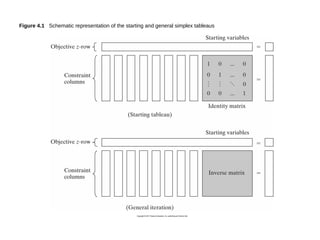
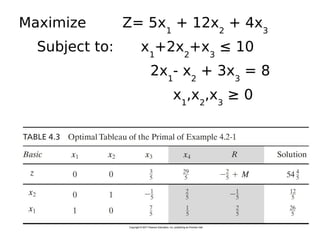
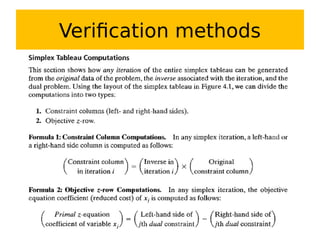
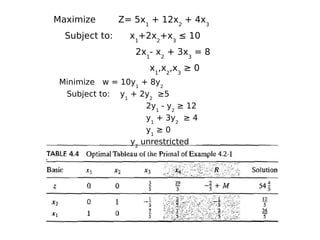
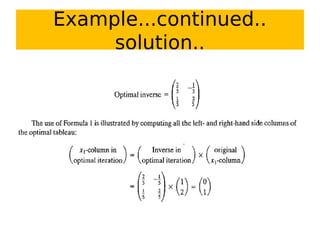
This document discusses duality in linear programming. It defines the dual problem as another linear program systematically constructed from the original or primal problem, such that the optimal solutions of one provide the optimal solutions of the other. The document provides rules for constructing the dual problem based on whether the primal problem is a maximization or minimization problem. It also gives examples of writing the dual of a primal problem and solving both problems to verify the optimal objective values are equal. Finally, it discusses economic interpretations of duality and the relationship between primal and dual problems and solutions.