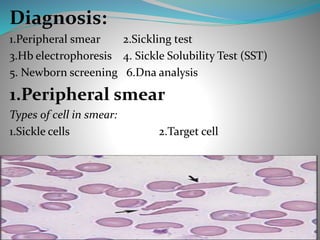
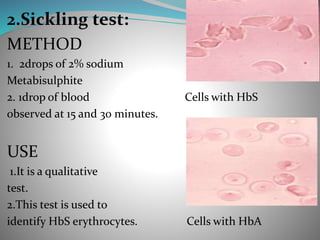
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder caused by a mutation in the hemoglobin gene. This mutation causes red blood cells to become rigid, sticky and sickle shaped. When these irregular cells block small blood vessels, it can cause pain, organ damage and other severe complications. Common symptoms include anemia, pain crises, susceptibility to infection. Diagnosis involves blood tests to identify abnormal hemoglobin S. Treatment focuses on pain management, antibiotics, blood transfusions, and hydroxyurea which can help reduce symptoms and increase life expectancy. Newborn screening and genetic counseling can help prevent sickle cell anemia.