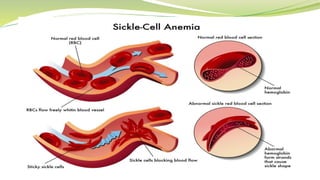
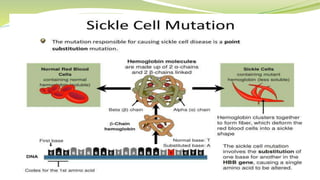
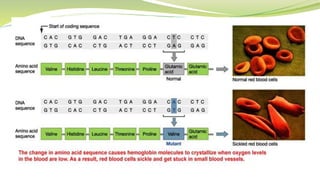
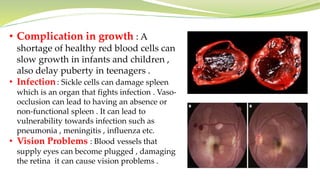
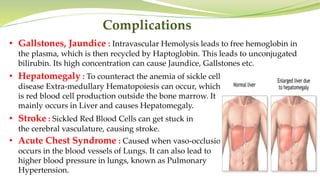
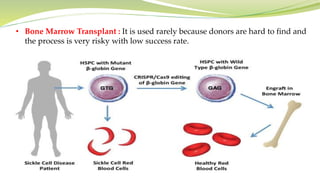
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder where red blood cells become rigid, sticky and crescent shaped. This causes blockages in blood vessels which can lead to pain, organ damage and other complications. It is caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene that produces abnormal hemoglobin. Symptoms include anemia, pain crises, susceptibility to infection and organ damage. While there is no cure, treatments focus on managing pain, preventing infections, blood transfusions and newer therapies like hydroxyurea.