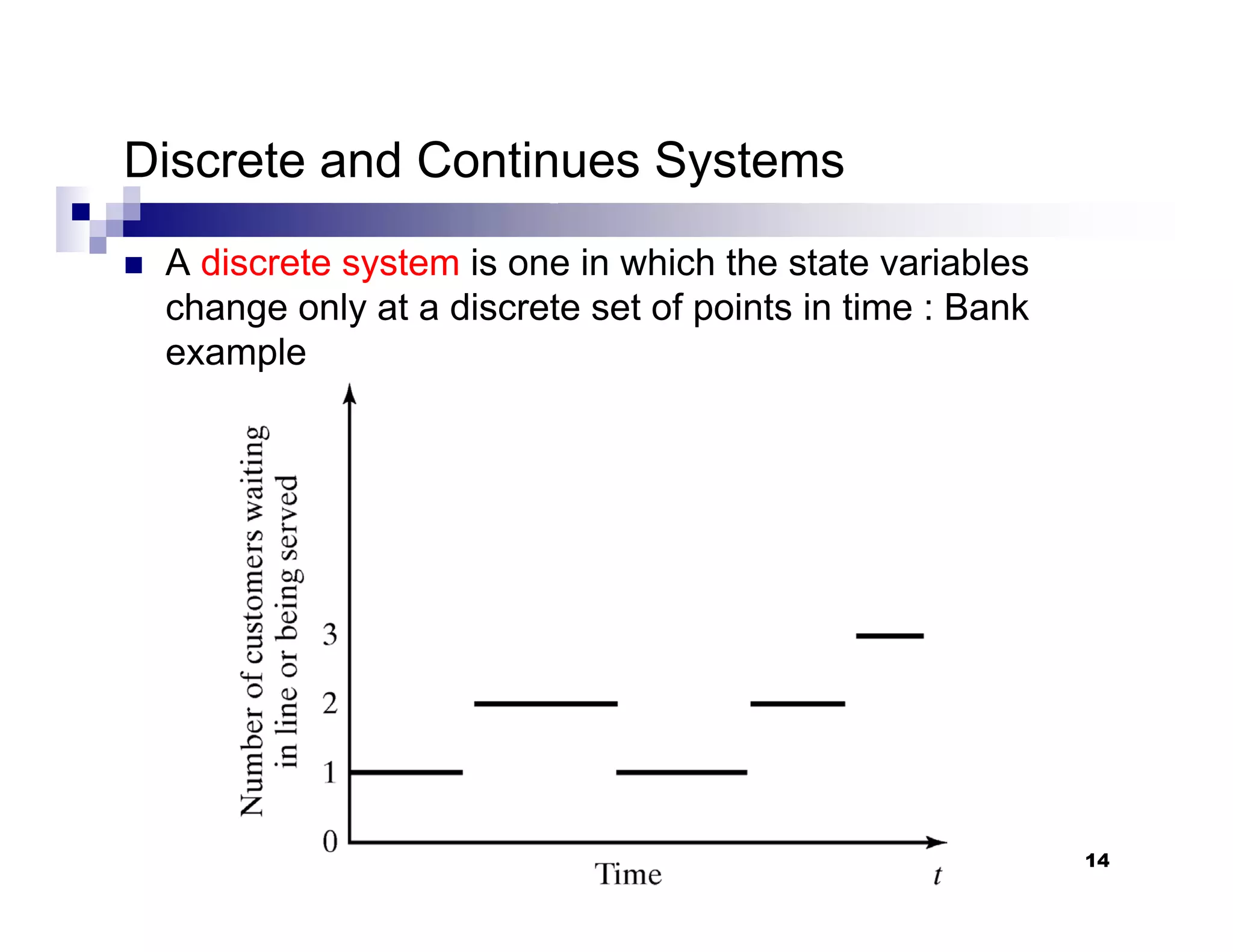
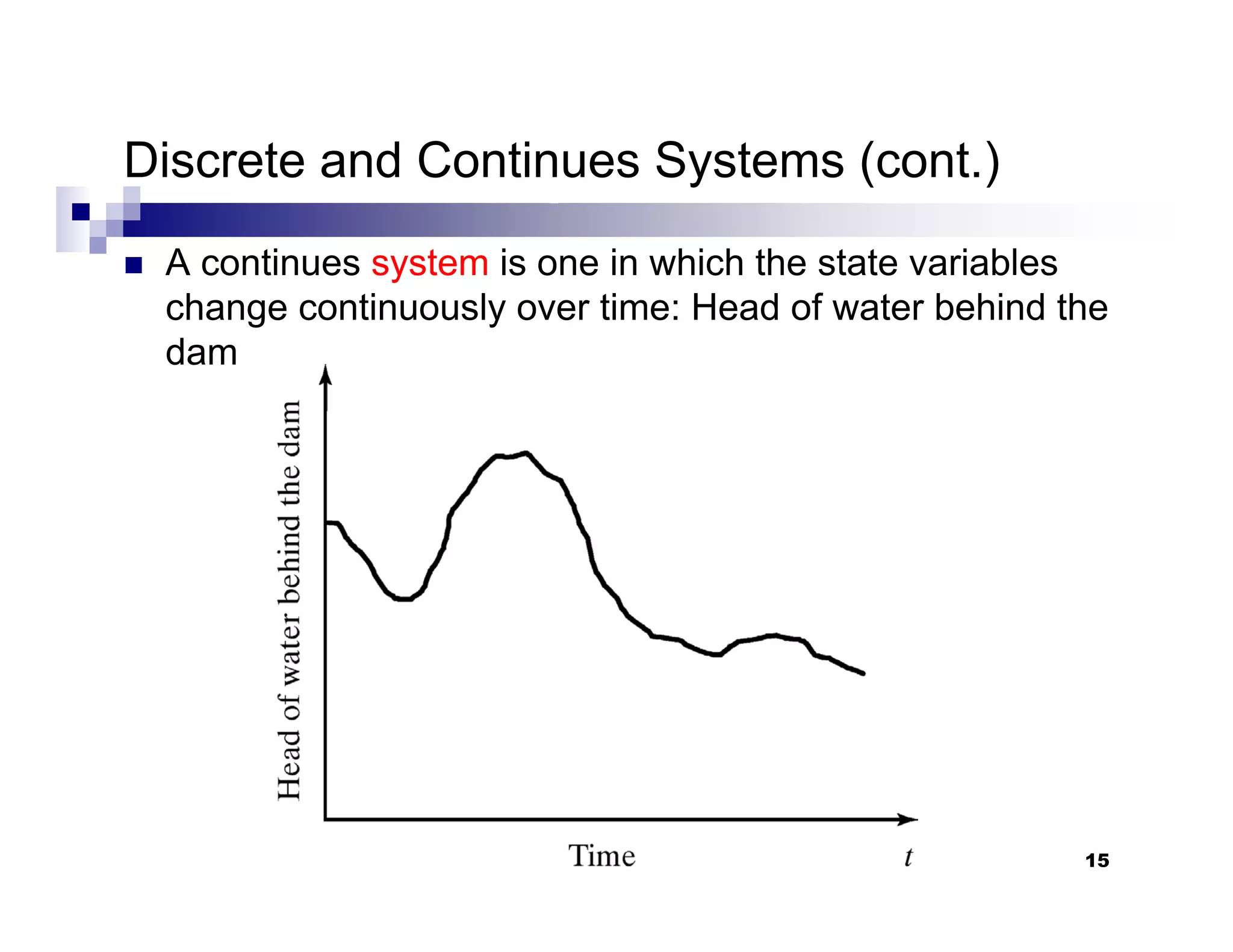
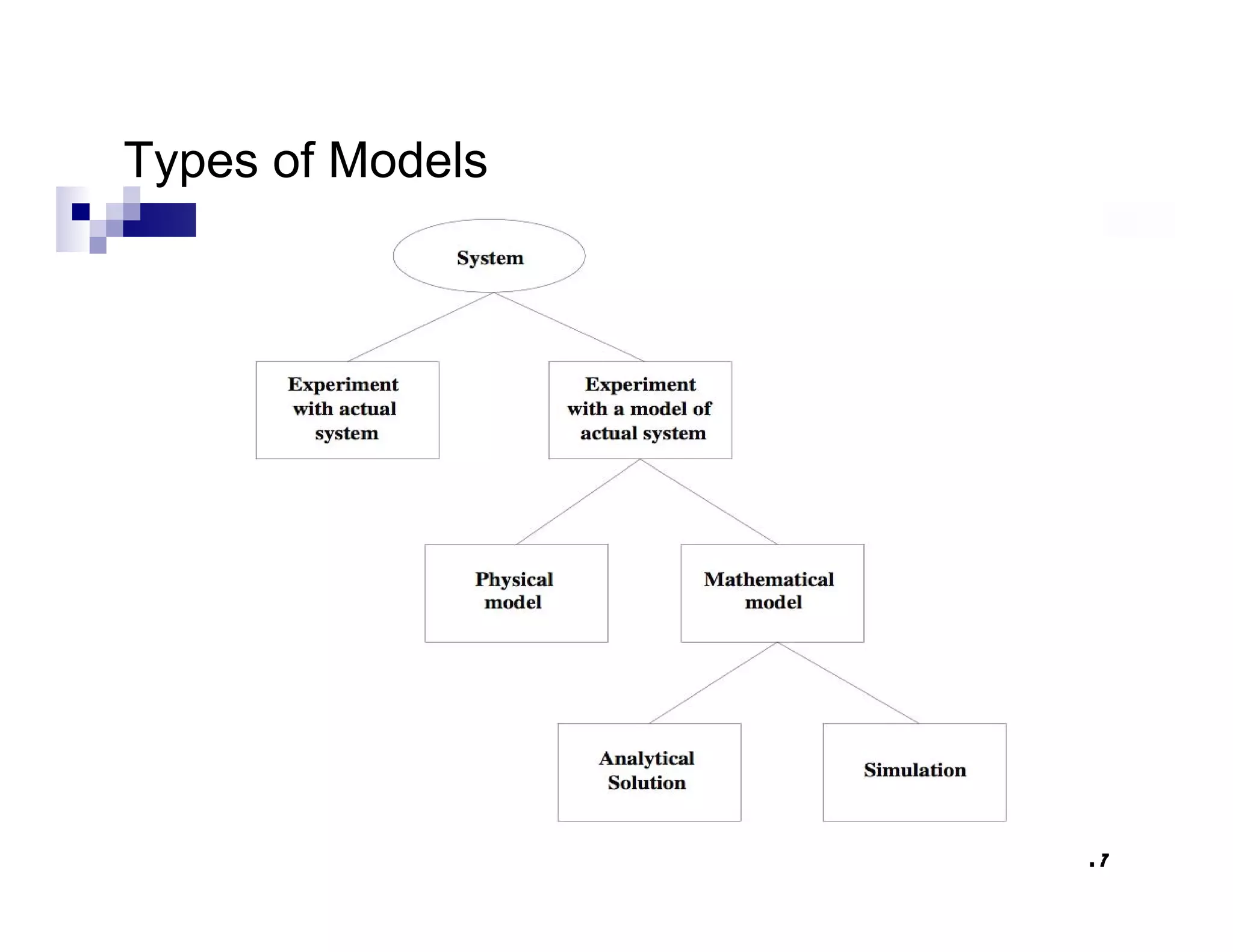
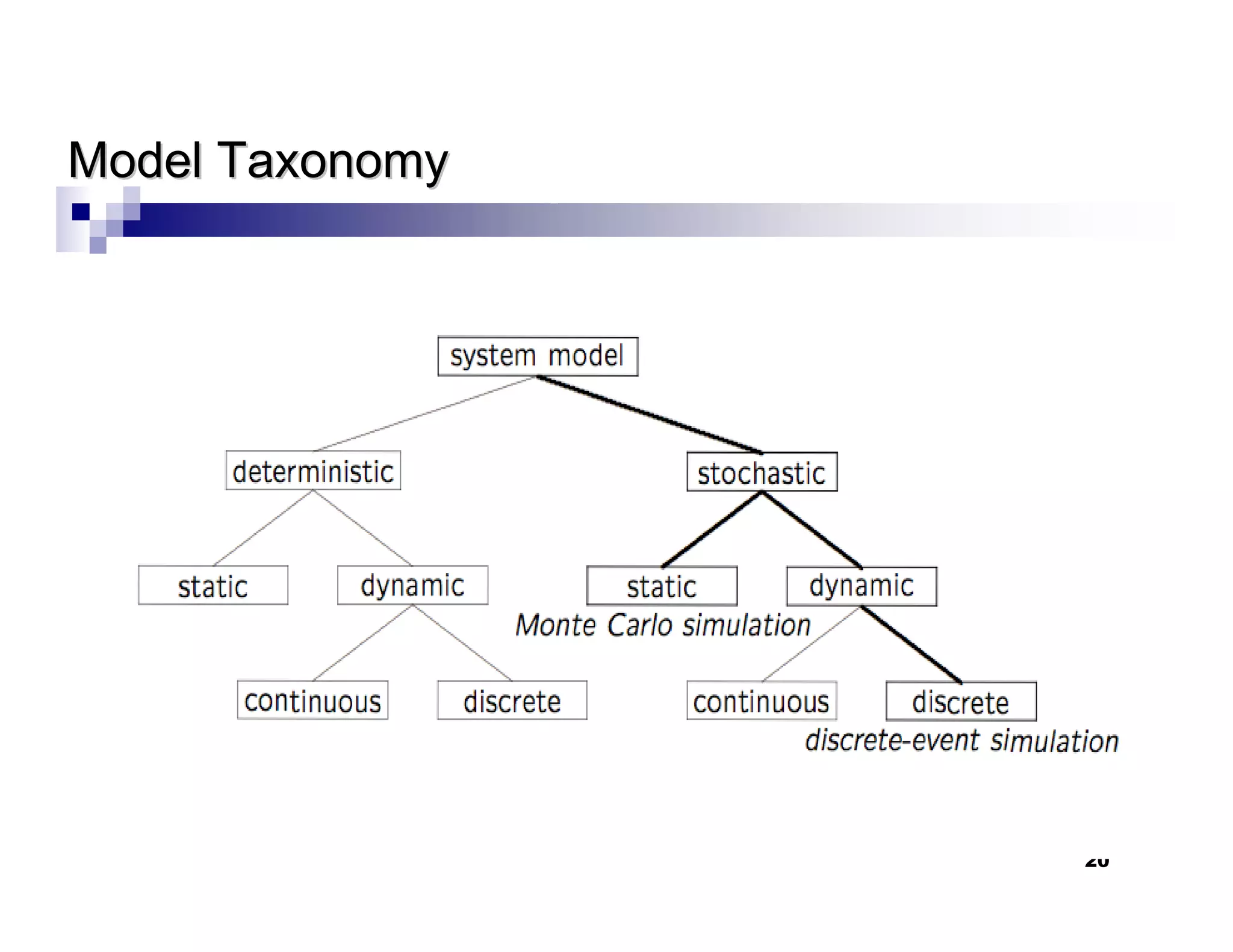
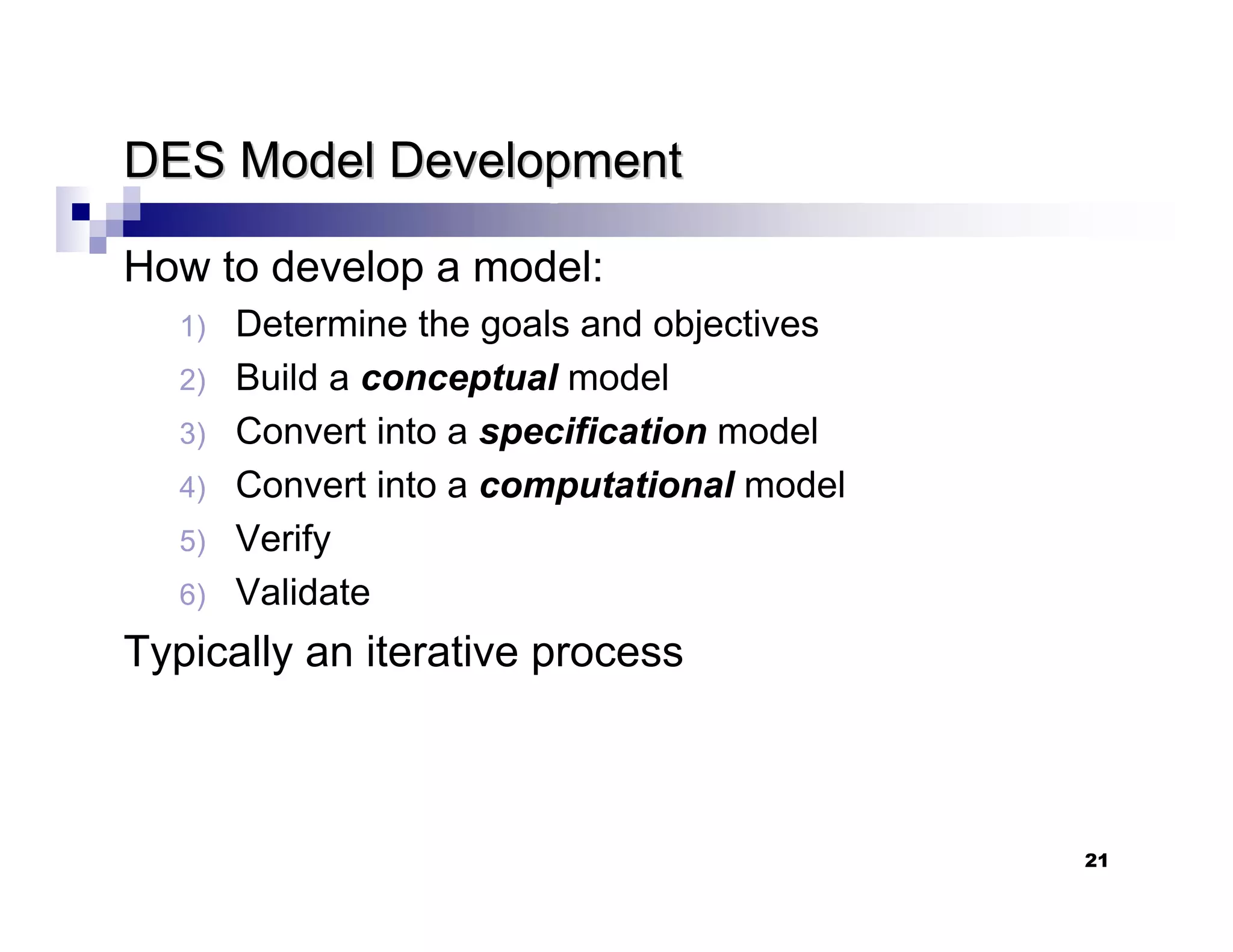
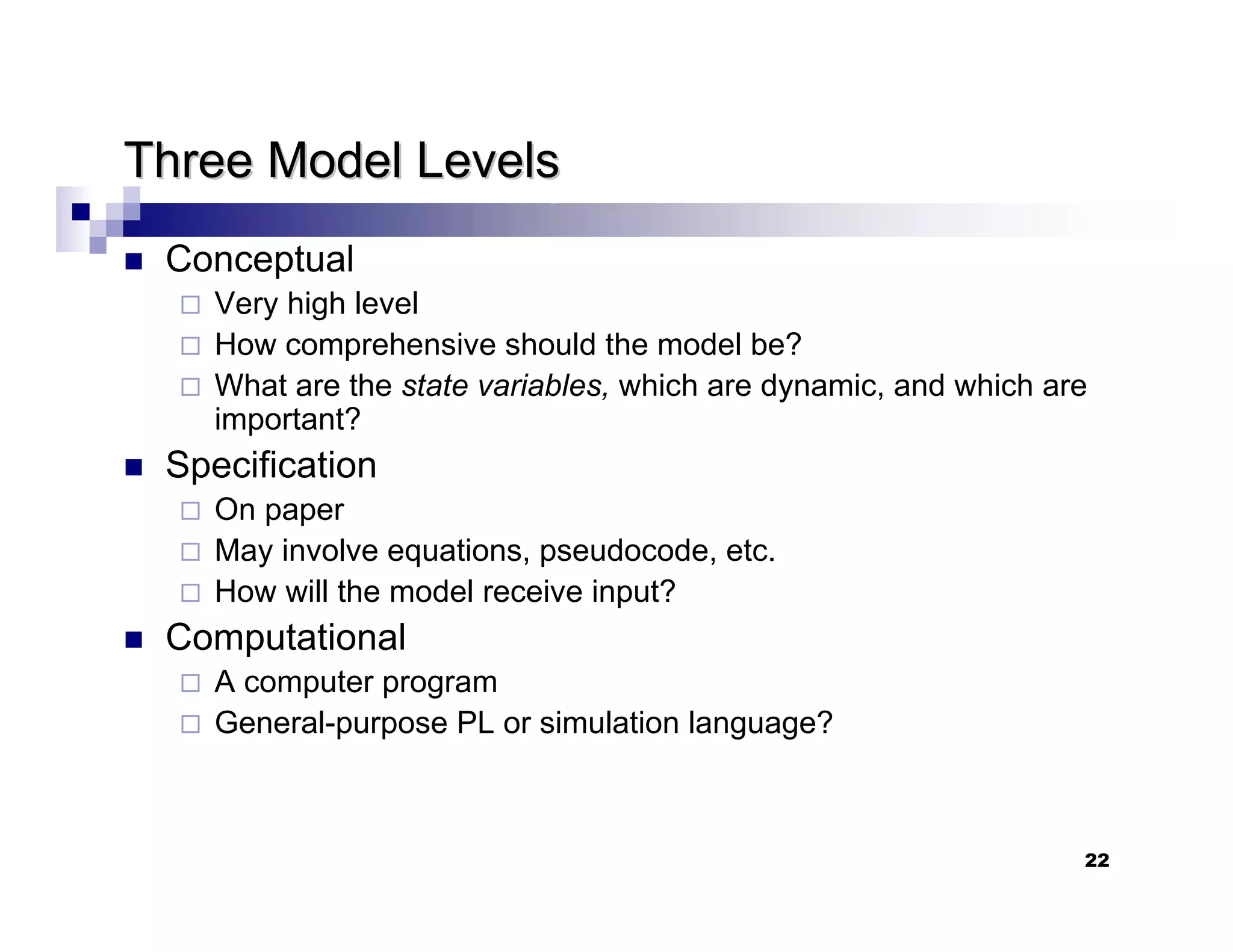
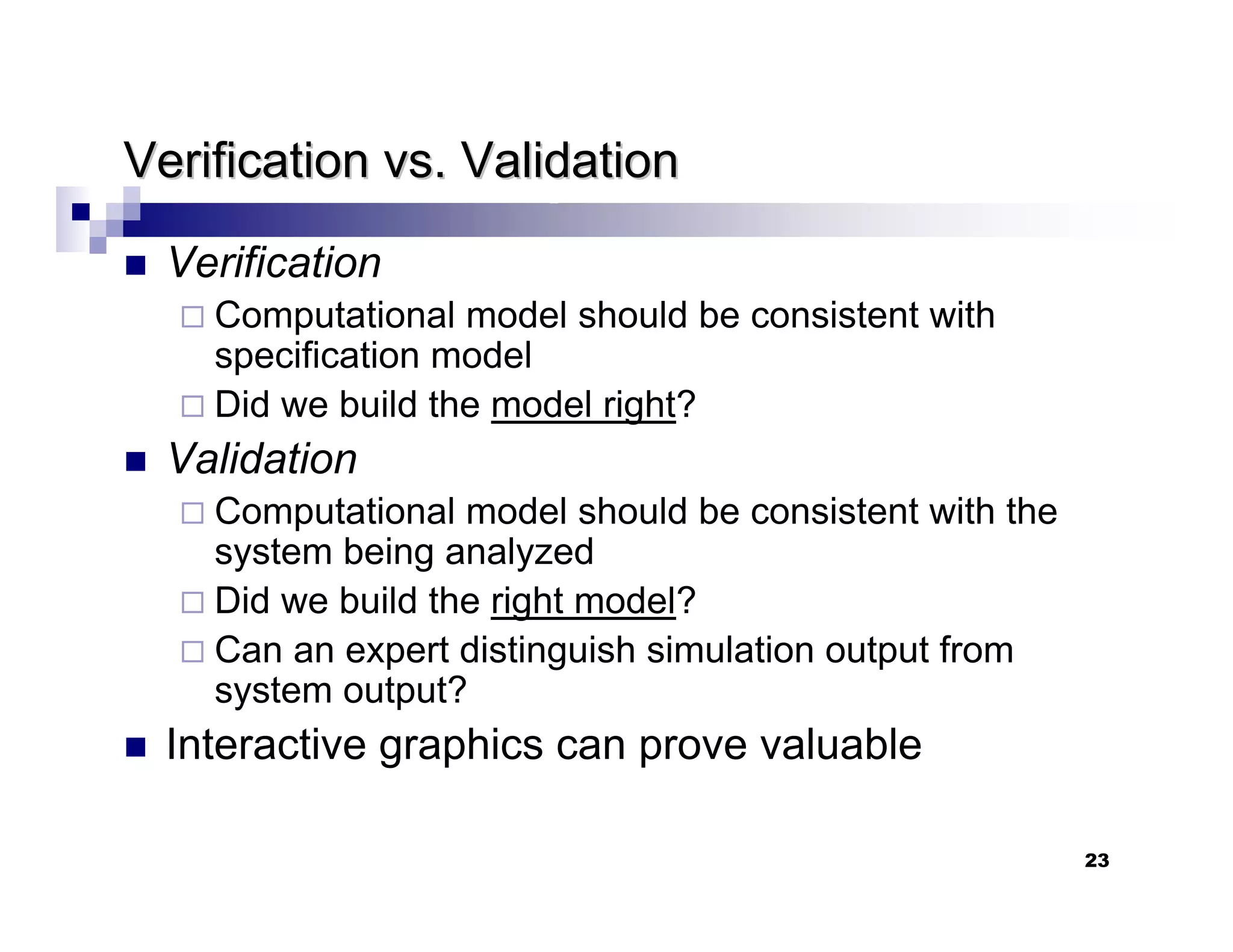
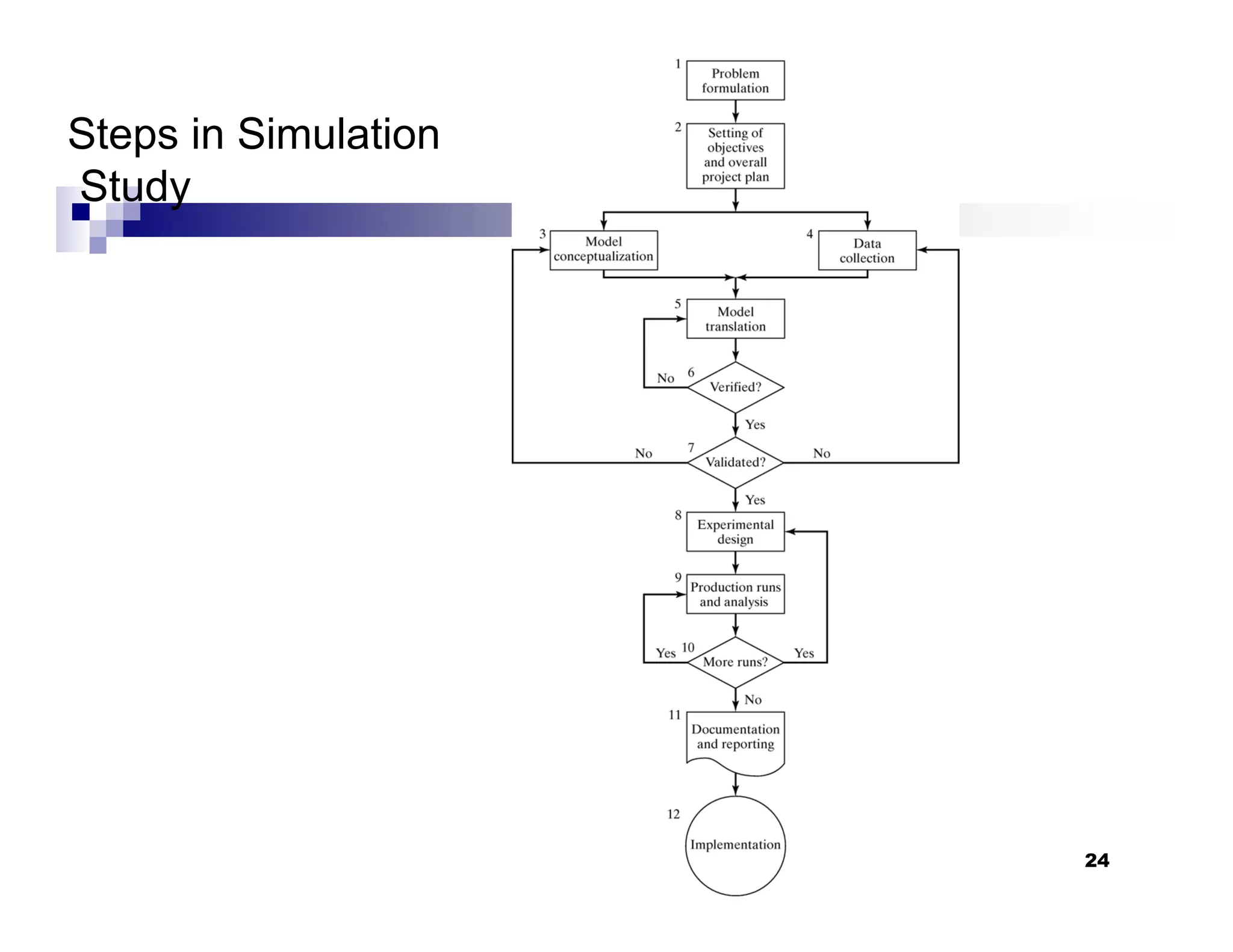
This chapter introduces discrete-event simulation and outlines the key steps in a simulation study. It defines simulation as imitating the operation of a real-world process over time through a conceptual model. Simulation allows experimenting with "what if" scenarios to analyze the potential effects of changes. The chapter describes when simulation is an appropriate tool, its advantages and disadvantages, common application areas, and components of systems and models. It distinguishes between discrete and continuous systems and events, and outlines the development process for discrete-event simulation models.