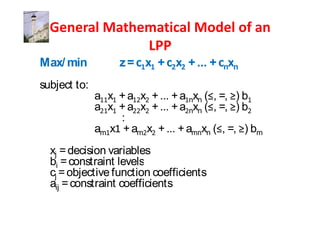
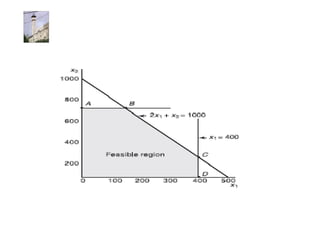
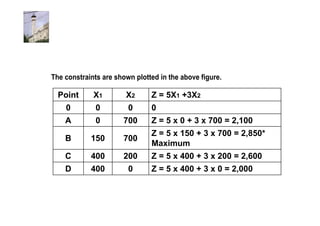
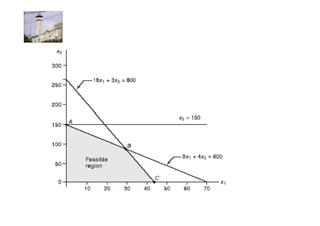
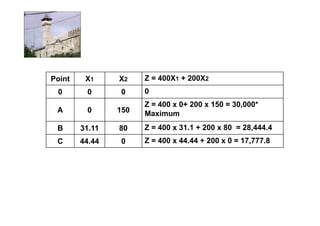
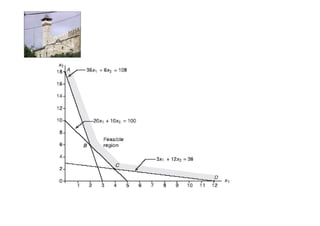
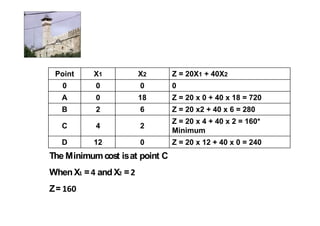
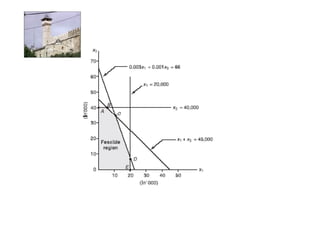
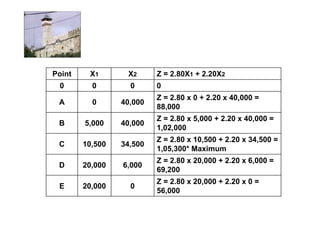
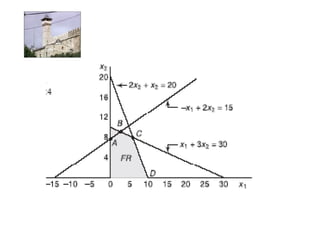
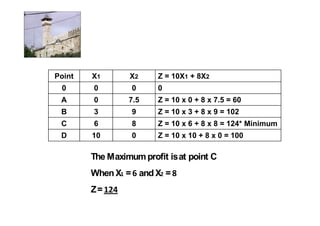
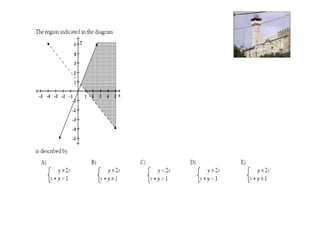
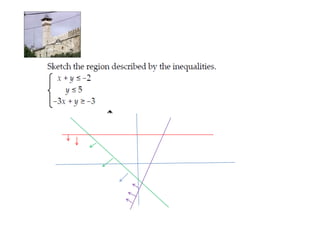
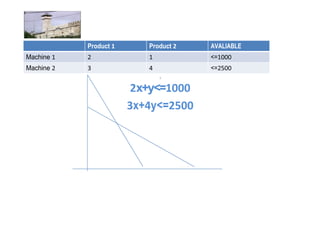
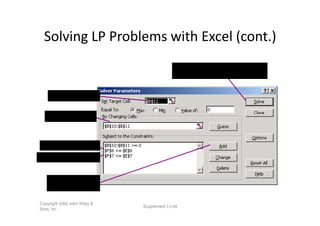
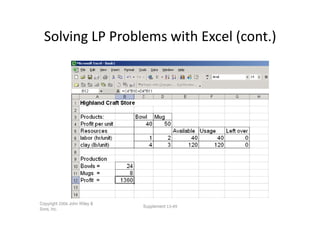
Linear programming is a technique for optimizing allocation of limited resources to activities based on constraints and an objective function. The key steps are to represent constraints graphically, identify the feasible region, and determine the optimal point that maximizes/minimizes the objective function value within the feasible region. Solving a linear programming problem graphically involves plotting the constraints and objective function on a coordinate plane and finding their intersection points.