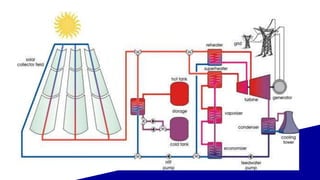
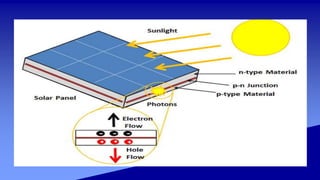
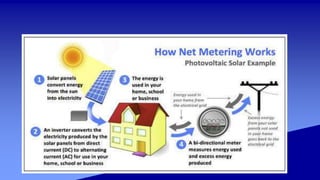
Solar power plants can generate electricity either directly using photovoltaic cells or indirectly using concentrated solar power that heats a liquid to power steam turbines. Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors to focus sunlight and heat a liquid for steam generation. Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Solar power has advantages of no fuel costs or pollution but higher initial costs than other technologies.