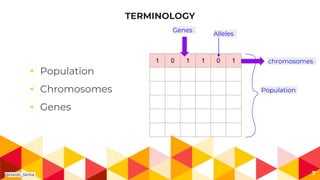
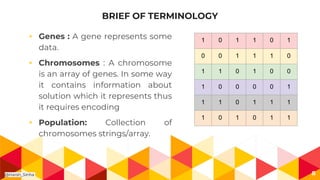
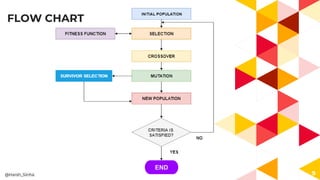
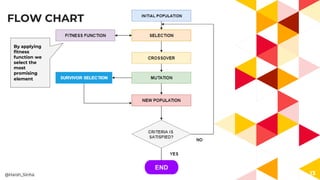
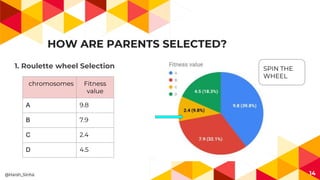
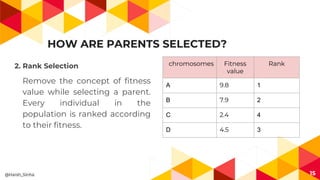
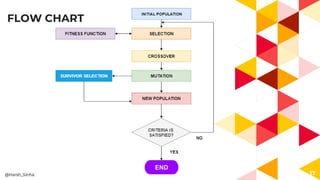
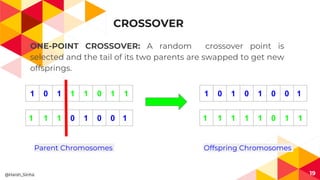
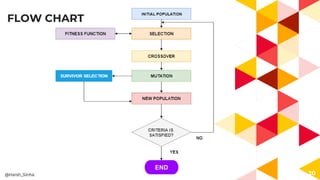
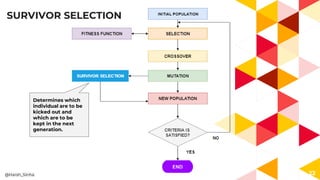
The presentation covers genetic algorithms, an optimization technique inspired by Darwin's 'survival of the fittest' that employs genetic operators like selection, crossover, and mutation to find optimal solutions for complex problems. It details the terminology, processes involved, and its applications in various fields, as well as the drawbacks of using genetic algorithms. The document concludes with examples of when genetic algorithms are particularly useful.