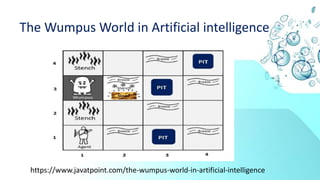
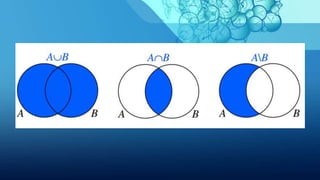
The document discusses sources and approaches to handling uncertainty in artificial intelligence. It provides examples of uncertain inputs, knowledge, and outputs in AI systems. Common methods for representing and reasoning with uncertain data include probability, Bayesian belief networks, hidden Markov models, and temporal models. Effectively handling uncertainty through probability and inference allows AI to make rational decisions with imperfect knowledge.