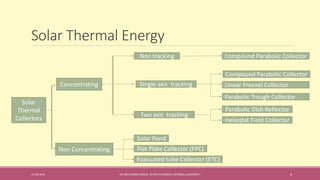
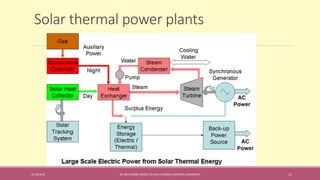
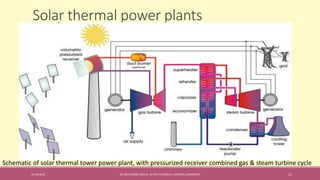
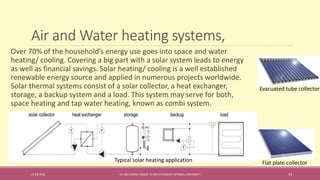
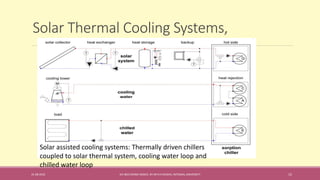
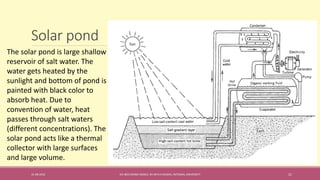
The document provides an extensive overview of solar thermal energy and its applications, detailing various systems such as solar thermal collectors, concentrated solar power technologies, and solar heating/cooling solutions. It highlights the functioning of different solar thermal systems, their advantages in energy generation and cost savings, and their suitability for various sectors including residential, commercial, and industrial. The text also discusses innovative applications such as solar cooking, solar drying, and solar-powered water pumps, emphasizing the environmental benefits of utilizing solar energy.