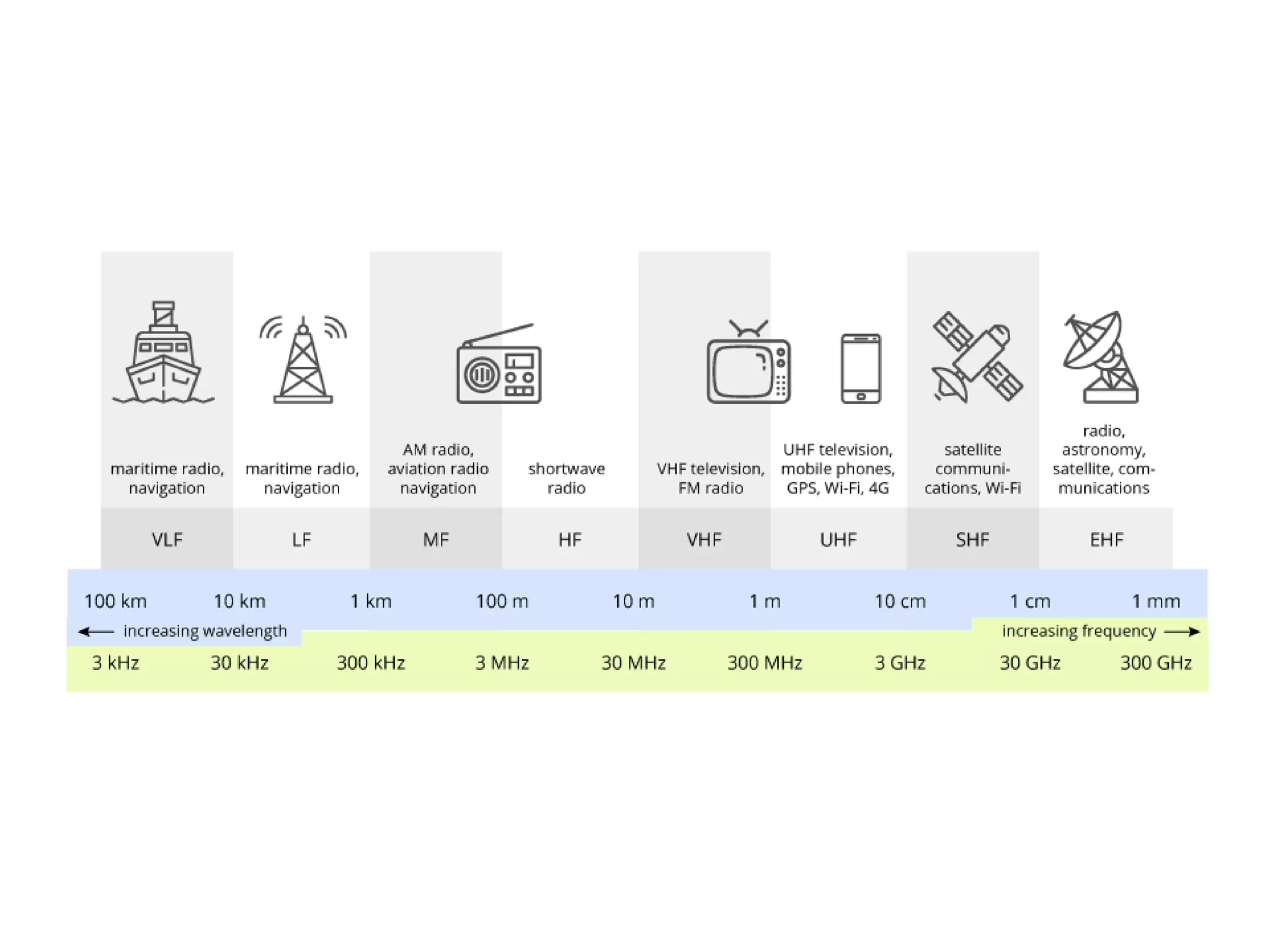
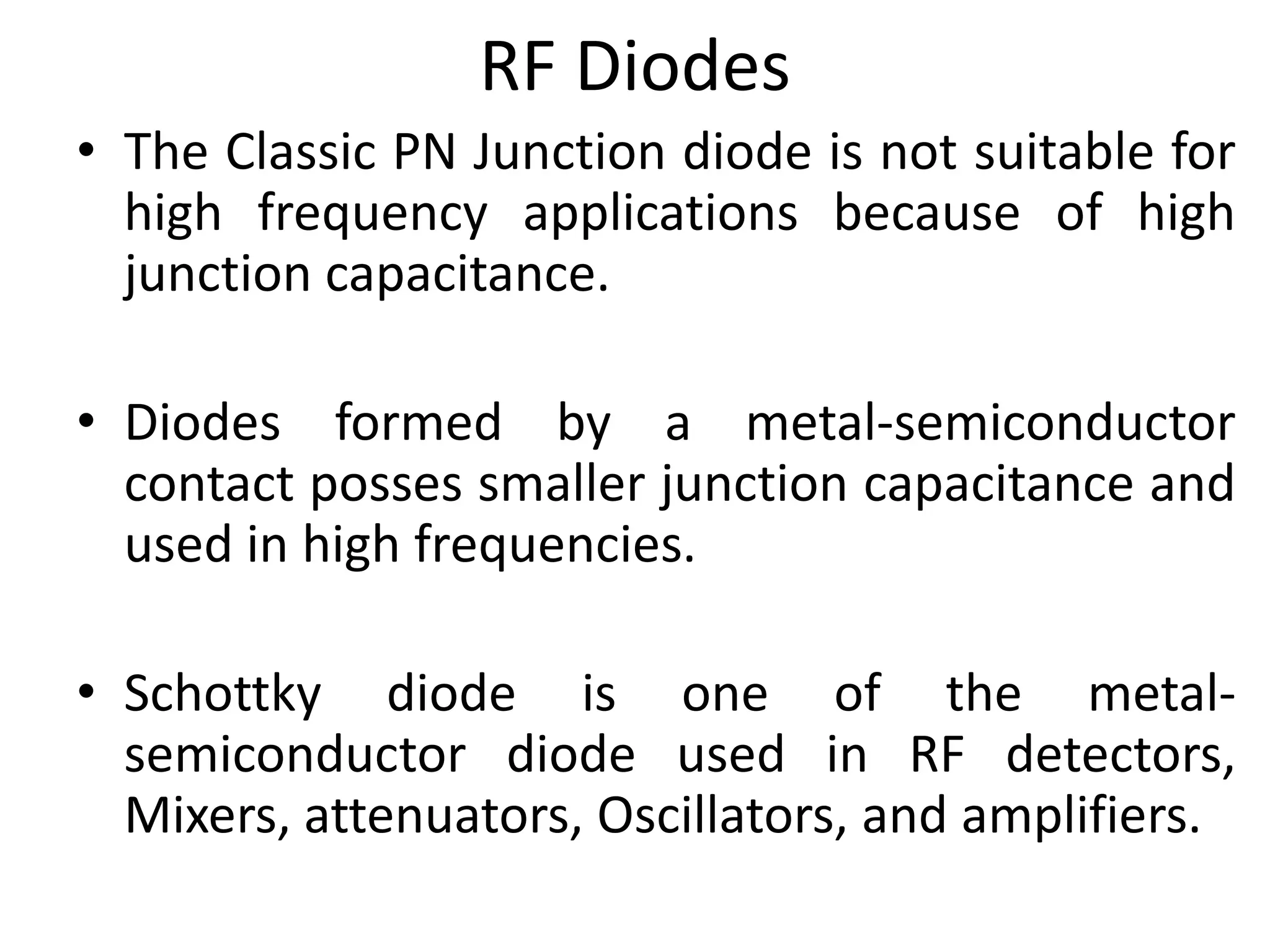
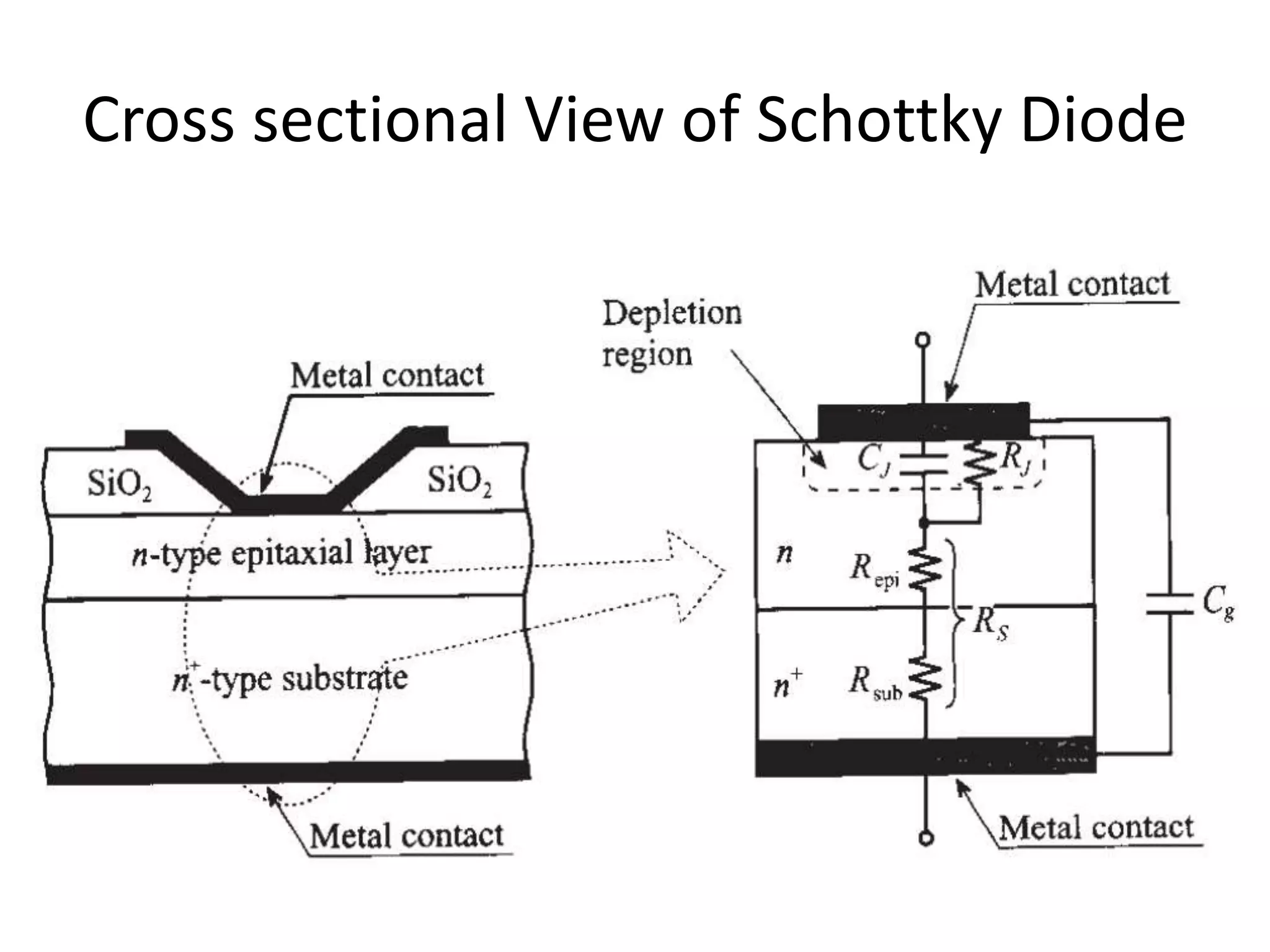
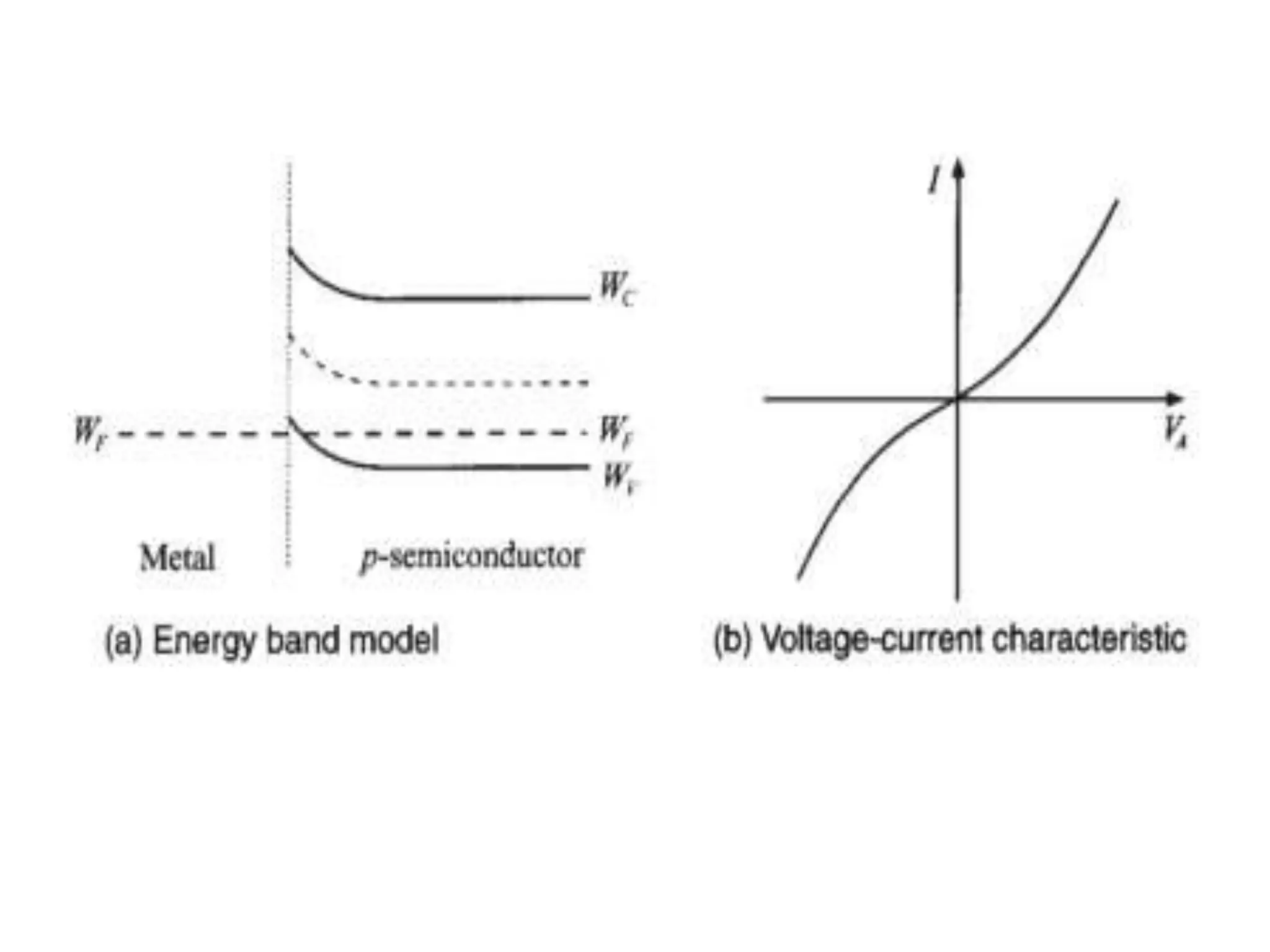
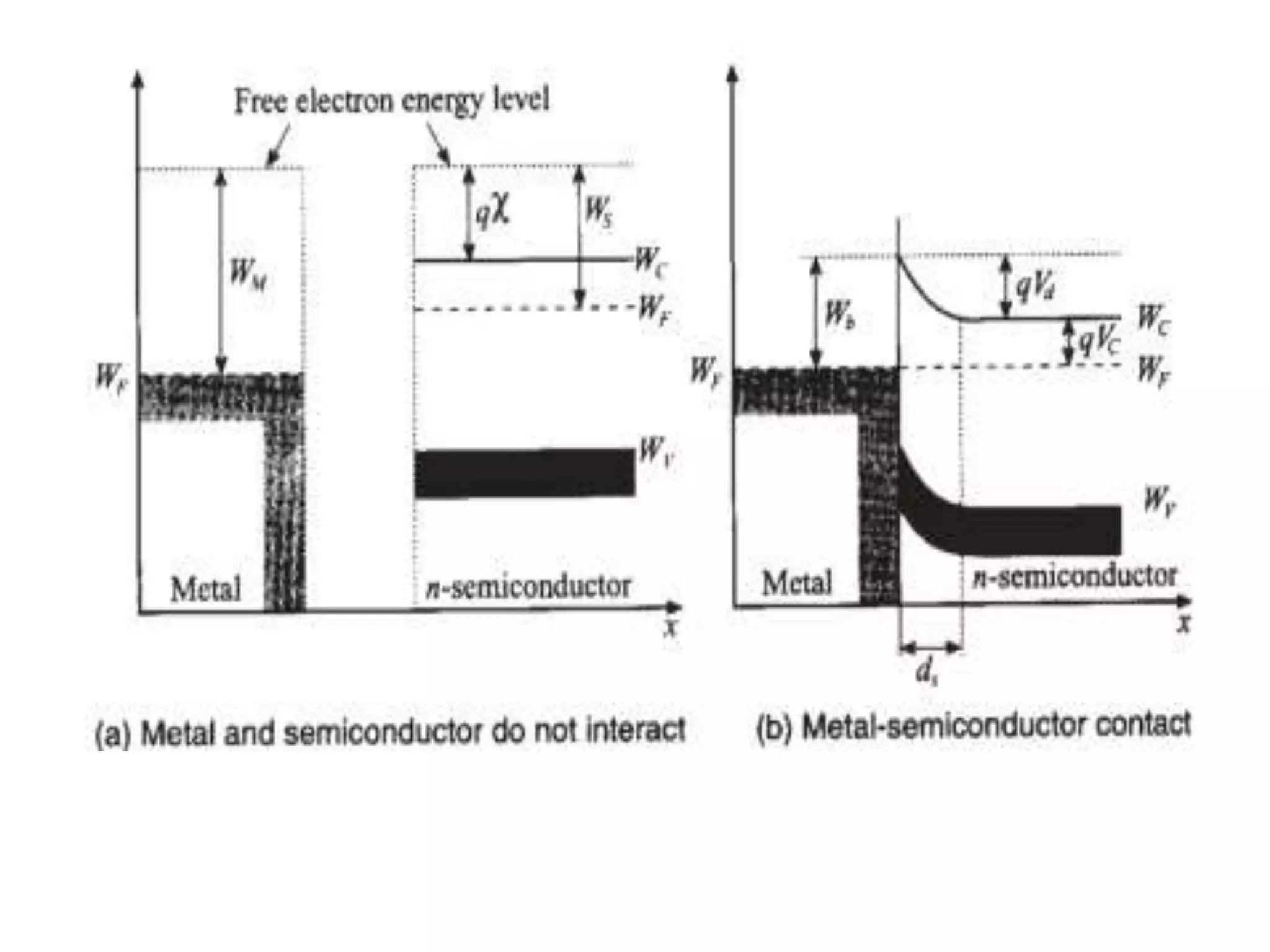
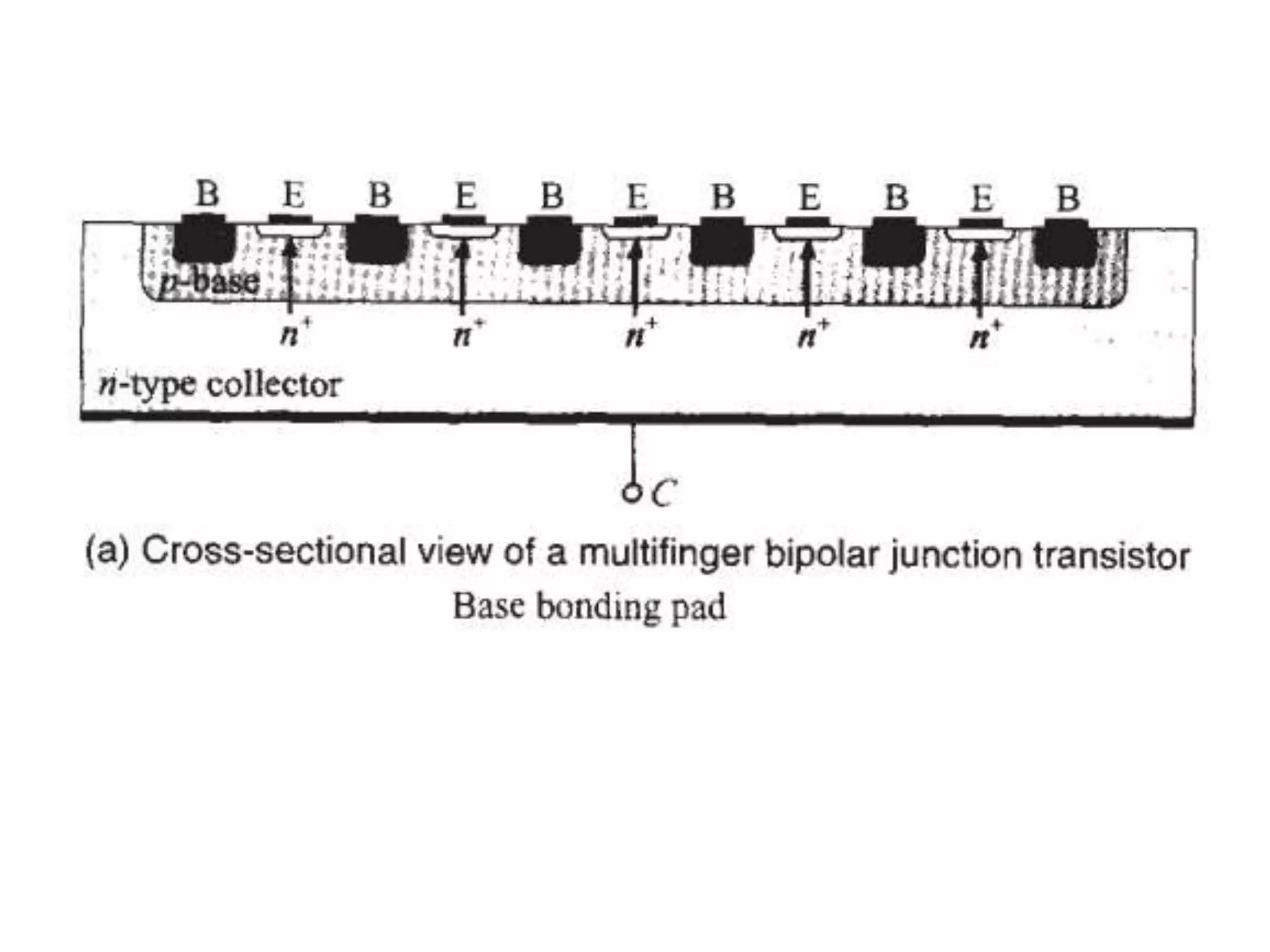
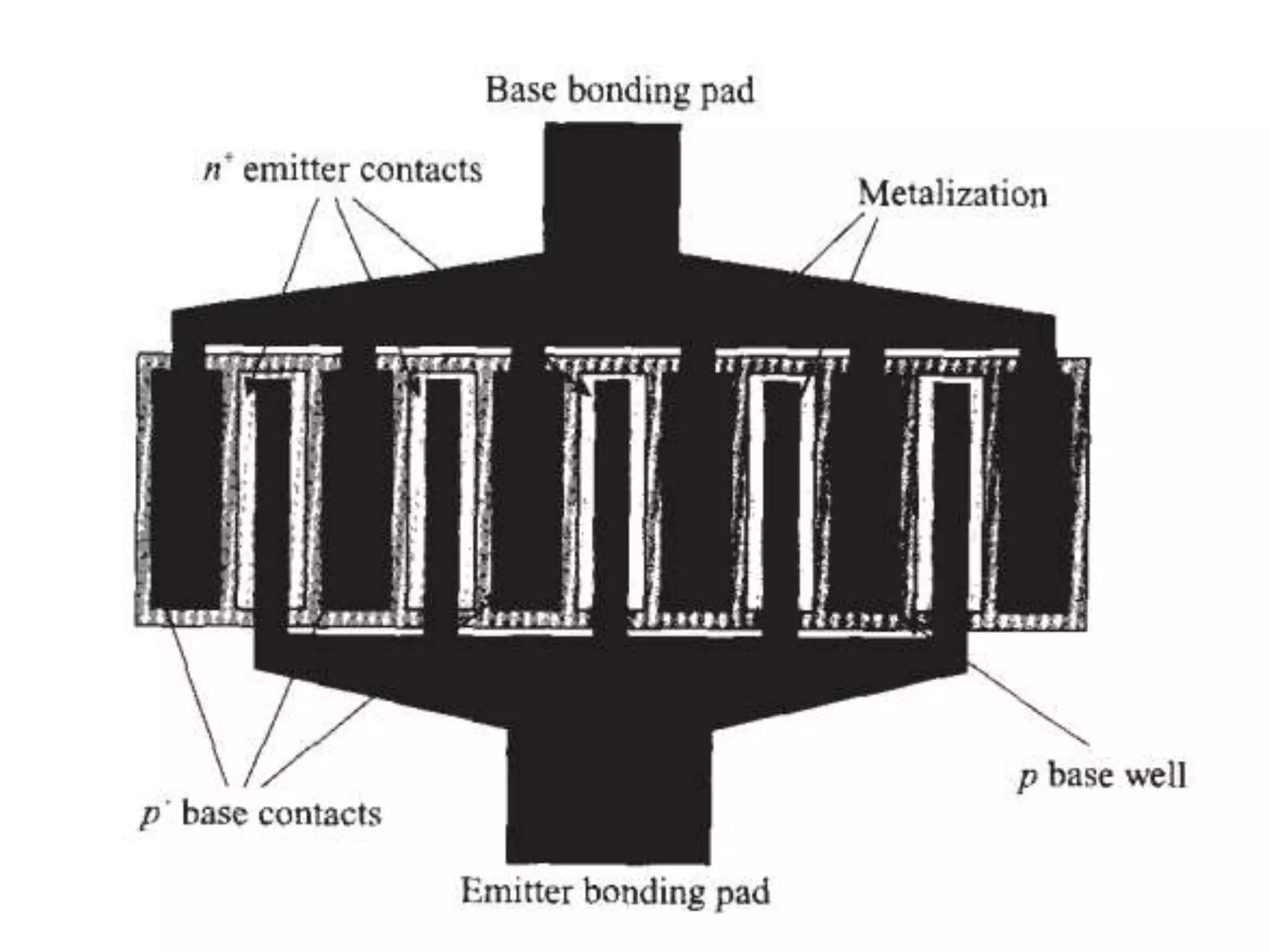
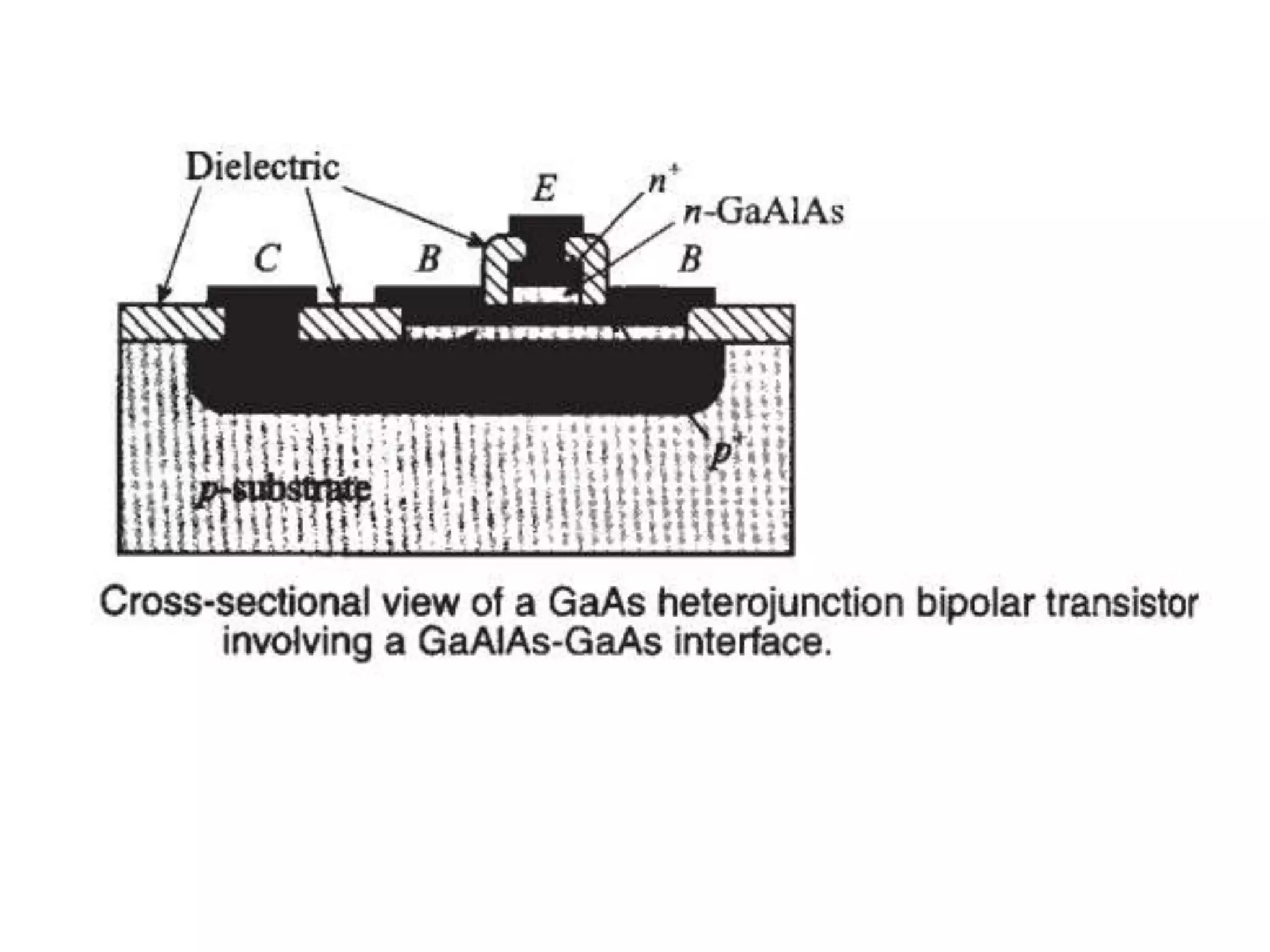
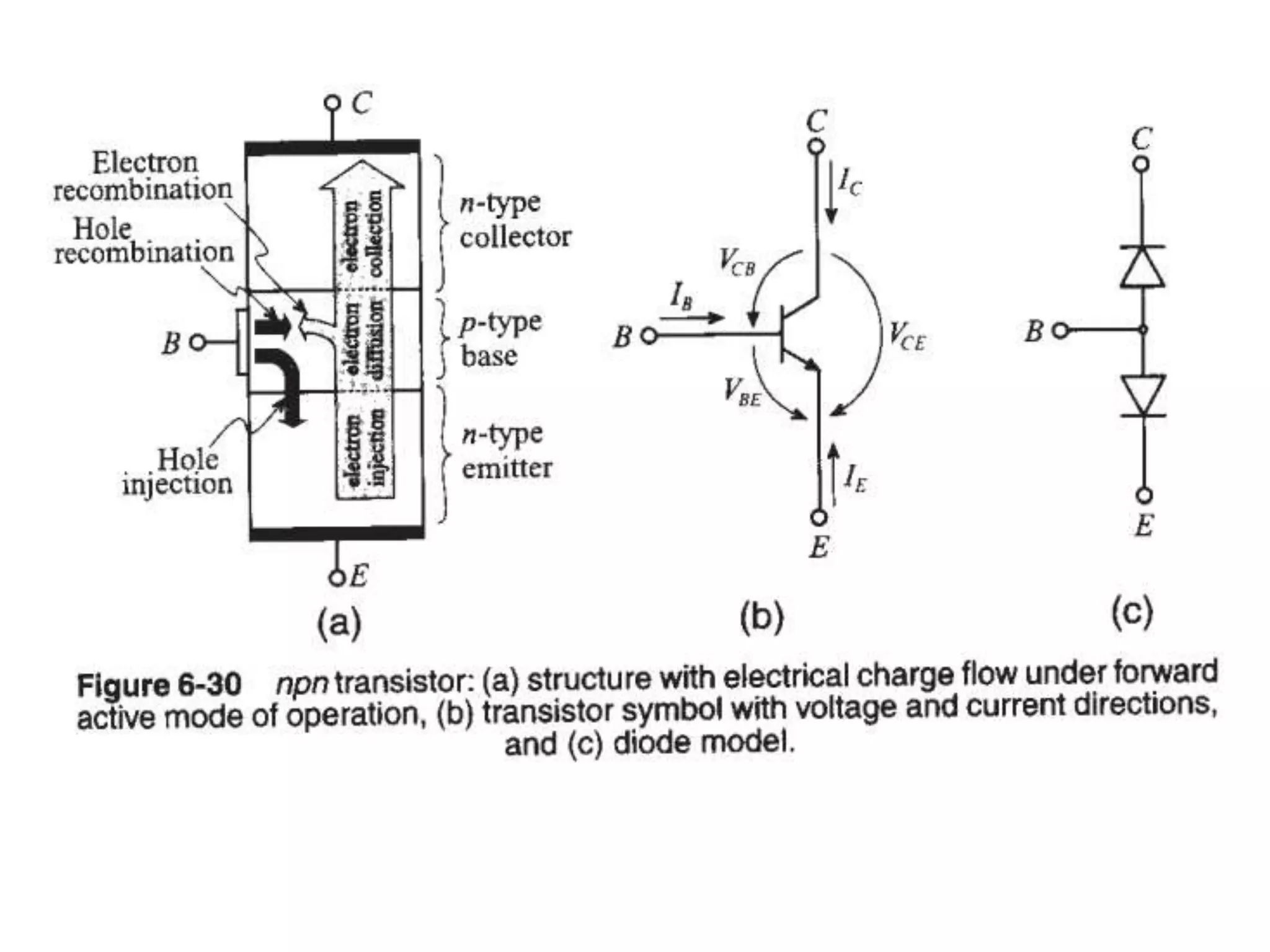
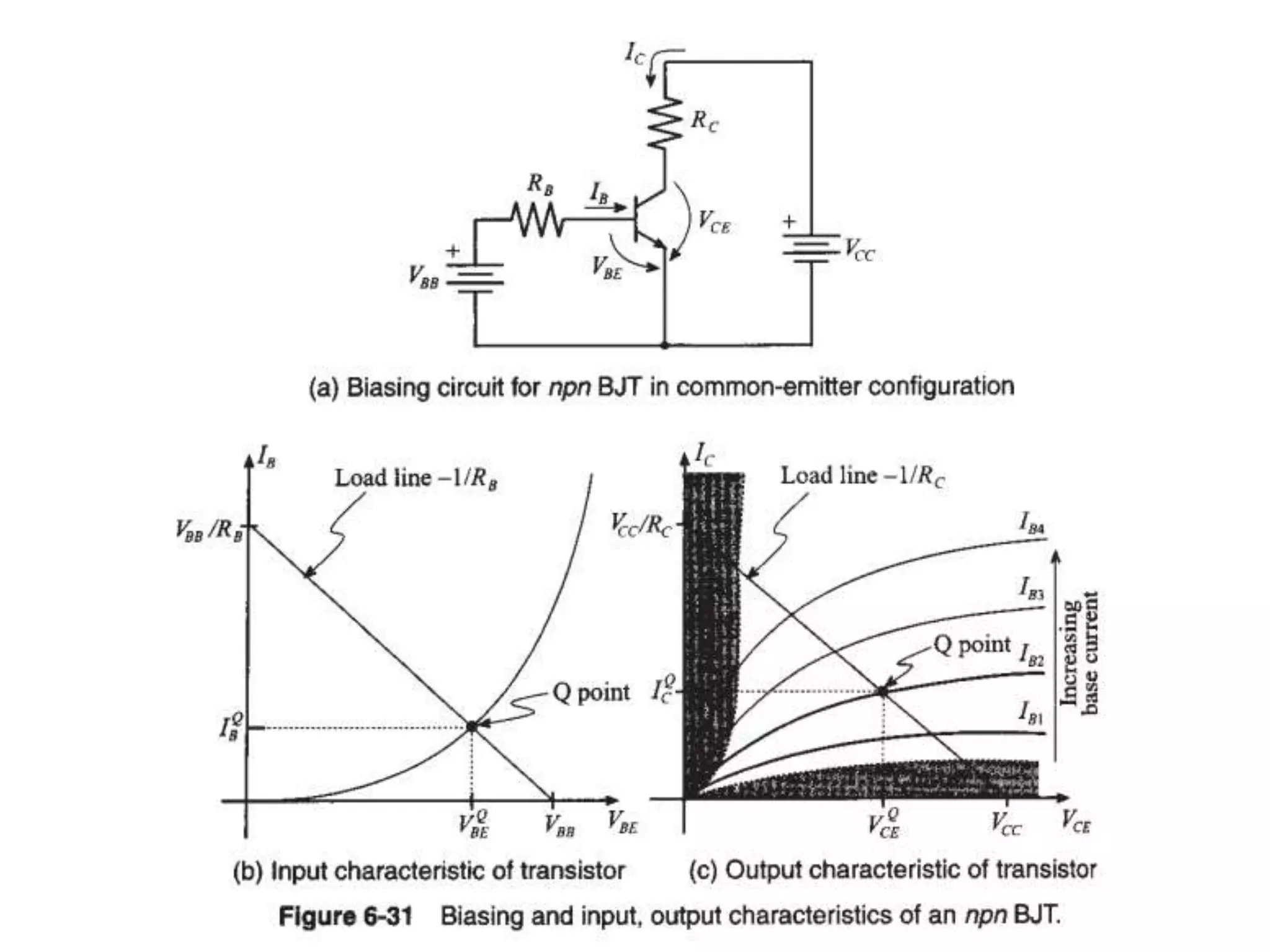
This document discusses concepts in RF system design, including active RF components like transistors and basic RF concepts. It covers the frequency range of RF, semiconductor materials used in RF like GaN, GaAs, and SiGe. Specific RF devices discussed include Schottky diodes, which are used in RF detectors, mixers, oscillators and amplifiers due to their smaller junction capacitance. Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field effect transistors (FETs) are also covered, noting that BJTs are widely used in RF applications due to their low cost, operating frequency, low noise performance and high power handling capacity through specialized construction designs.