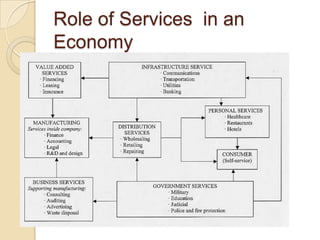
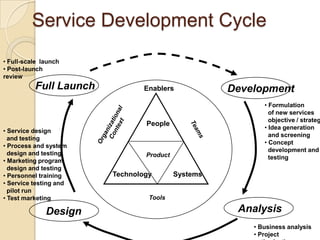
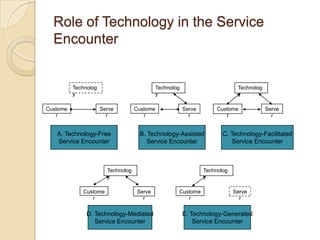
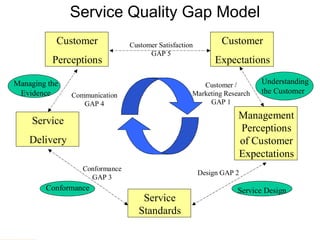
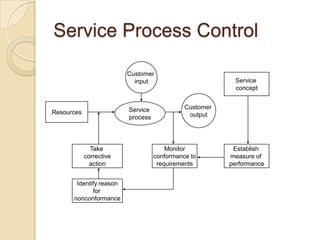
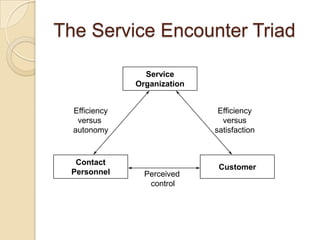
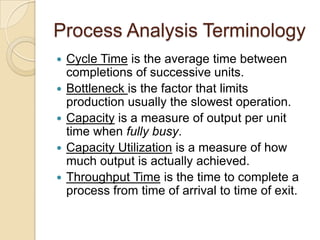
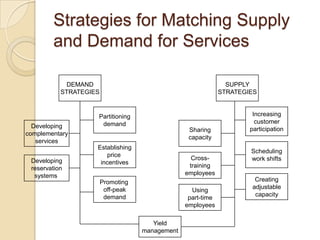
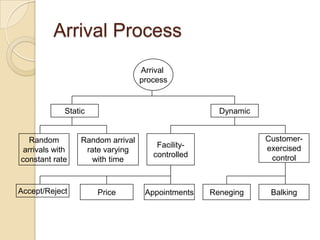
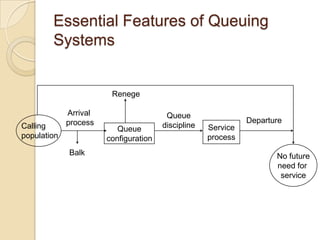
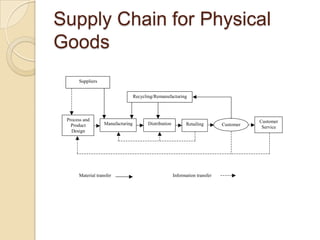
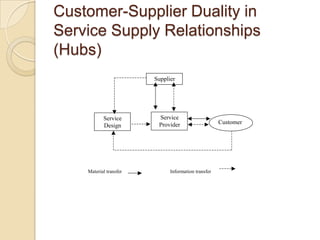
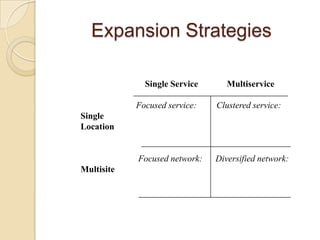
This document discusses several key concepts in operations management for the service industry. It covers the service development cycle, including formulation, design, testing, and launch. It also discusses the role of technology in service encounters, models for service quality and process control, forecasting methods, strategies for matching supply and demand, essential features of queuing systems, and inventory models. Finally, it provides an overview of expansion strategies for service firms.