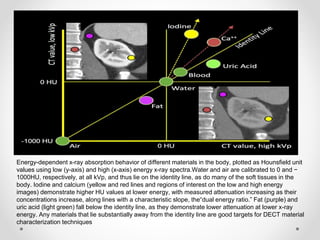
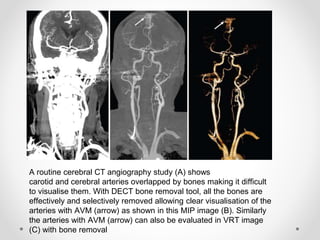
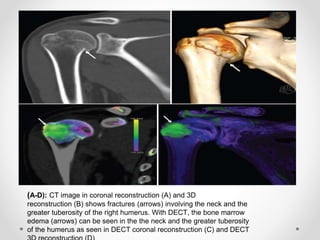
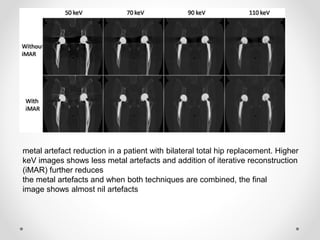
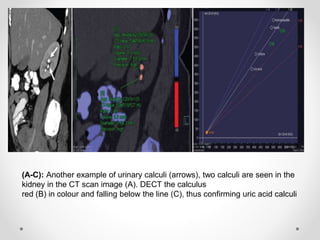
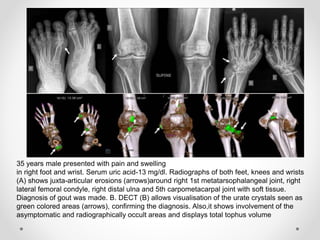
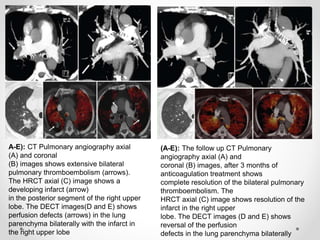
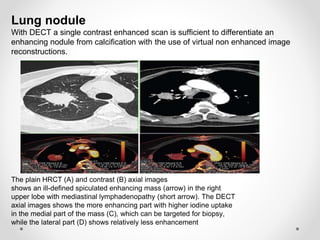
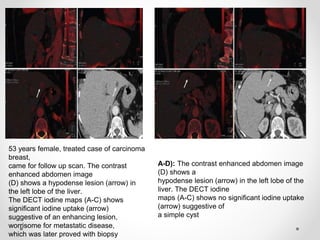
Dual energy CT uses two x-ray spectra to distinguish materials based on their differential attenuation properties. This allows reconstruction of various image sets and material-specific images without contrast. Key applications include bone removal, virtual non-calcium imaging, uric acid stone differentiation, gout detection, perfusion imaging, and differentiating enhancing lesions from calcification. Dual energy CT provides material-specific information useful for diagnosis and treatment planning in various clinical contexts.