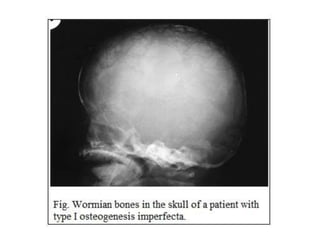
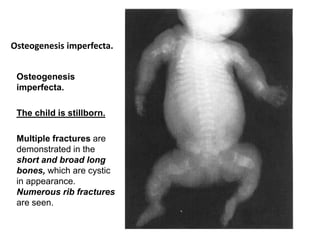
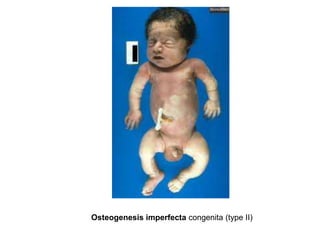
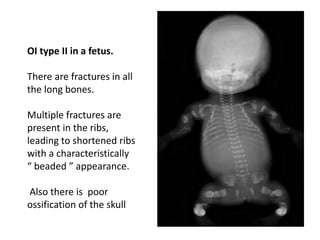
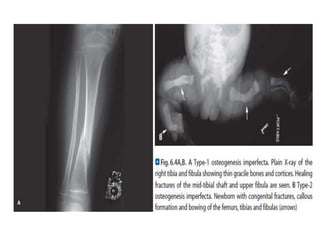
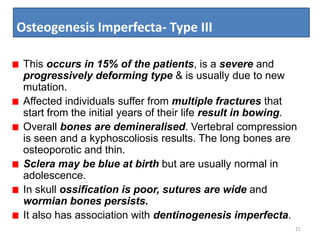
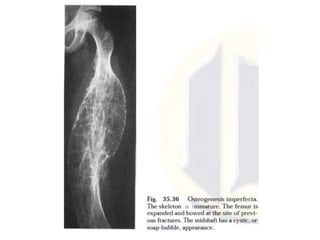
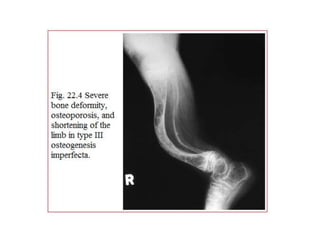
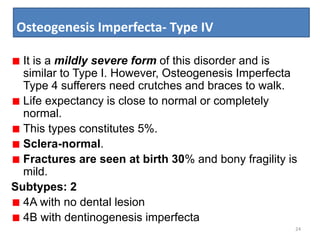
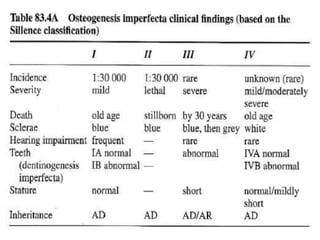
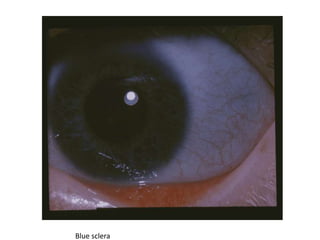
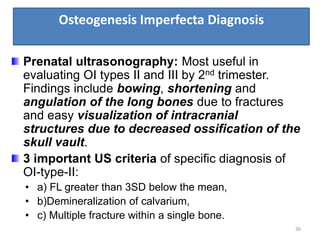
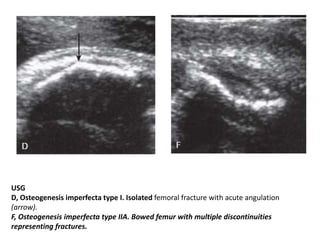
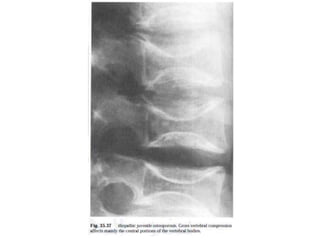
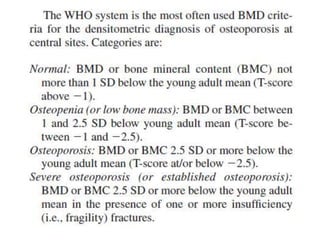
Osteogenesis imperfecta is a genetic disorder characterized by fragile bones that fracture easily. It results from a defect in type I collagen production, the main protein in bone matrix, which leads to low bone mass and increased bone fragility. The condition ranges from mild to lethal. Types are classified based on severity and inheritance. Diagnosis involves examining for blue sclera and bone fractures or deformities on imaging. Treatment focuses on physiotherapy, orthopedic surgery, and bisphosphonates to increase bone strength. Differential diagnoses include child abuse and juvenile osteoporosis.