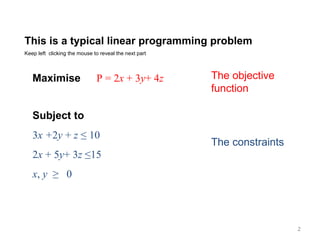
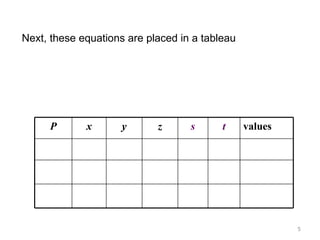
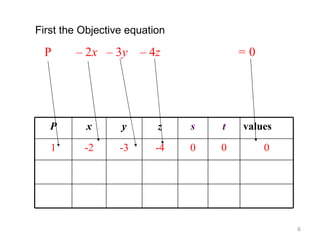
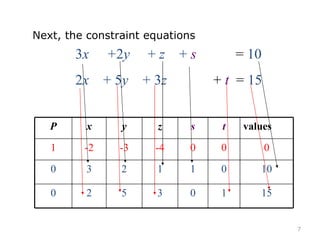
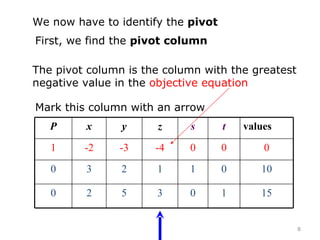
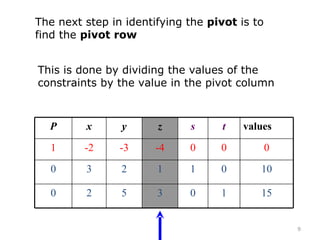
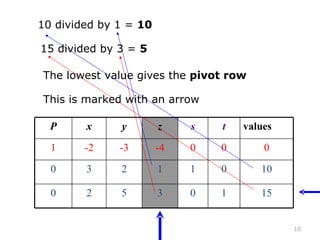
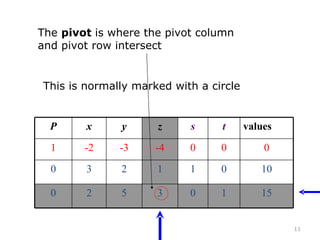
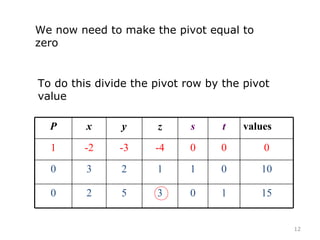
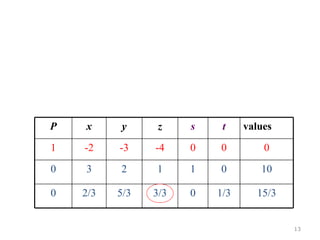
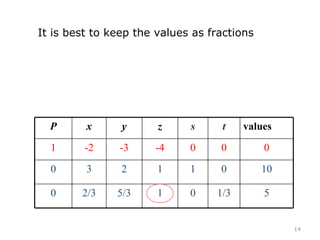
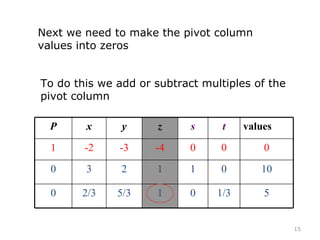
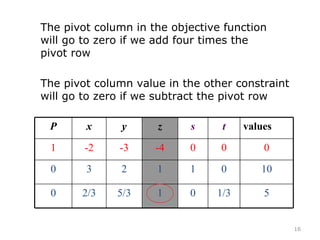
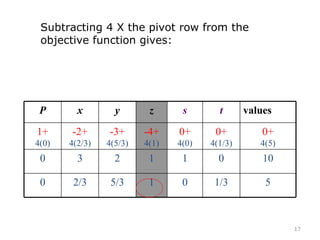
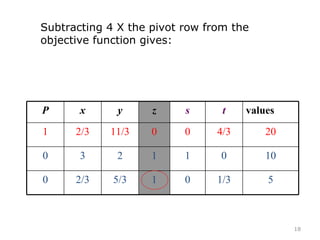
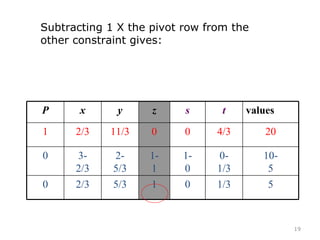
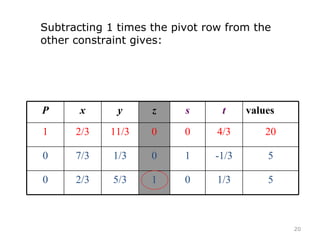
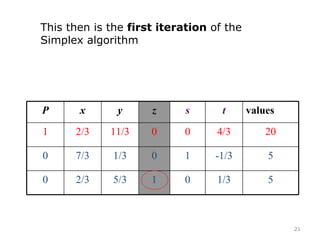
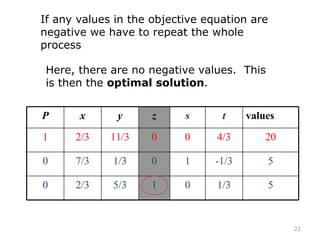
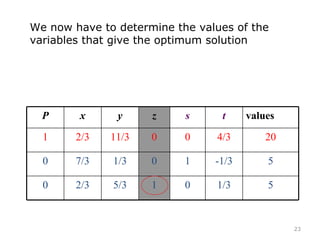
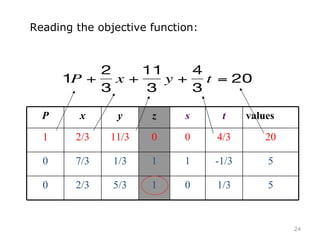
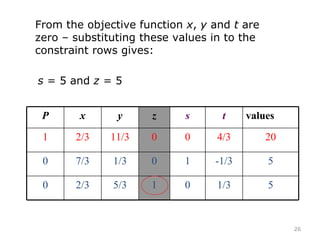
This document summarizes the steps of the simplex method to solve linear programming problems. It begins by rewriting the objective function and constraints to equalities by adding slack variables. It then places these equations in a tableau and identifies the pivot column and row. The pivot is used to make entries in the pivot column and row zeros through row operations. This process is repeated iteratively until an optimal solution is found where all objective coefficients are non-negative. The example problem provided is maximizing a function subject to two constraints, and the optimal solution found is presented.