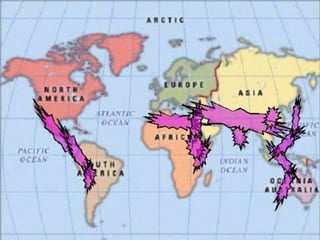
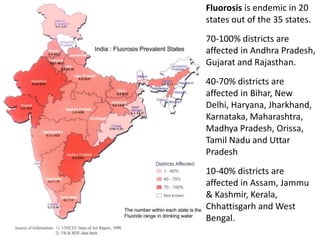
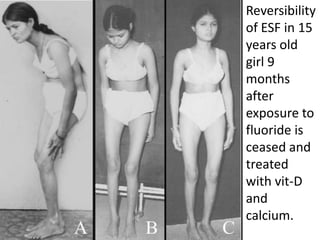
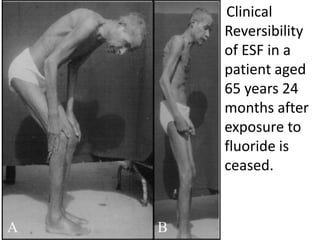
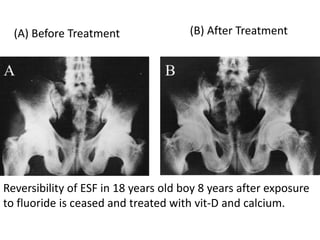
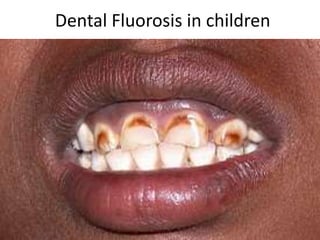
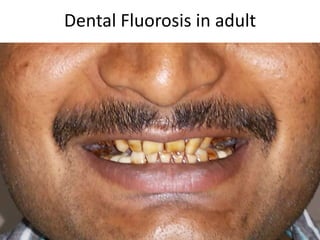
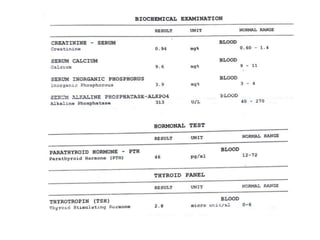
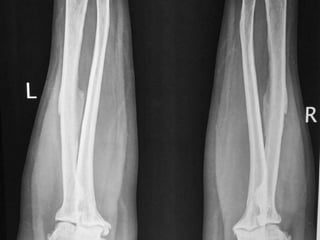
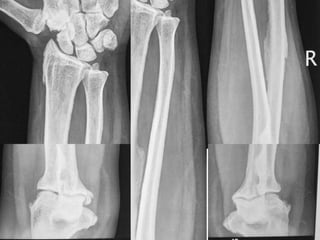
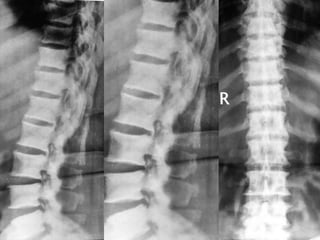
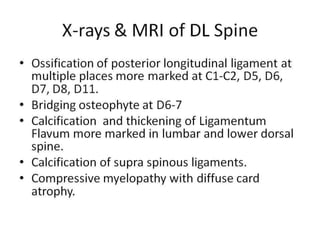
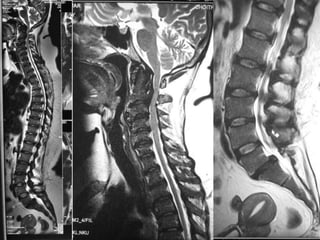
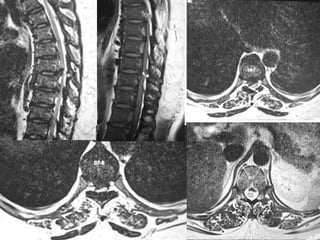
Skeletal fluorosis is caused by excessive fluoride intake over long periods of time. The main sources of fluoride are drinking water, tea, and indoor air pollution from burning coal. Fluoride is deposited in bones and teeth. At low levels it strengthens teeth and bones, but at high levels it leads to skeletal and dental fluorosis. Skeletal fluorosis causes bone and joint pain and stiffness, and if severe, bone deformities and crippling. It is a major public health problem affecting millions in India, China, and other parts of Asia and Africa. Reducing fluoride intake and ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D can help prevent and treat skeletal fluorosis.