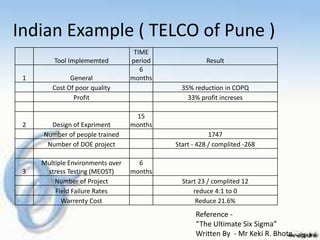
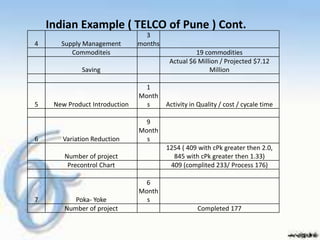
The document discusses quality management programs and systems such as Statistical Process Control (SPC), Total Quality Management (TQM), and Six Sigma. It provides details on the Six Sigma methodology, including the DMAIC process and benefits of Six Sigma in reducing defects and costs. The document also presents examples of Six Sigma implementations at Motorola and an Indian company, and discusses some costs and limitations of the Six Sigma approach.