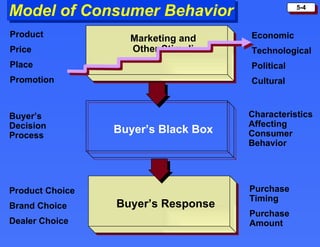
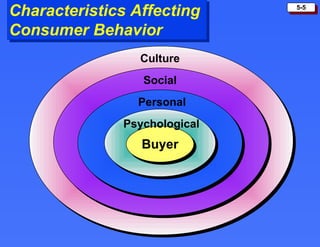
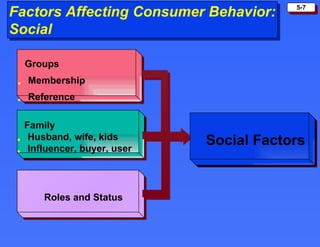
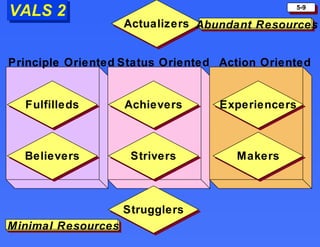
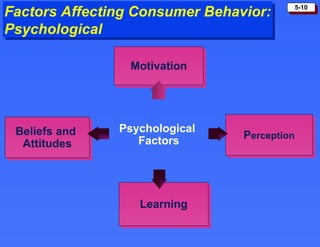
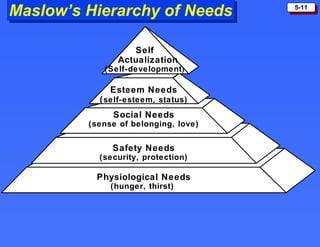
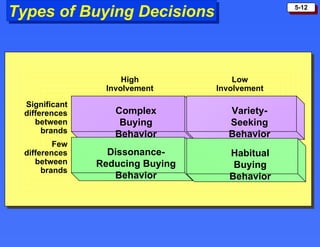
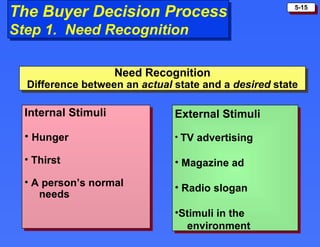
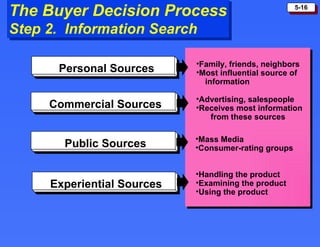
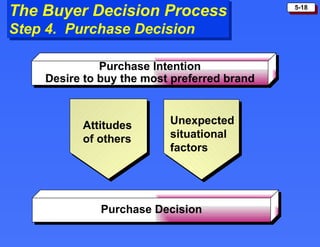
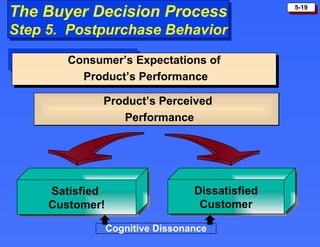
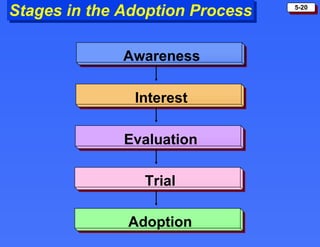
The document discusses consumer buying behavior and the factors that influence consumer purchase decisions. It outlines a simple model of consumer behavior involving marketing stimuli, the buyer's black box of characteristics and decision making processes, and the buyer's response. It then discusses the psychological, social, cultural, and personal characteristics affecting consumer behavior and lists the stages in the buyer decision process.