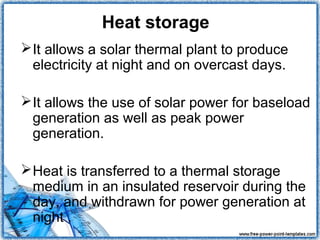
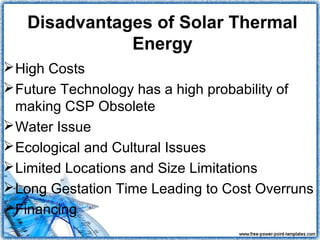
This document discusses power generation from solar thermal plants. It describes how solar thermal energy collectors are classified as low, medium, or high temperature based on their use. Low temperature collectors are used to heat pools, medium for water and air heating, and high temperature concentrate sunlight for electricity production. Heat is collected, stored, and transferred for power generation during the day and at night. Conversion rates from solar to electrical energy are highest for dish/Stirling systems at 31.25% and around 20% for trough and Fresnel systems. Applications include residential and commercial water and space heating.