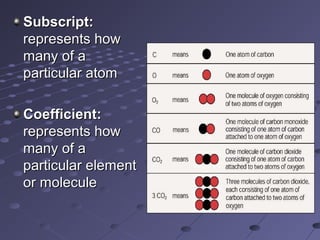
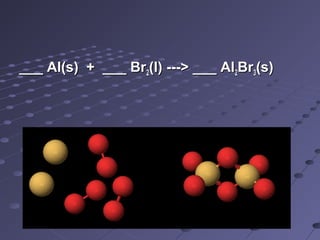
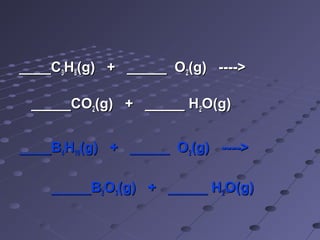
This document discusses chemical equations and reactions. It explains that chemical equations are used to represent chemical reactions, and that they consist of reactants on the left side of the arrow yielding products on the right. It also describes how to balance chemical equations by adjusting coefficients so that the same number of each type of atom is on both sides of the equation. Balancing chemical equations ensures conservation of mass during chemical reactions.