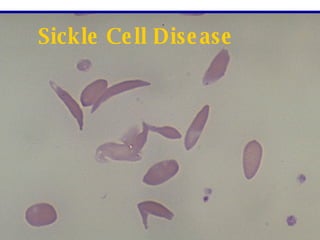
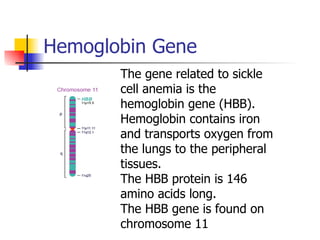
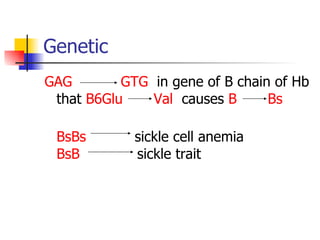
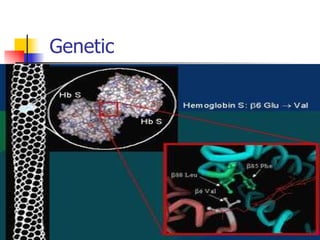
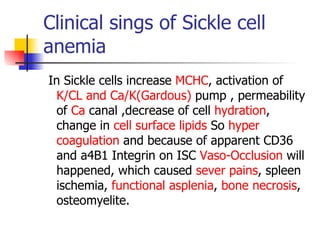
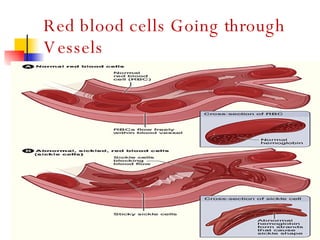
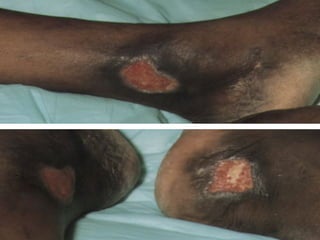
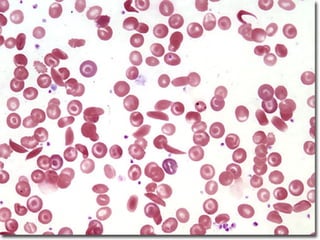
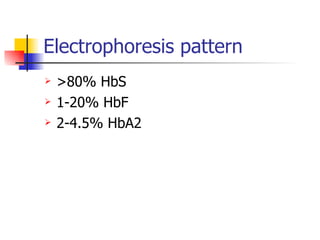
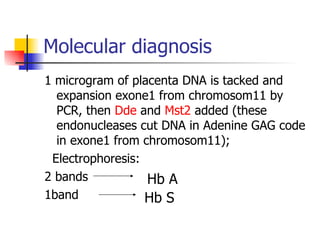
The document discusses sickle cell disease, which is caused by a mutation in the hemoglobin beta gene. The mutation causes a glutamic acid to valine substitution that results in abnormal hemoglobin S. This leads red blood cells to take on a sickle shape and causes symptoms like anemia, pain crises, infections, and organ damage. The main treatment options are blood transfusions, medications, stem cell transplant, and gene therapy, as there is currently no cure for sickle cell disease.