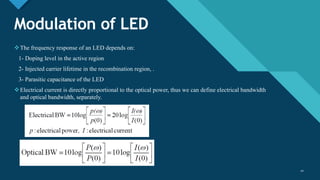
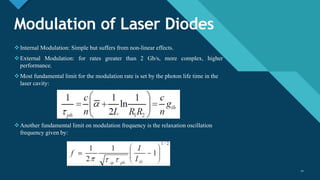
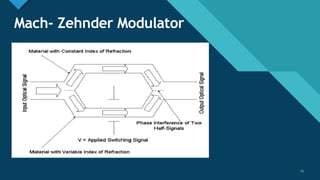
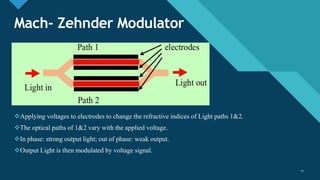
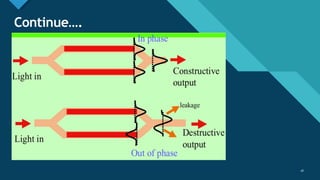
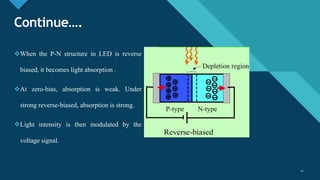
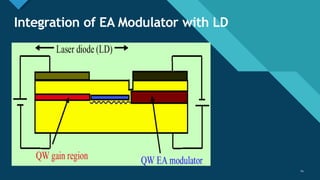
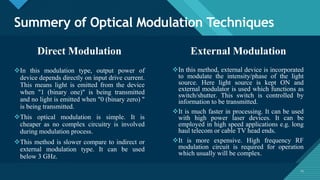
This document discusses different types of optical modulation techniques, including direct modulation and external modulation. Direct modulation involves superimposing the modulating signal directly onto the driving current of the light source, such as a laser diode. External modulation separates the light generation and modulation processes, where a continuous wave light source is modulated externally after generation. Some key advantages of external modulation are wider modulation bandwidth and better performance, though it is more complex and expensive. The document also covers modulation parameters, direct and analog modulation, limitations of direct modulation, and external modulation techniques like Mach-Zehnder and electro-absorption modulators.