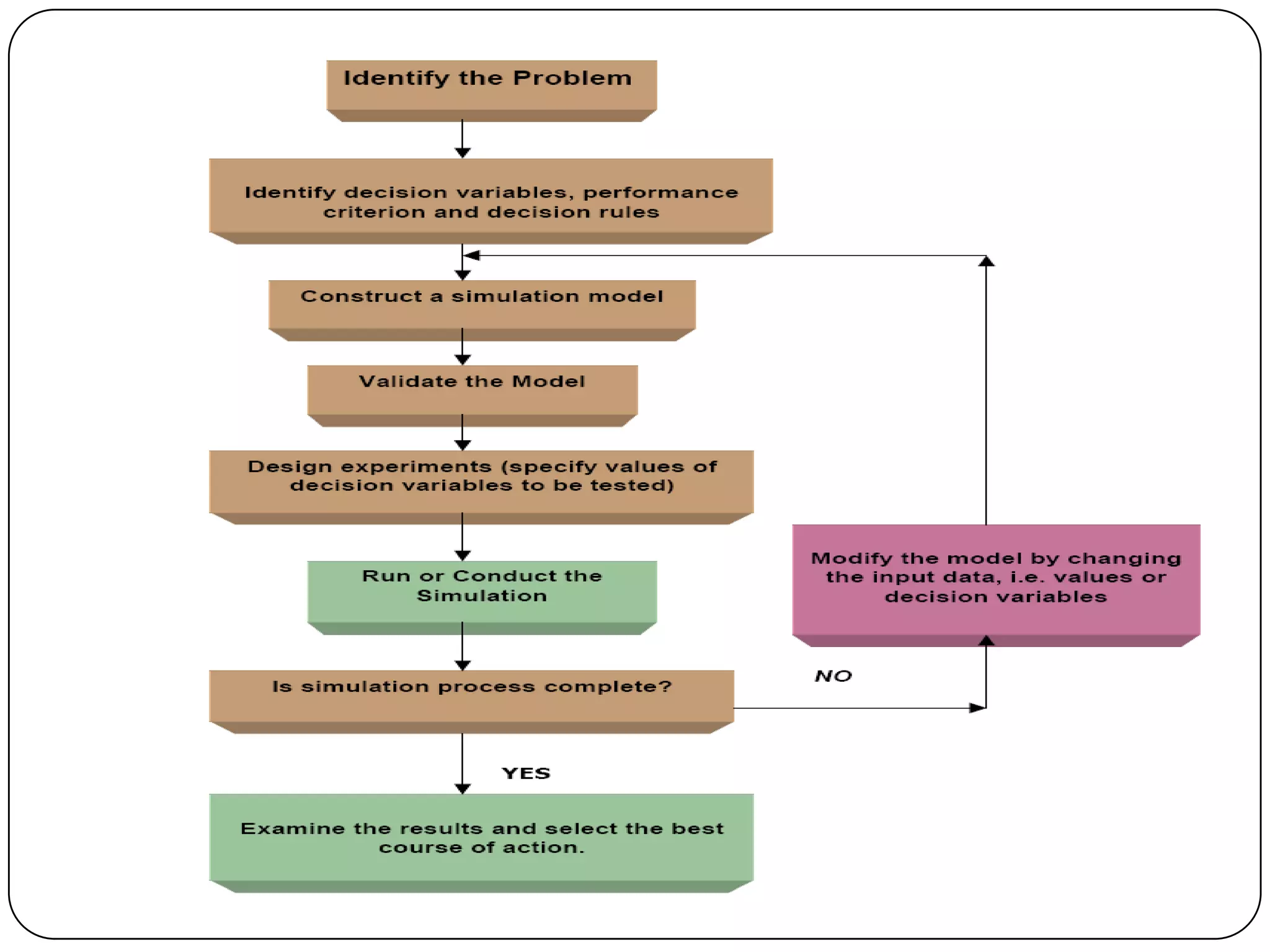
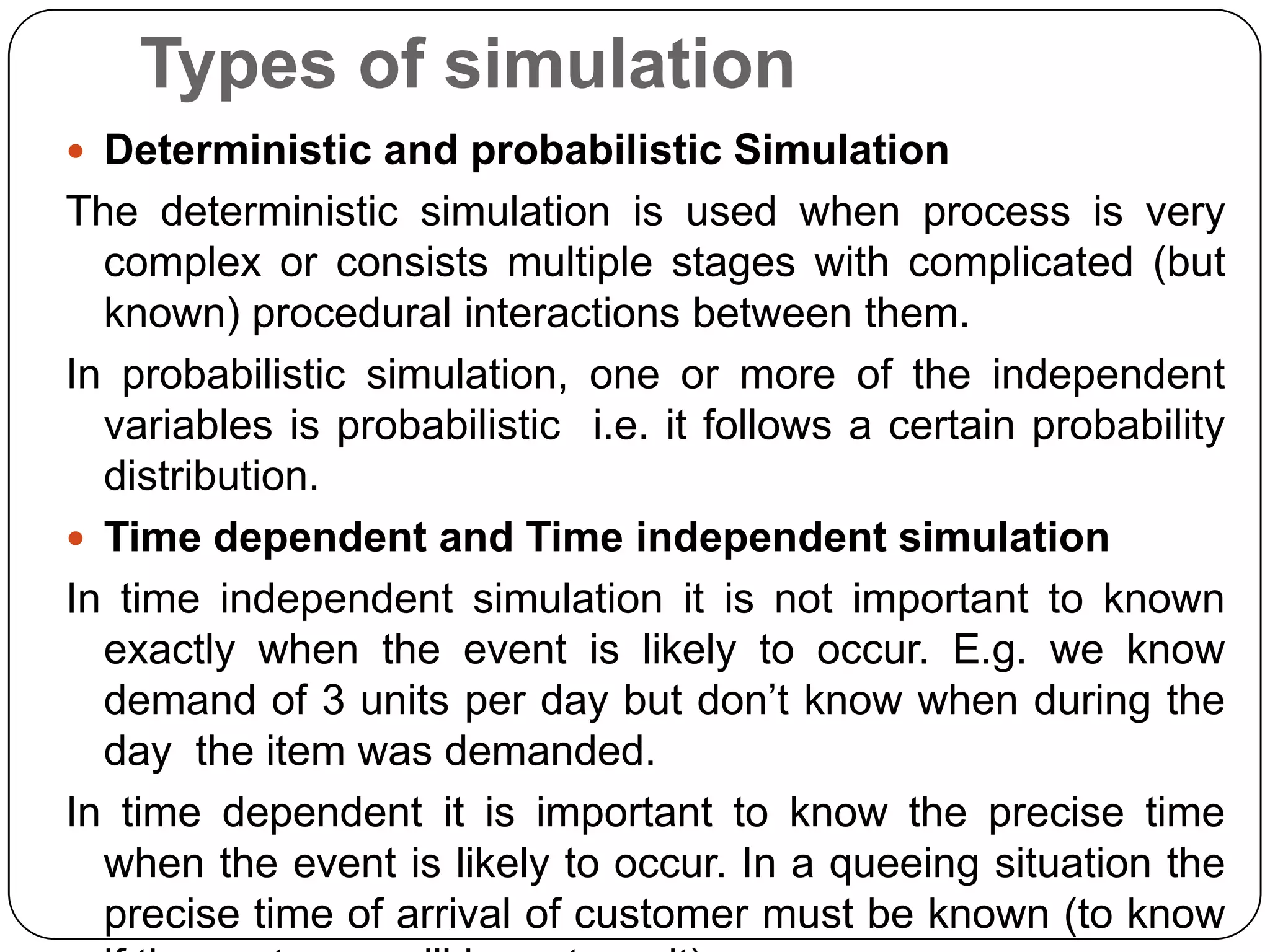
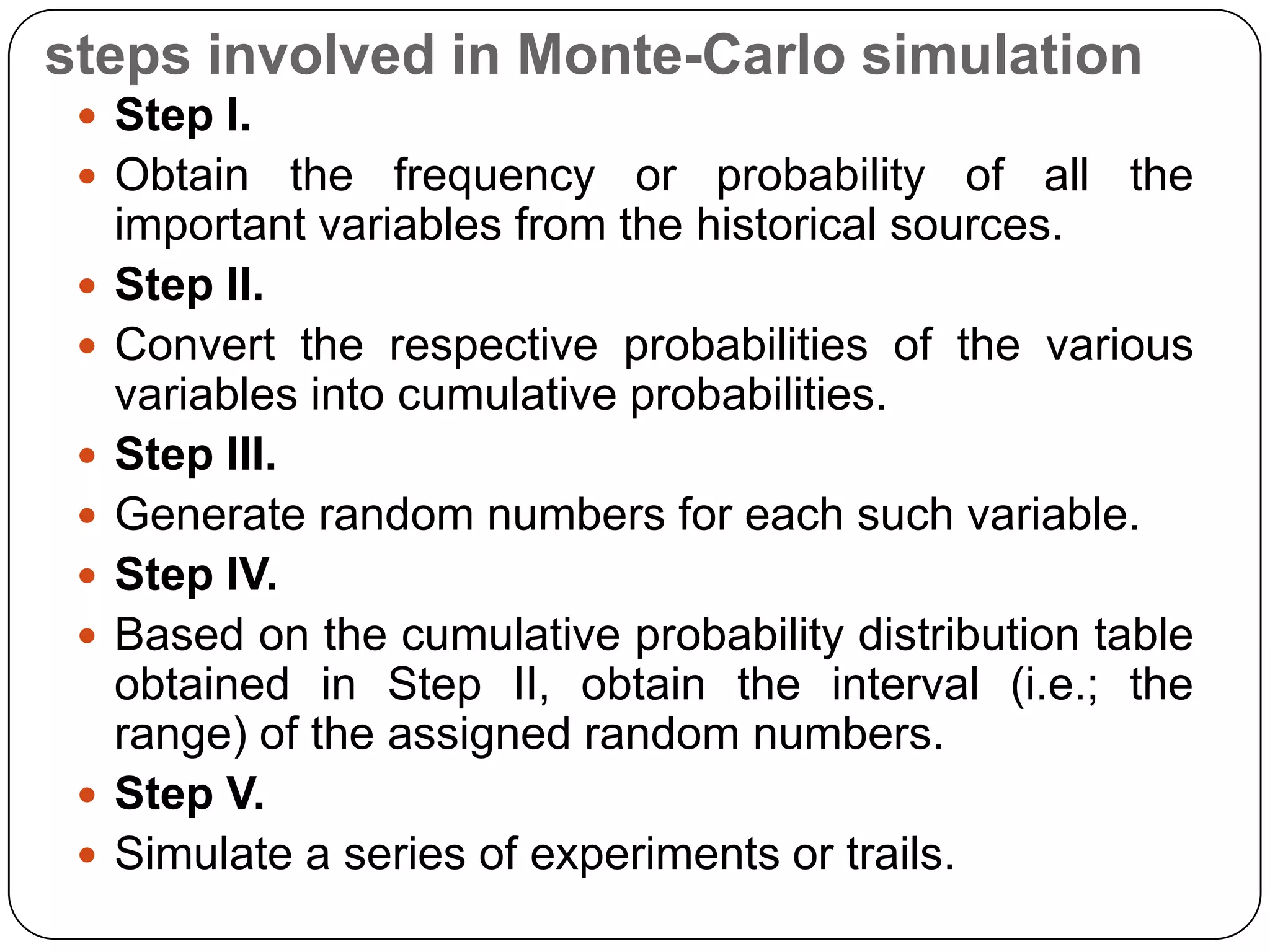
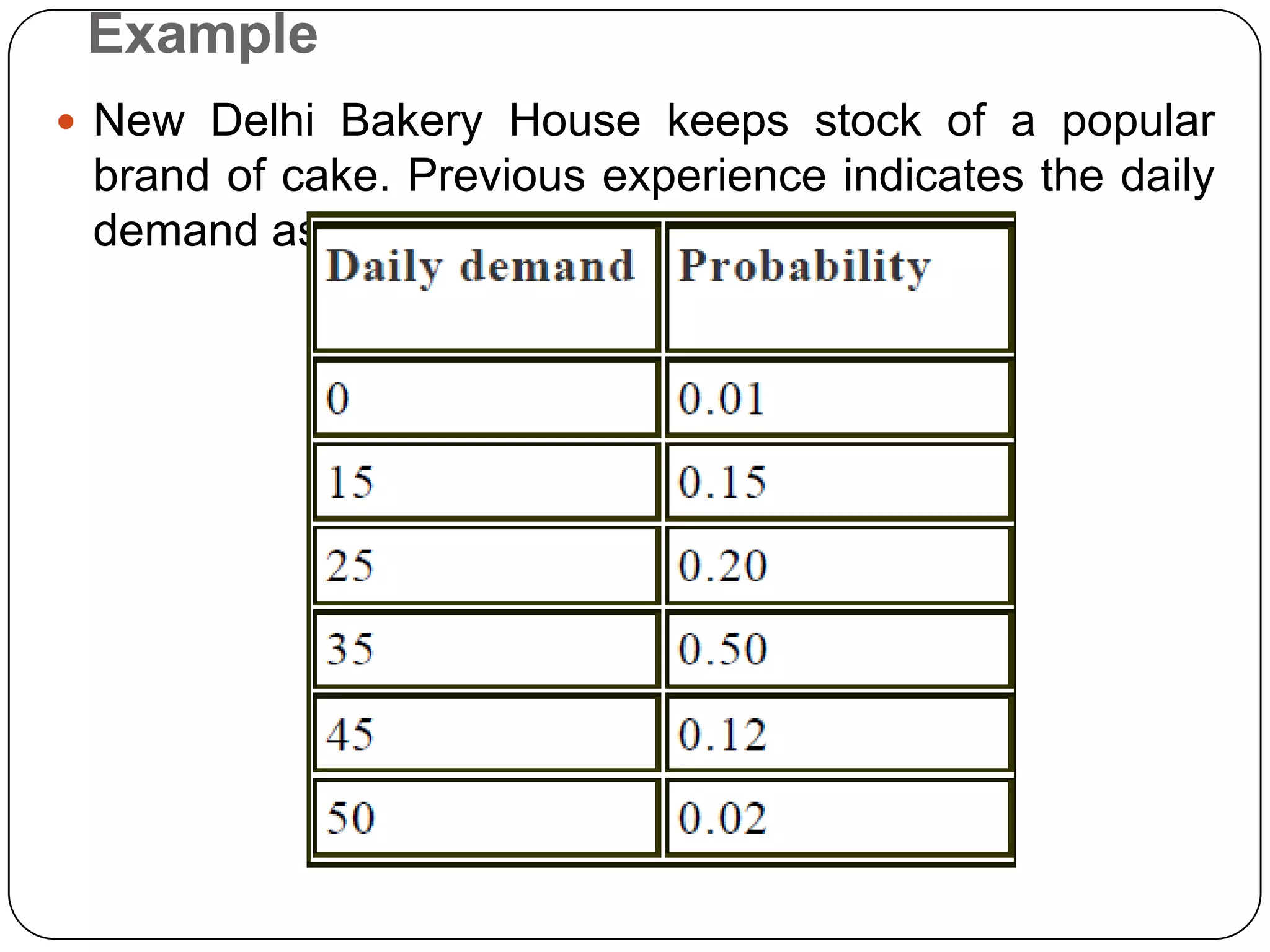
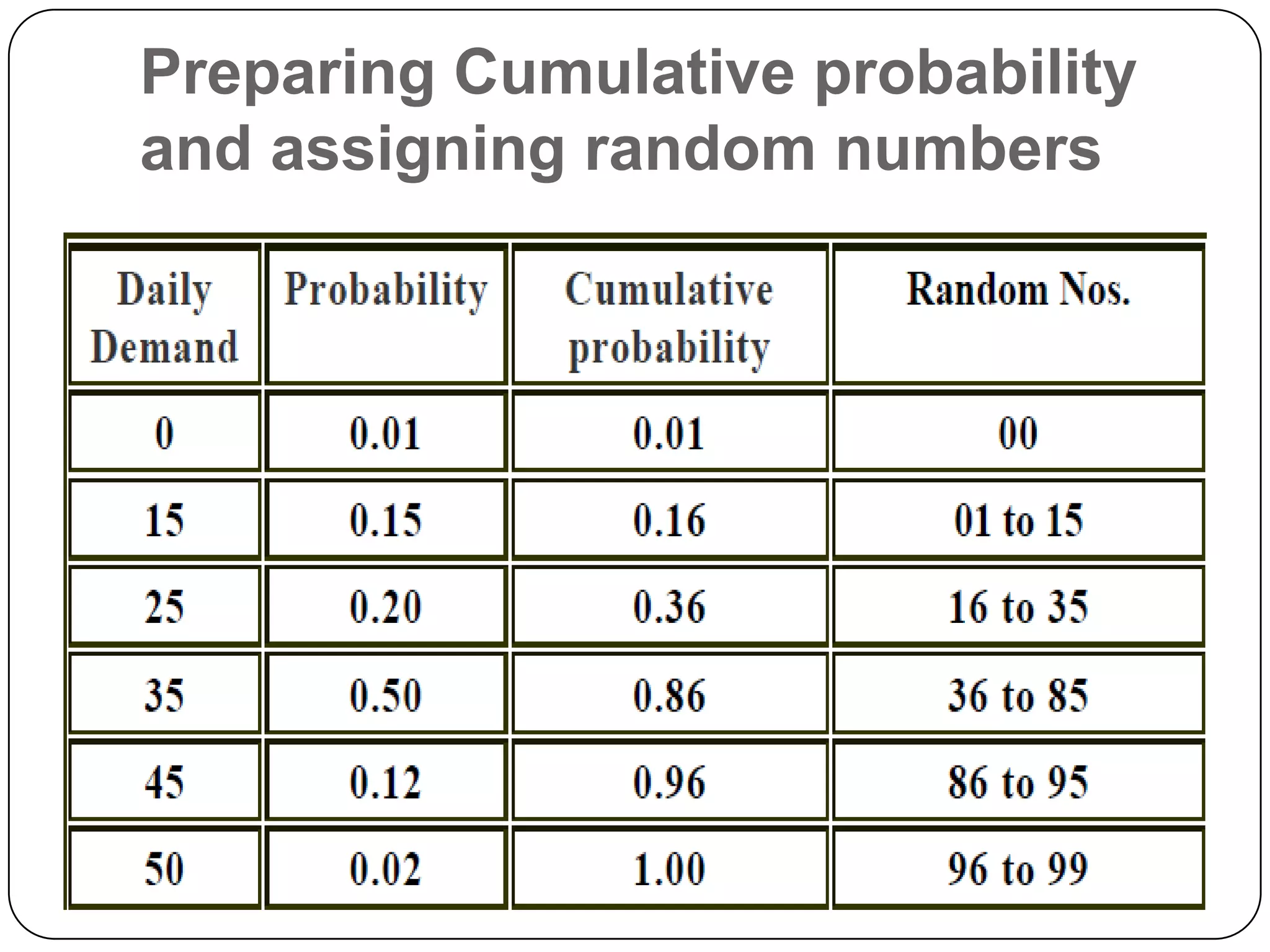
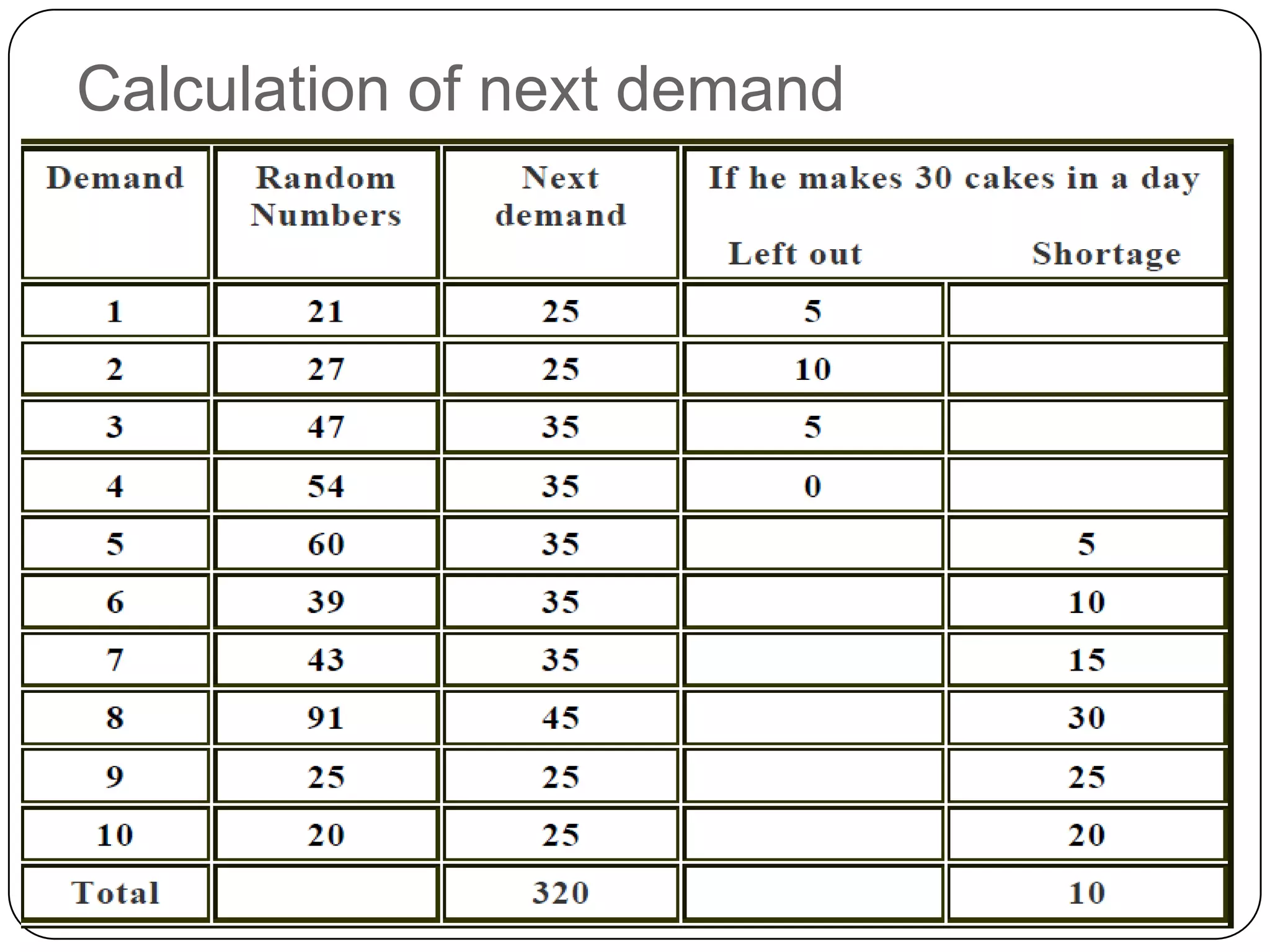
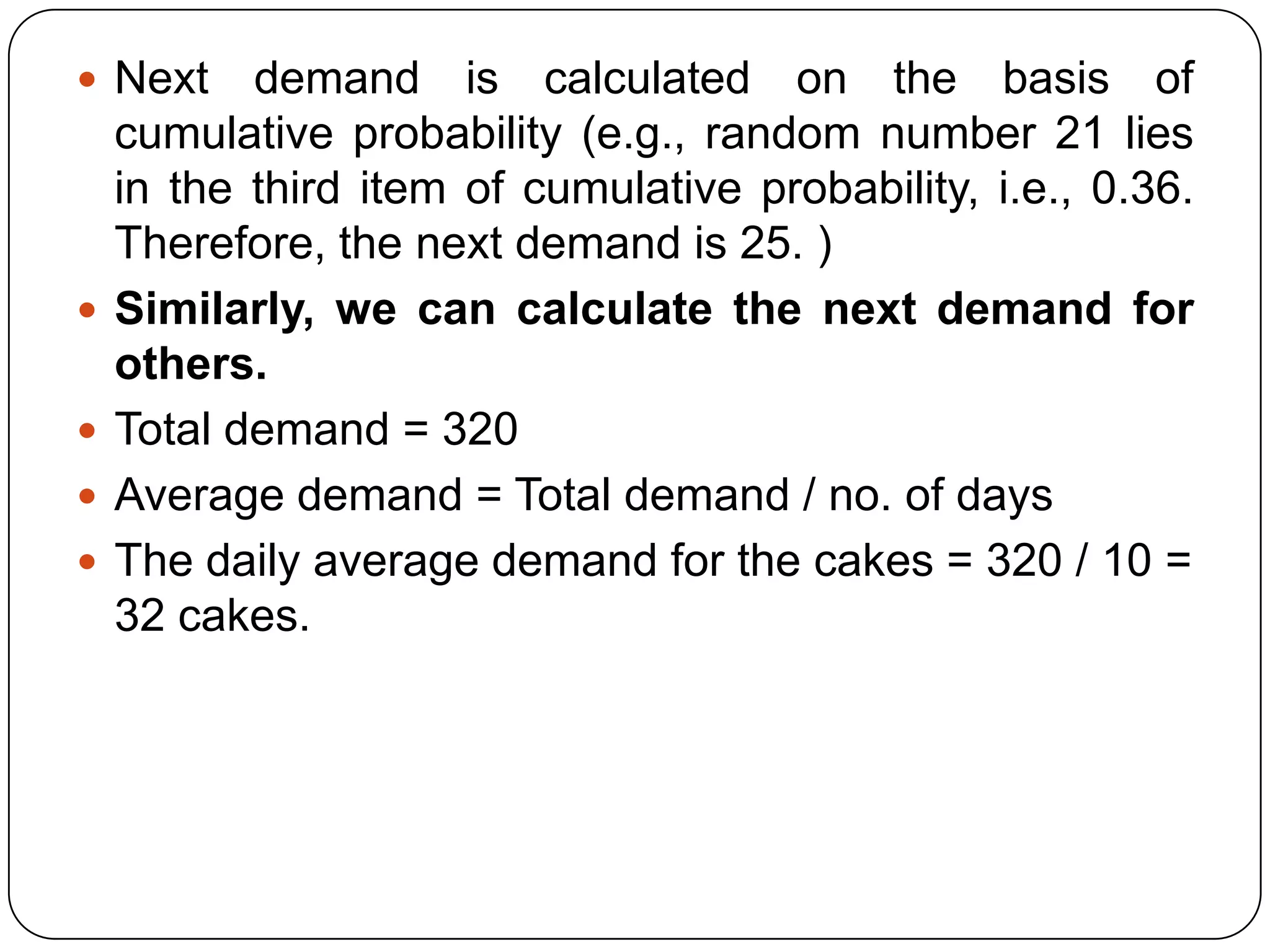
The document discusses simulation theory and the Monte Carlo method of simulation. It defines simulation as imitating reality and explains that simulation is used to understand complex systems when real experimentation is not possible or analytical solutions are unknown. It describes the Monte Carlo method as using probability distributions and random numbers to simulate random systems. The key steps are: (1) obtaining variable probabilities from data, (2) converting to cumulative probabilities, (3) generating random numbers, (4) mapping random numbers to probability intervals to determine outcomes, and (5) repeating simulations. An example demonstrates using cumulative probabilities and random numbers to simulate daily cake demand for a bakery.