Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times





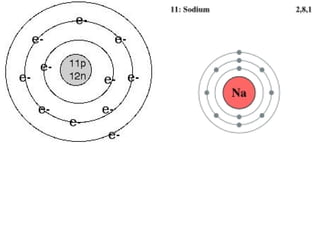


The document is an agenda for a chemistry class that includes reviewing the periodic table, discussing the ionic charges of magnesium and fluorine, drawing isotopic symbols for carbon-14 and hydrogen-3, and completing a worksheet on atomic structure and the Bohr model. The class objectives are to explain the usefulness of the shell model, describe how to set up the shell model, and know how many electrons are in each energy level.







