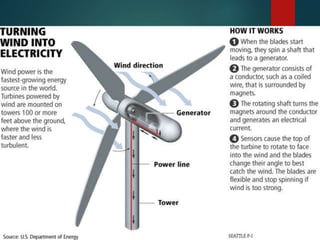
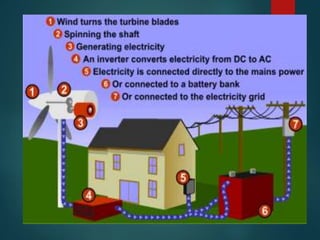
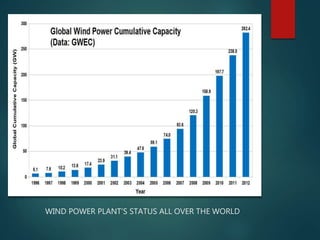
This document provides an overview of wind power plants. It discusses the typical parts of a wind turbine, including the rotor, transmission system, generator, and yaw and control systems. The document also outlines the advantages of wind power in being a renewable and pollution-free source of energy. However, it notes disadvantages such as the irregular and variable nature of wind and higher capital costs. Additionally, the document reviews the present scenario of wind power in India, which has the fifth largest installed capacity in the world, and is led by states like Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.