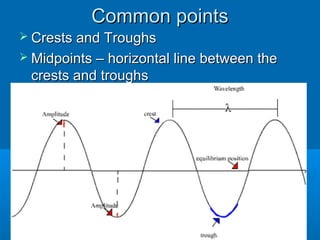
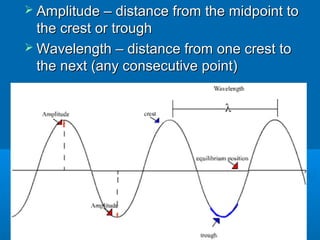
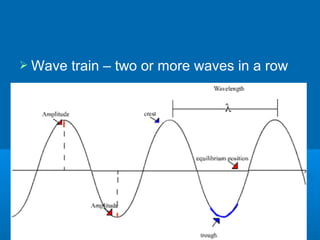
1. This document discusses different types of waves including transverse, longitudinal, and electromagnetic waves. It defines key wave properties such as amplitude, wavelength, frequency, period, and wave speed.
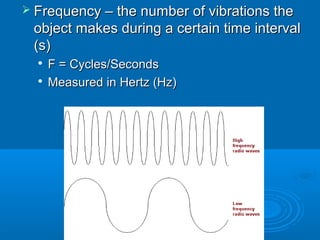
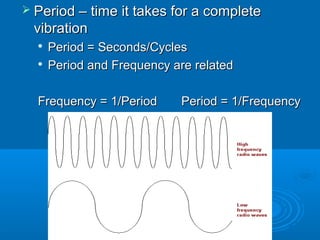
2. Frequency is defined as the number of vibrations per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). Period is the time for one full vibration. Frequency and period are inversely related.
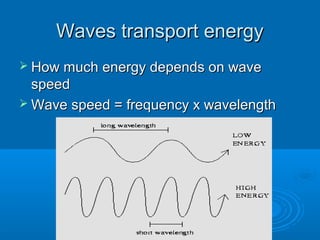
3. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating wave properties like frequency, period, wavelength, and wave speed from information given about the wave.