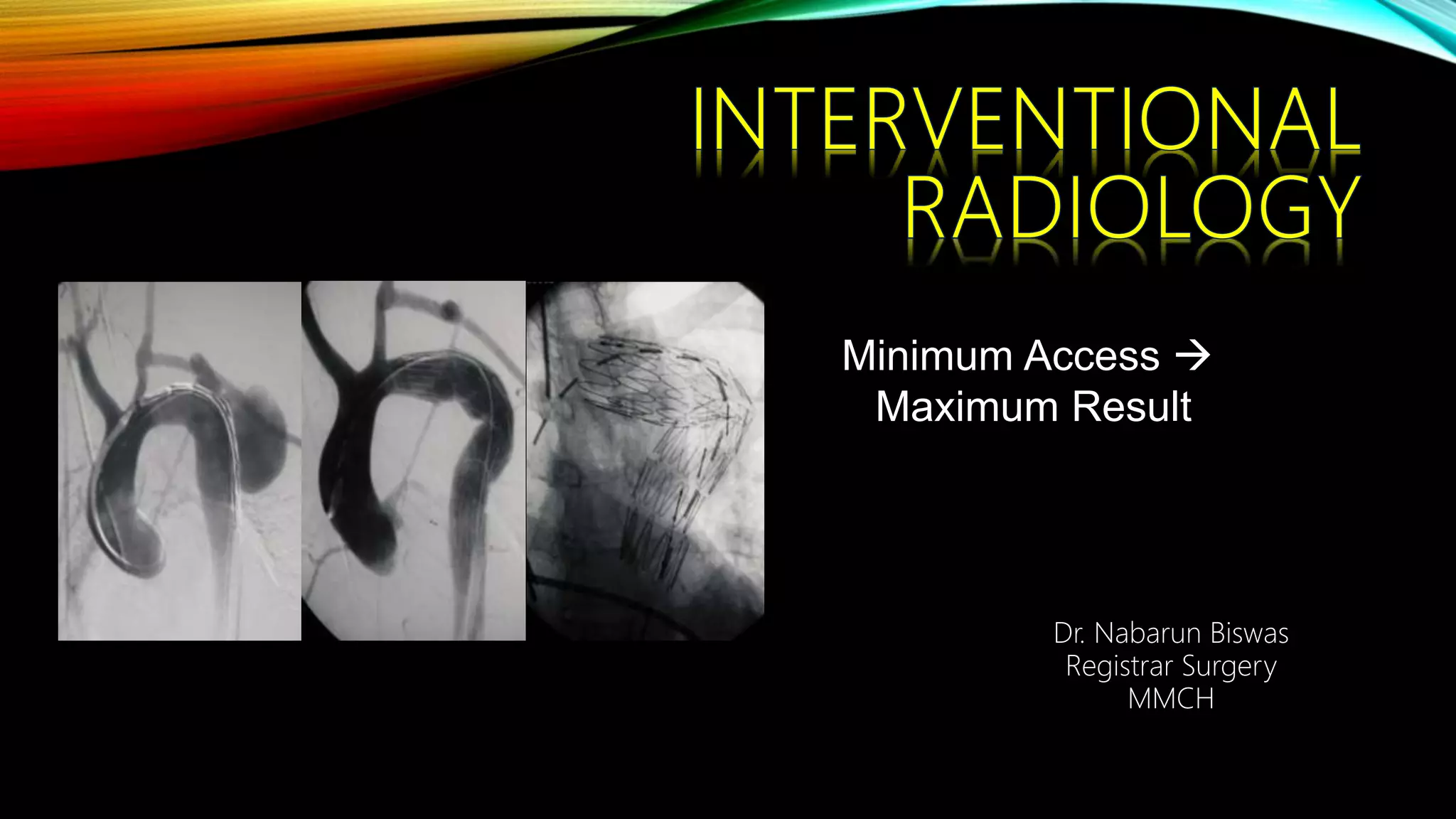
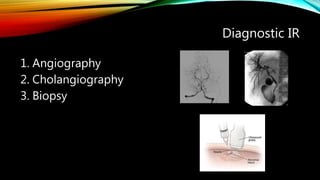
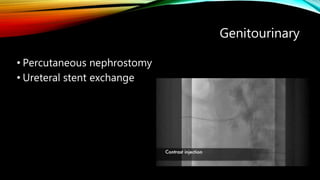
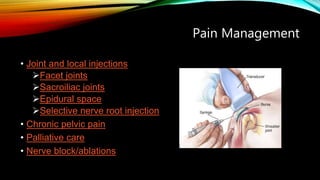
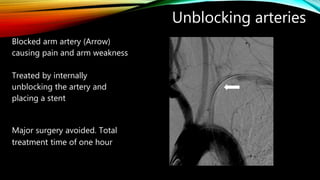
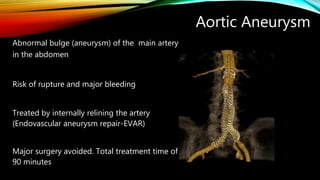
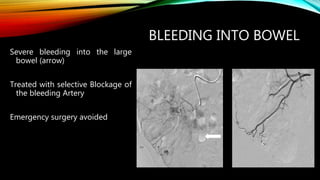
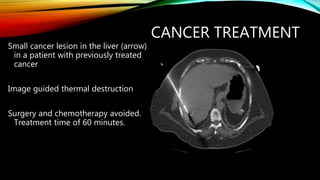
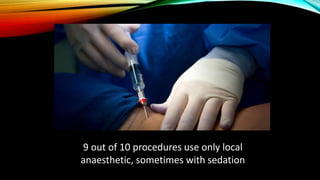
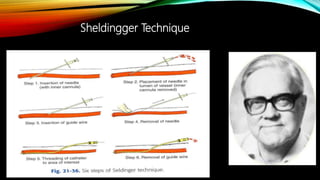
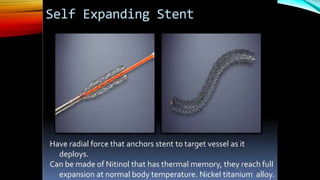
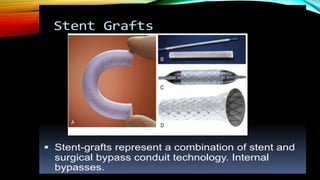
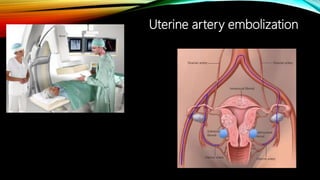
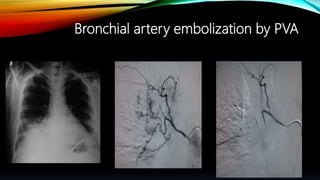
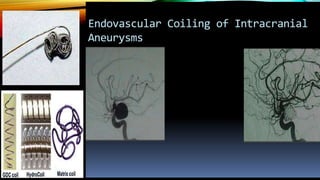
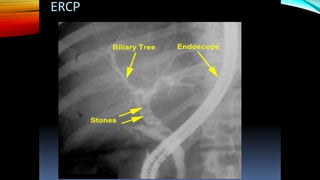
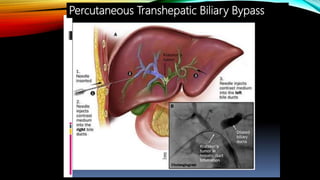
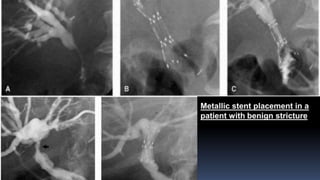
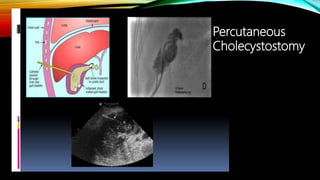
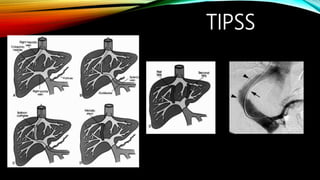
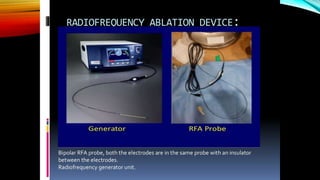
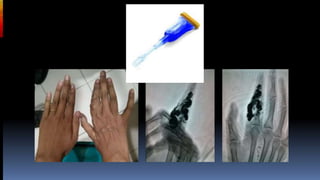
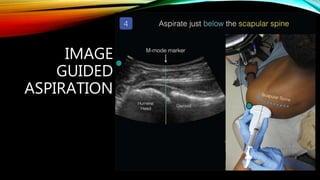
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical subspecialty that performs minimally invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance. IR can be used for both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Some common IR procedures include angioplasty to unblock arteries, stent placement to treat aneurysms, tumor ablation, drainage catheter placement, and pain management injections. IR treatments can avoid the need for open surgery and allow many patients to be treated as outpatients. IR utilizes imaging technologies like fluoroscopy, CT, MRI, and ultrasound to guide small catheters and wires to access the inside of the body for both diagnostic testing and treatments.