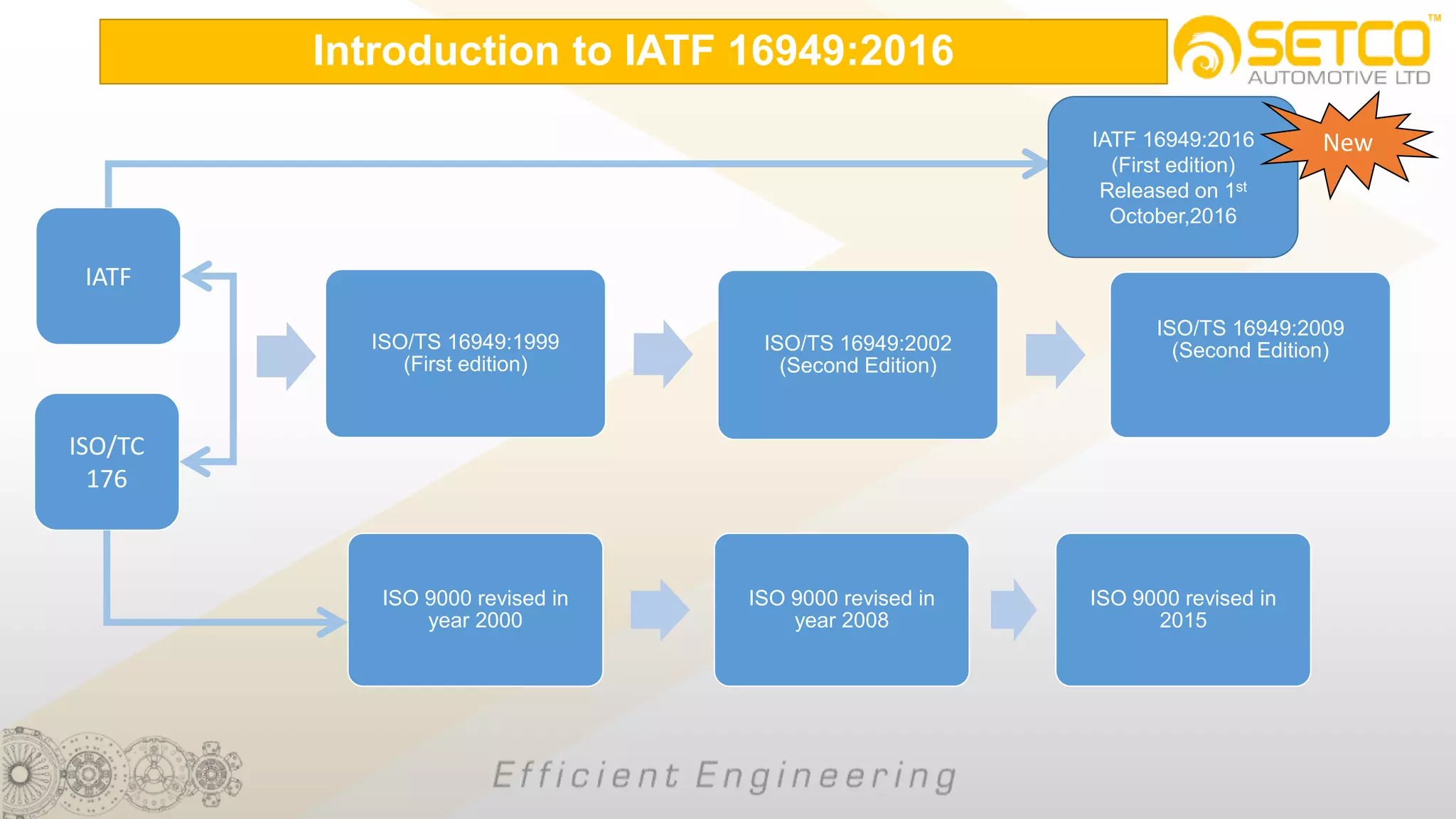
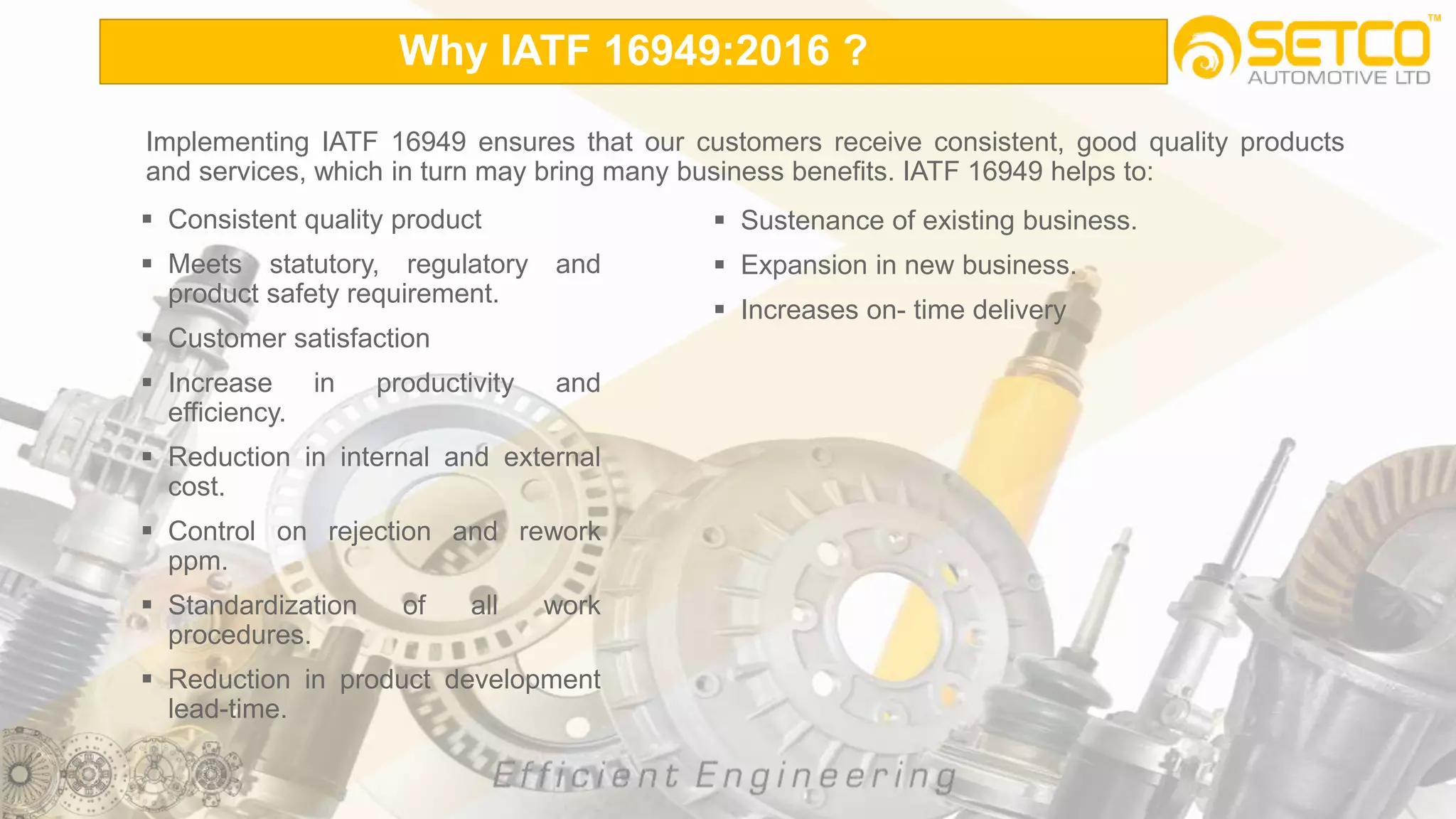
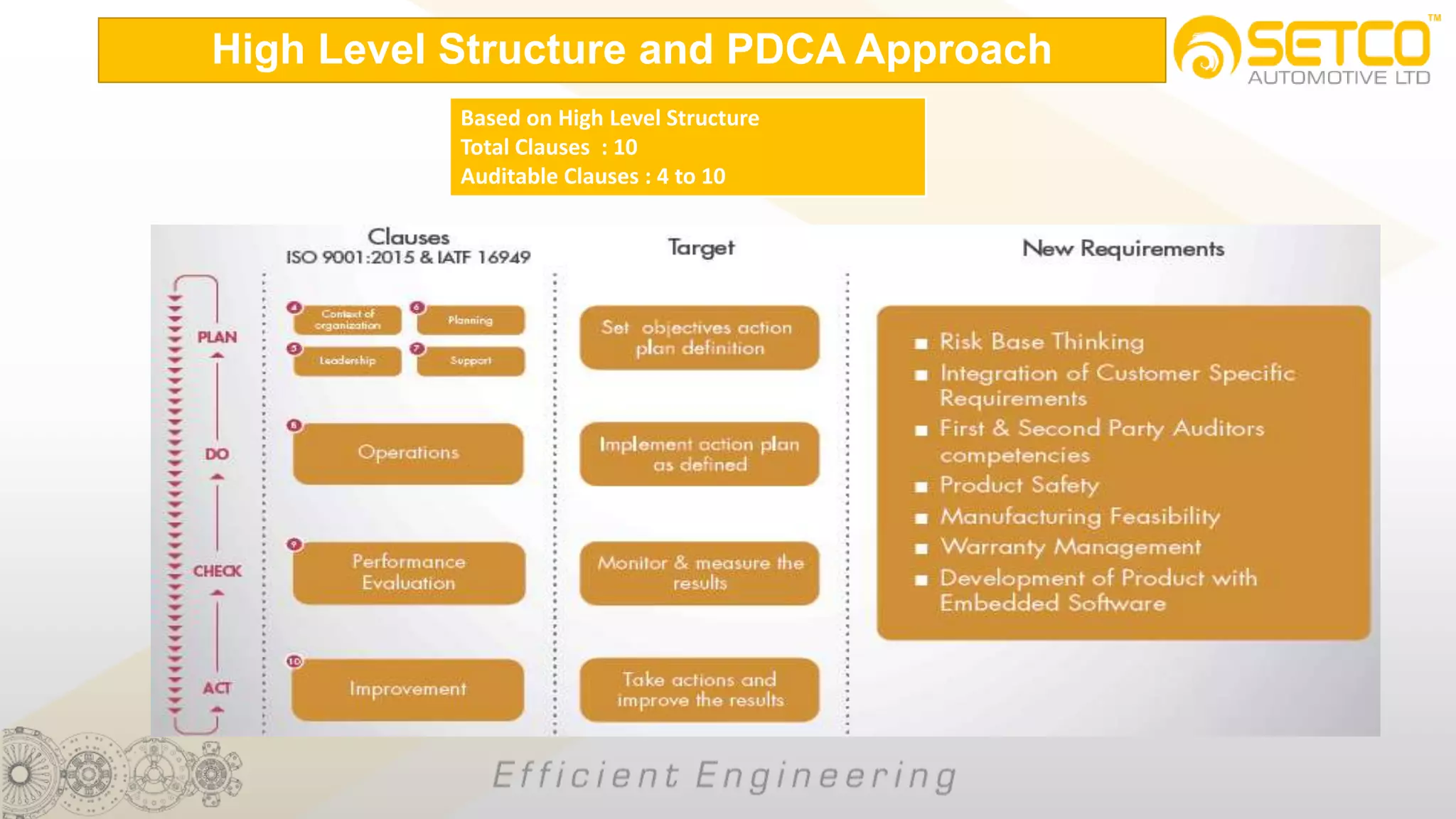
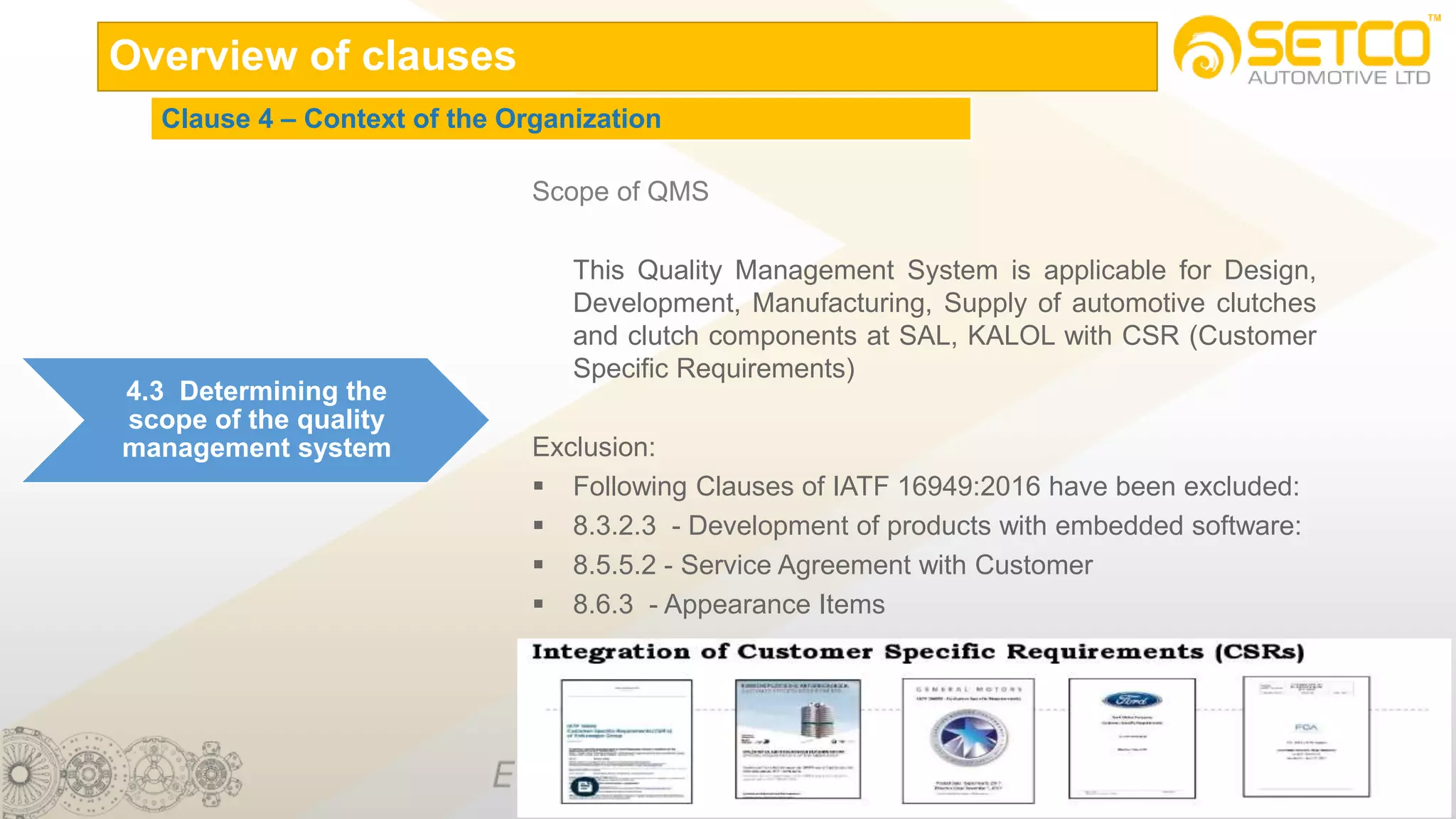
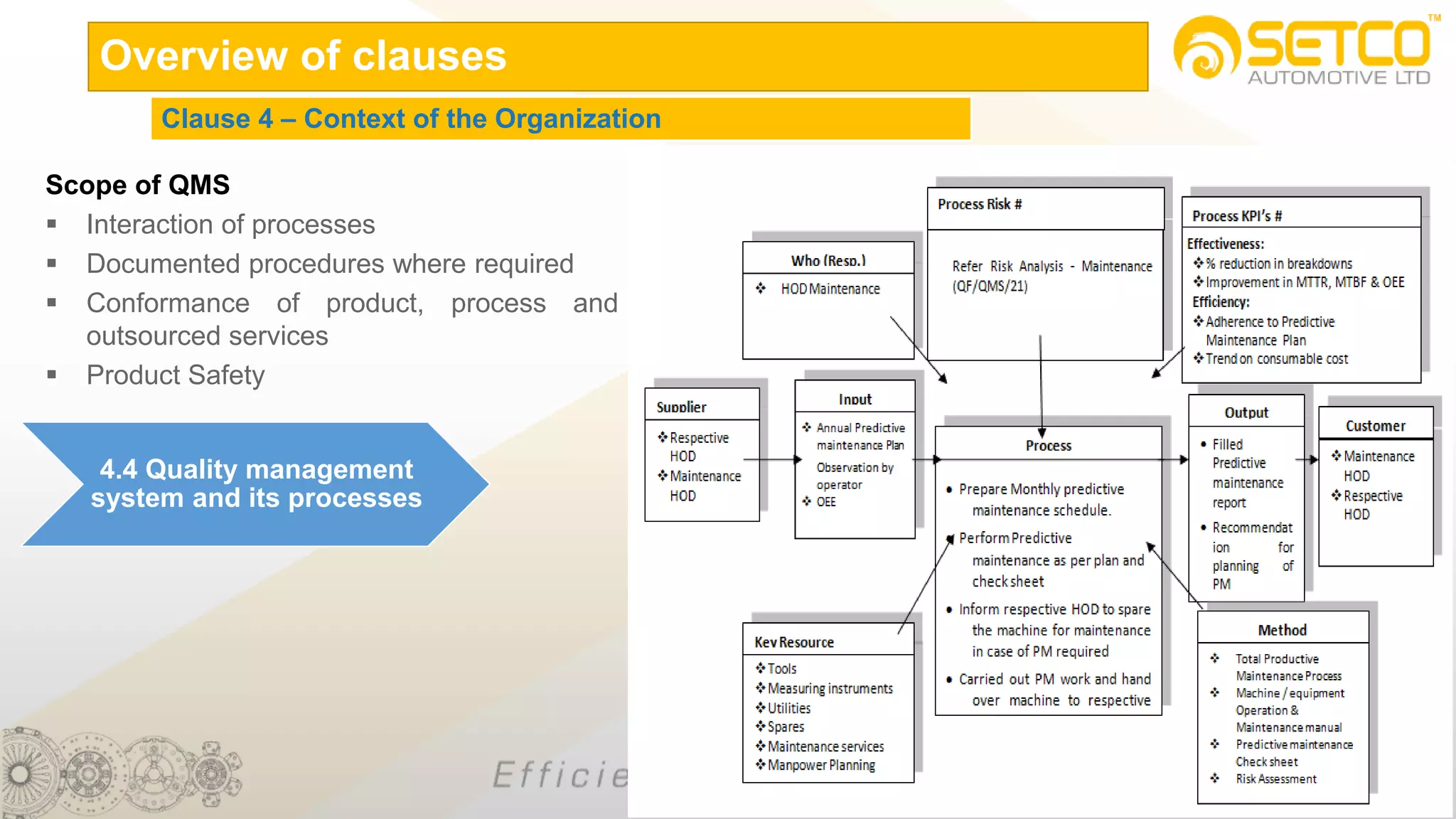
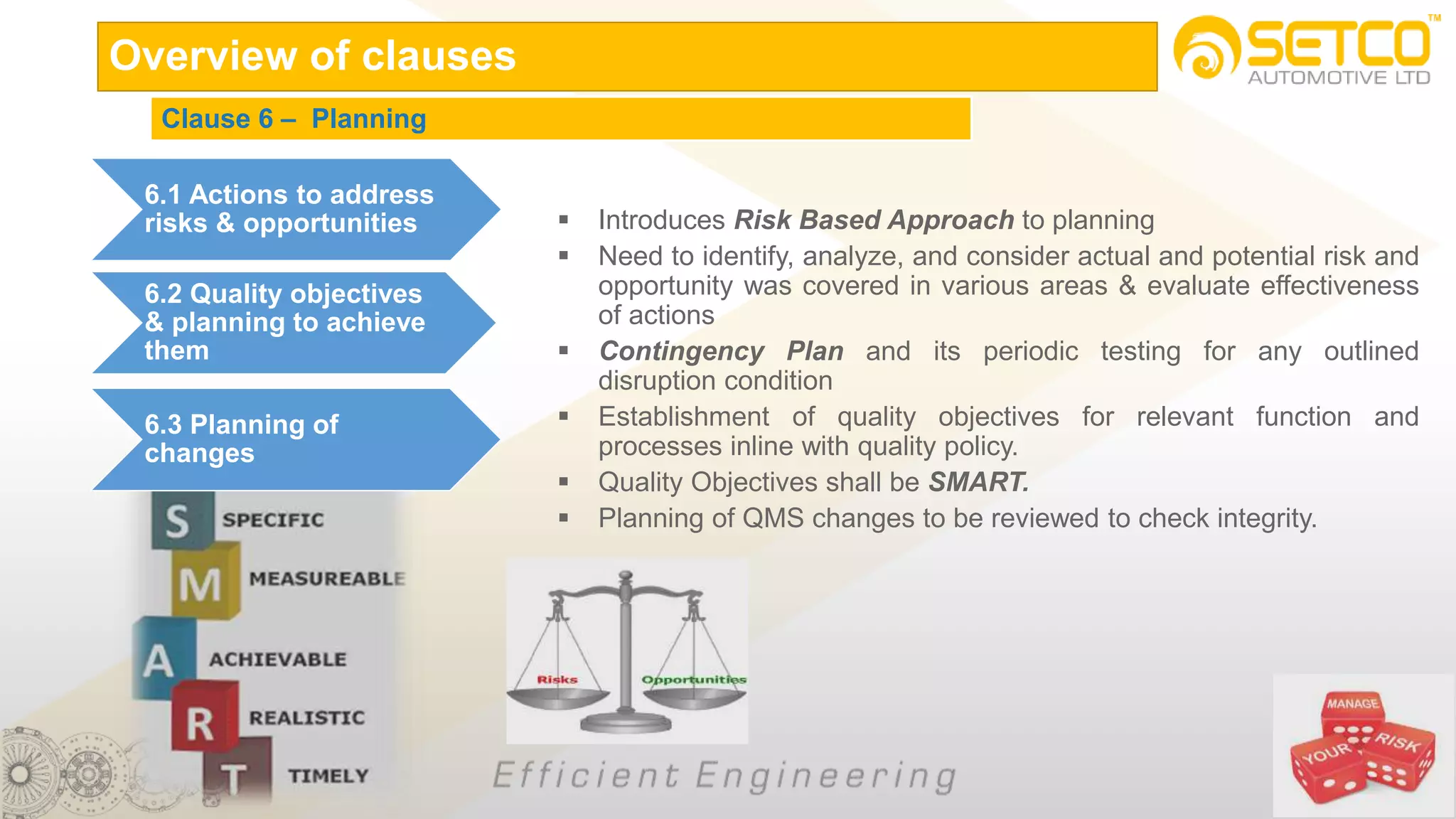
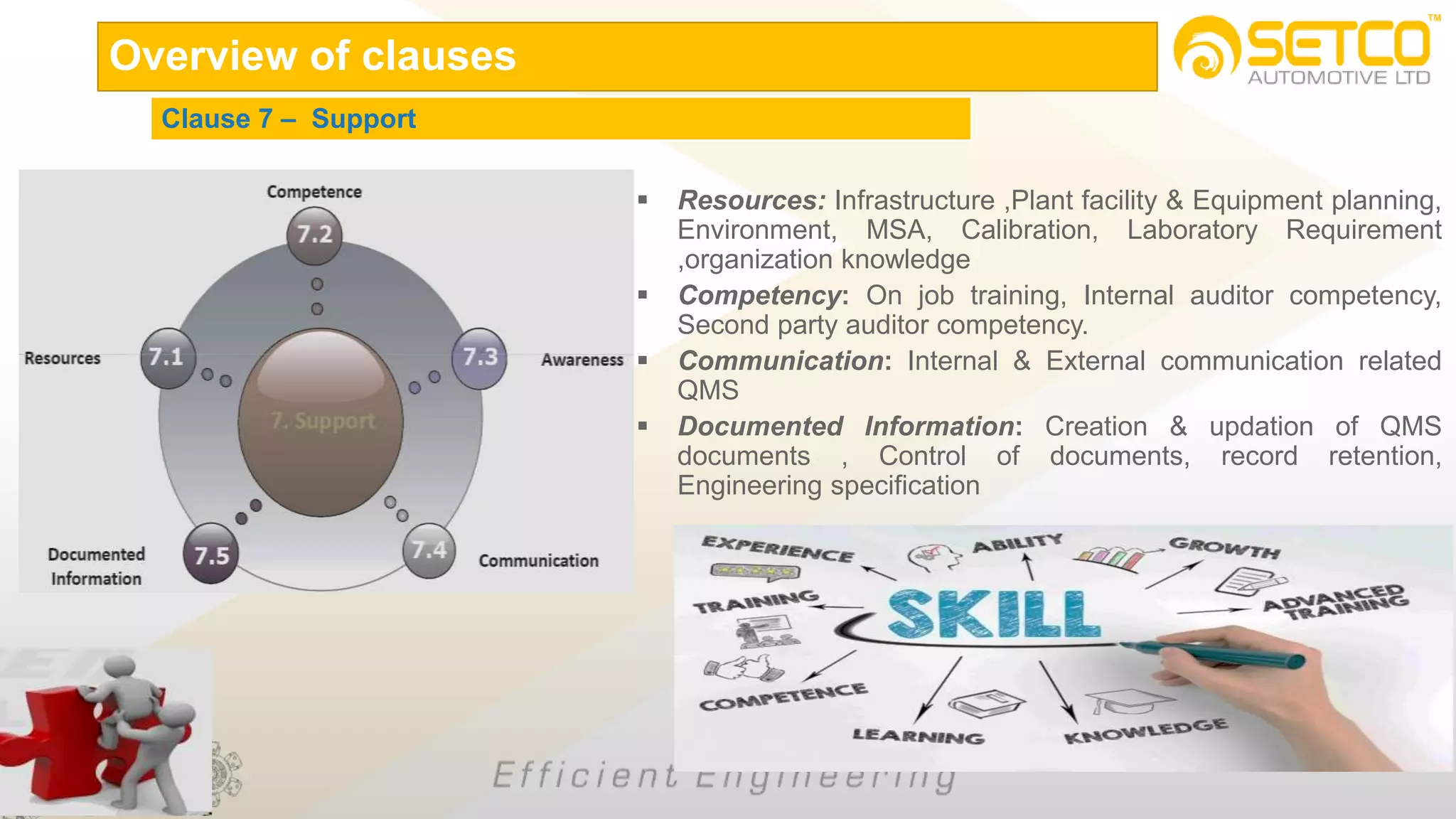
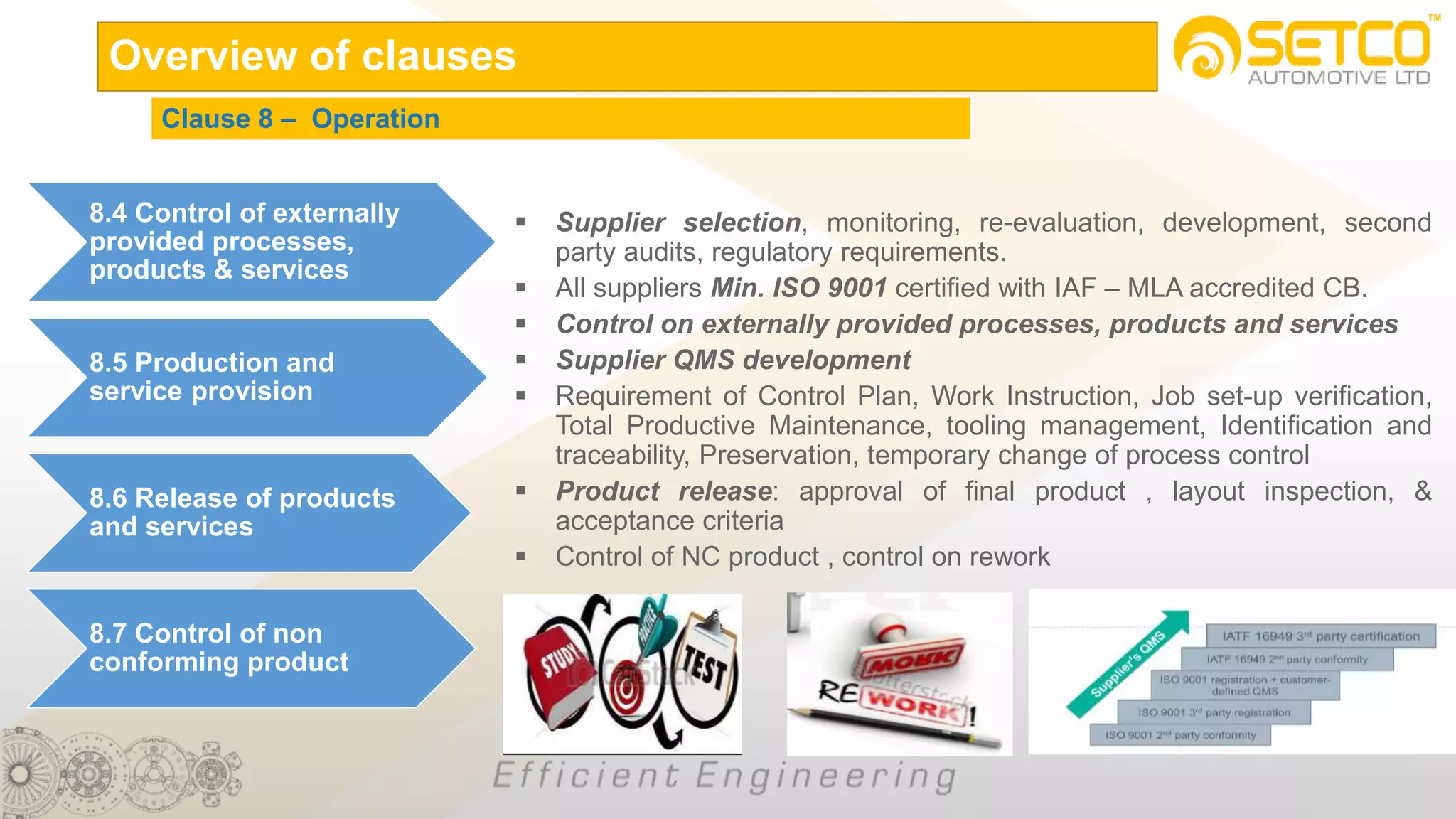
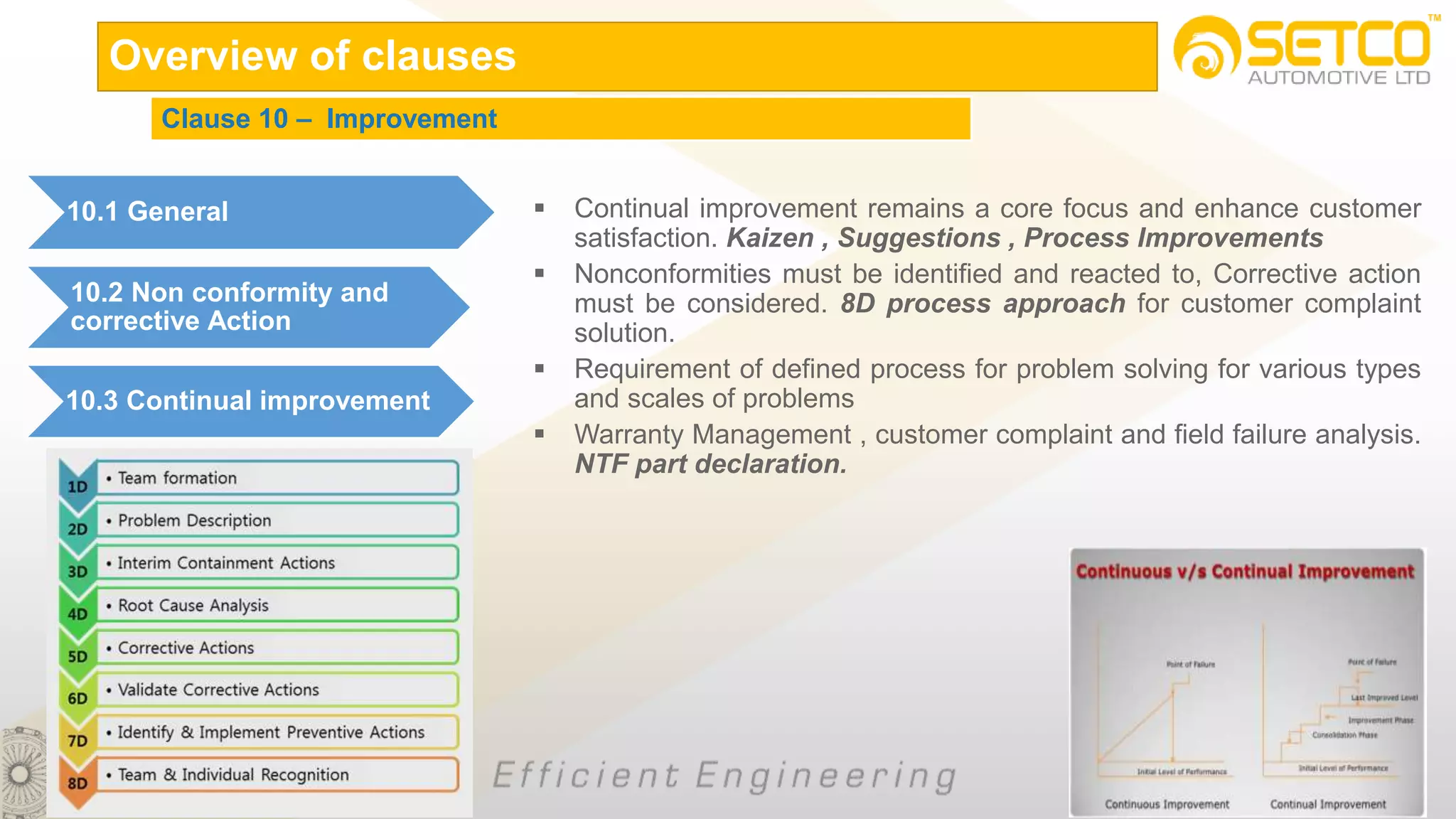
IATF 16949:2016 is an automotive quality management system standard that is based on ISO 9001:2015 with additional automotive industry requirements. It aims to prevent defects, reduce variation and waste, and promote continual improvement. The standard contains 10 clauses covering quality management principles, leadership involvement, risk-based planning, resource management, production control, performance evaluation, and continual improvement. Key aspects include supplier management, design and development processes, internal auditing, management reviews, and corrective and preventive action.