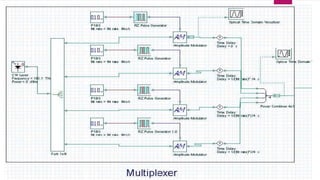
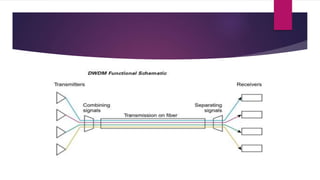
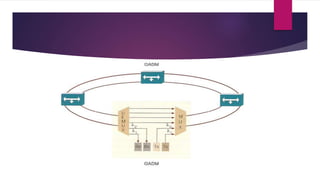
Optical multiplexers allow multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously over a single optical fiber link. There are different optical multiplexing techniques, including wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and optical time division multiplexing (OTDM). WDM assigns each signal a unique wavelength, while OTDM separates signals in the time domain. Optical multiplexers and demultiplexers use passive optical filters to combine and separate the wavelength signals. This increases bandwidth utilization and reduces transmission costs.