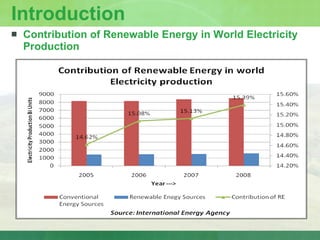
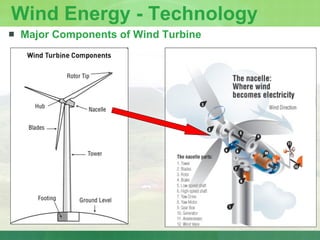
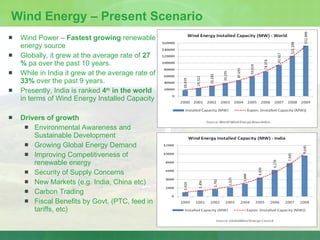
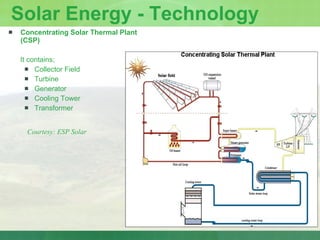
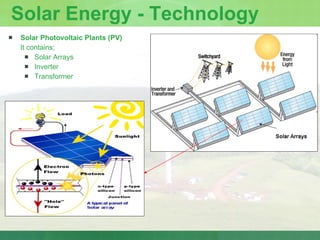
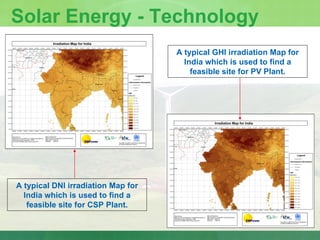
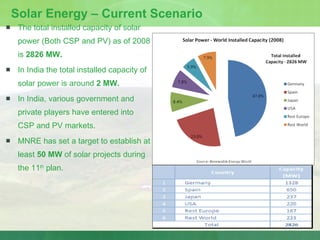
The document provides an introduction to renewable energy sources for power generation. It discusses various renewable energy technologies including wind and solar energy. For wind energy, it describes the technology behind wind turbines and key components. It also discusses solar photovoltaic and concentrating solar thermal plant technologies. The document then provides current installed capacities and scenarios for wind and solar energy in India.