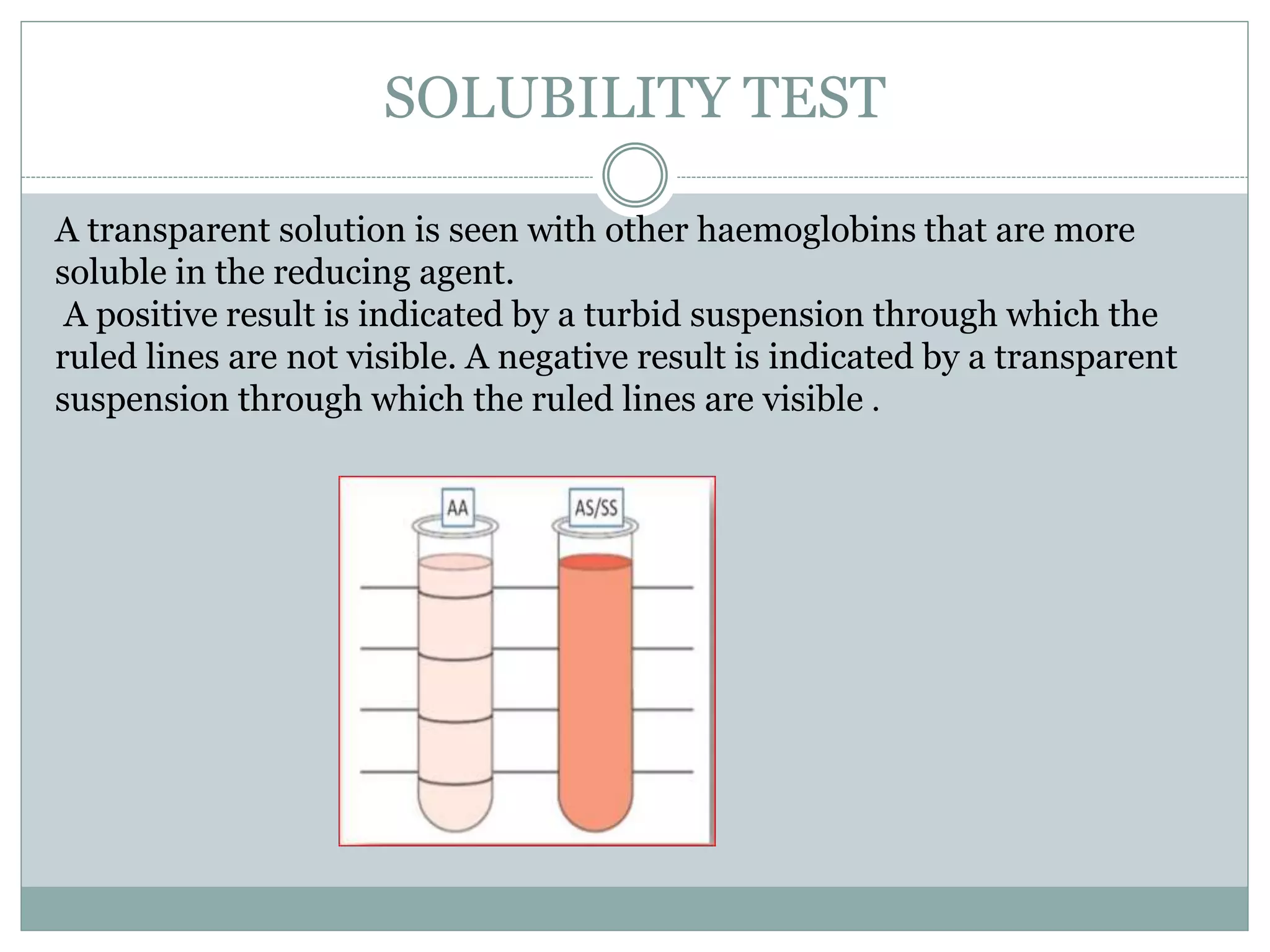
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene. This mutation causes red blood cells to take on a sickle, or crescent, shape that can block blood vessels. The disease results in chronic anemia, painful sickle cell crises, and increased susceptibility to infections. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, requiring mutations from both parents. Diagnosis involves tests like solubility, sickling, electrophoresis, and HPLC that detect abnormal hemoglobin S. The disease has significant health impacts and management focuses on preventing complications.


















![HOW RED CELLS RE DAMAGED
As HbS polymers grow, they herniate through the
membrane skeleton and project from the cell
ensheathed by only the lipid bilayer.
This severe derangement in membrane structure
causes the influx of Ca[2]+ions, which induce the
cross-linking of membrane proteins and activate an
ion channel that permits the efflux of K+ and H2O.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sicklecellanaemia-170922065242/75/Sickle-cell-anaemia-20-2048.jpg)