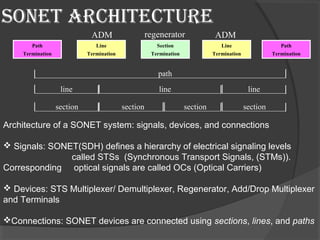
Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or LEDs. SONET was developed to replace earlier asynchronous systems for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over fiber without synchronization problems. SONET defines four layers - path, line, section, and photonic - to move signals across the network. It also defines a hierarchy of electrical signaling levels called STSs and corresponding optical signals called OCs. SONET networks can be configured in point-to-point, multipoint, ring or mesh topologies and provide advantages like reduced complexity, protection, bandwidth efficiency